Abstract
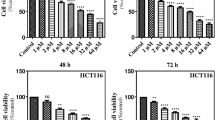
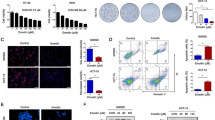
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common malignancies worldwide and evidence suggests that Ras signaling regulates various hallmarks of cancer via regulating several effector pathways such as ERK and PI3K. The aim of the present study is to understand the efficacy of a flavonoid myricetin for the first time in inhibiting the downstream target p21 activated kinase 1 (PAK1) of Ras signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. The analysis of gene expression revealed that myricetin inhibits PAK1 by abrogating the Ras-mediated signaling by decelerating Wnt signaling, the downstream of Erk/Akt, thereby inducing intrinsic caspase-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis by downregulating the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and survivin and upregulating pro-apoptotic Bax. The results also provide striking evidence that the myricetin inhibits the development of HCC by inhibiting PAK1 via coordinate abrogation of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT and their downstream signaling Wnt/β-catenin pathway, thus being a promising candidate for cancer prevention and therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farazi PA, DePinho RA (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer 6:674–687
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ (2008) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 58:71–96
Anzola M (2004) Hepatocellular carcinoma: role of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses proteins in hepatocarcinogenesis. J Viral Hepat 11:383–393
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F (2004) Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology 127:S35–S50
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Cleries R, Diaz M (2005) Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 9:191–211
Buchmann A, Bauer-Hoffmann R, Mahr J, Drinkwater NR, Luz A, Schwarz M (1991) Mutational activation of c-Ha-ras gene in liver tumors of different rodent strains: correlation with susceptibility to hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:333–338
Downward J (2003) Targeting RAS signaling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:11–22
Bagheri-Yarmand R, Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation via p21-activated kinase-1 signaling regulates heregulin- h1-mediated angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 275:39451–39457
Carter JH, Douglass LE, Deddens JA, Colligan BM, Bhatt TR, Pemberton JO, Konicek S, Hom J, Marshall M, Graff JR (2004) Pak-1 expression increases with progression of colorectal carcinomas to metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 10:3448–3456
Kumar R, Gururaj AE, Barnes CJ (2006) p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Can 6:459–471
Bokoch GM (2003) Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72:743–781
Molli PR, Li DQ, Murray BW, Rayala SK, Kumar R (2009) PAK signaling in oncogenesis. Oncogene 28:2545–2555
Higuchi M, Onishi K, Kikuchii C, Gotoh Y (2008) Scaffolding function of PAK in the PDK1–Akt pathway. Nat Cell Biol 10:1356–1364
Mao K, Kobayashi S, Jaffer ZM, Huang Y, Volden P, Chernoff J, Liang Q (2008) Regulation of Akt/PKB activity by P21-activated kinase in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:429–434
Ding Q, Xia W, Liu JC, Yang JY, Lee DF, Xia J, Bartholomeusz G, Li Y, Pan Y, Li Z, Barquo RC, Kin J, Lai CC, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Hung MC (2005) Erk associates with and primes GSK-3beta for its inactivation resulting in upregulation of beta-catenin. Mol Cell 19:159–170
De Luca A, Maiello MR, D’Alessio A, Pergameno M, Normanno N (2012) The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets 16:S17–S27
Gopal U, Venkatraman J, Devaraj N, Devaraj H (2011) Nuclear translocation of b-catenin correlates with CD44 upregulation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 357:283–293
Gonzalez FJ (2006) Role of β-catenin in the adult liver. Hepatology 43:650–653
Lau WY, Lai EC (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and recent advances. Hepato Pancreat Dis Int 7:237–257
Chahar MK, Sharma N, Dobhal MP, Joshi YC (2011) Flavonoids: a versatile source of anticancer drugs. Pharmacogn Rev 5:1–12
Ong KC, Khoo HE (1997) Biological effects of myricetin. Gen Pharmacol 29:121–126
Shih YW, Wu PF, Lee YC, Shi MD, Chiang TA (2009) Myricetin suppresses invasion and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells: possible mediation by blocking the ERK signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 57:3490–3499
Cheng L, Sung CL, Jin K, Jun SC (2011) Effects of myricetin, an anticancer compound, on the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen and its main metabolite, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, in rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 36:175–182
Hai W, Kim C, Song S, Kang C (2001) Study on mechanism of multistep hepatotumorigenesis in rat: development of hepatotumorigenesis. J Vet Sci 2:53–58
Khan SM, Devaraj H, Devaraj SN (2011) Chrysin abrogates early hepatocarcinogenesis and induces apoptosis in N-nitrosodiethylamine induced preneoplastic nodules in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:85–94
Khan SM, Devaraj H, Devaraj SN (2011) Methylated chrysin, a dimethoxy flavone, partially suppresses the development of liver preneoplastic lesions induced by N-Nitrosodiethylamine in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:173–178
King J (1965) The dehydrogenases or oxidoreductase-lactate dehydrogenase. In: Van D (ed) Practical clinical enzymology. Nostrand Company Ltd., London, pp 83–93
King J (1965) The hydrolases-acid and alkaline phosphatases. In: Van D (ed) Practical clinical enzymology. Nostrand Company Ltd., London, pp 191–208
King J (1965) The transferases—alanine and aspartate transaminases. In: Van D (ed) Practical clinical enzymology. Nostrand Company Ltd., London, pp 121–128
Rosali SB, Rau D (1972) Serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in alcoholism. Clin Chim Acta 39:41–47
Bergmeyer HU, Bernt E (1974) Aminotransferases and related enzymes. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 735–763
Sell S, Beckar FF (1978) Alpha feto protein. Natl Cancer Inst 60:19–26
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Sivaramakrishnan V, Shilpa PNM, Kumar VRP, Devaraj SN (2008) Attenuation of N- nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocellular carcinogenesis by a novel flavonol—Morin. Chem Biol Interact 171:79–88
Sun F, Zheng XY, Ye J, Wu TT, Wang J, Chen W (2012) Potential anticancer activity of myricetin in human T24 bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Nutr Cancer 64:599–606
Zhang S, Wang L, Liu H, Zhao G, Ming L (2014) Enhancement of recombinant myricetin on the radiosensitivity of lung cancer A549 and H1299 cells. Diagn Pathol 9:68
Shields JM, Pruitt K, McFall A, Shaub A, Der CJ (2000) Understanding Ras: ‘it ain’t over ‘til it’s over’. Trends Cell Biol 10:147–154
Feig LA, Buchsbaum RJ (2002) Cell signaling: life or death decision of ras proteins. Curr Biol 12:R259–R261
Huynh N, Kevin HL, Baldwin GS, Hong H (2010) P21-activated kinase 1 stimulates colon cancer cell growth and migration/invasion via ERK- and AKT-dependent pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:1106–1113
Balmanno K, Chell SD, Gillings AS, Hayat S, Cook SJ (2009) Intrinsic resistance to the MEK1/2 inhibitorAZD6244 (ARRY-142886) is associated with weak ERK1/2 signalling and/or strong PI3K signalling in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 125:2332–2341
Wee S, Jagani Z, Xiang KX, Loo A, Dorsch M, Yao YM, Sellers WR, Lengauer C, Stegmeier F (2009) PI3K pathway activation mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancer Res 69:4286–4293
Almeida M, Han L, Bellido T, Manolagas SC, Kousteni S (2005) Wnt proteins prevent apoptosis of both uncommitted osteoblast progenitors and differentiated osteoblasts by beta-catenin-dependent and -independent signaling cascades involving Src/ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT. J Biol Chem 280:41342–41351
Mishra R (2010) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta: can it be a target for oral cancer. Mol Cancer 9:144
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Department of Biotechnology (Project No. BT/PR1440/AAQ/03/532/2010) for financial assistance.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iyer, S.C., Gopal, A. & Halagowder, D. Myricetin induces apoptosis by inhibiting P21 activated kinase 1 (PAK1) signaling cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 407, 223–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2471-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2471-6