Abstract
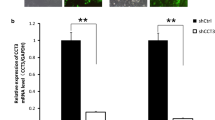
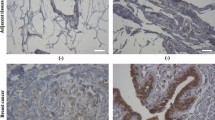
CD151 is a member of the tetraspanin family, which is involved in diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, motility, and invasion. However, the role of CD151 in breast cancer especially luminal and basal-like subtype breast cancer remains obscure. Here, we report the role of CD151 in the biological behaviors of luminal and basal-like subtype cell lines and the underlying molecular mechanism. A eukaryotic expression vector expressing both CD151 shRNA and GFP was transfected into MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468 cells. The CD151 gene-silencing effect is authenticated by real-time PCR and Western blot. Our data show that the capacity for proliferation, migration, and invasion of two kinds of cells is diminished after Knockdown of CD151 via lentivirus-mediated CD151 specific shRNA. Tumor cells are arrested in G0/G1 phase. Apoptosis is increased. Moreover, we also demonstrate that the expressions of mmp26 and CD147 are inhibited by knockdown of CD151. But the inhibition depends on the cell type. We can conclude that silencing gene CD151 inhibits expression of properties that are associated with the malignant phenotype of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468 cells. It may become a potential target in breast cancer therapy especially for luminal and basal subtypes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldhirsch A, Wood EP, Coates AS et al (2011) Strategies for subtypes dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22:1736–1747. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr304
The Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2012) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490:61–70. doi:10.1038/nature11412
Liu Y, Jiang Qiu-Y, Xin T et al (2012) Clinical significance of basal-like breast cancer in Chinese women in Heilongjiang Province. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prevention 13:2735–2738
Xue C, Wang X, Peng R et al (2012) Distribution, clinicopathologic features and survival of breast cancer subtypes in Southern China. Cancer Sci 103:1679–1687. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006
Funakoshi T, Tachibana I, Hoshida Y et al (2003) Expression of tetraspanins in human lung cancer cells: frequent down regulation of CD9 and its contribution to cell motility in small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 22:674–687. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206106
Hemler ME (2008) Targeting of tetraspanin proteins-potential benefits and strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:747–758. doi:10.1038/nrd2659
Sincock PM, Fitter S, Parton RG et al (1999) PETA-3/CD151, a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, is localized to the plasma membrane and endocytic system of endothelial cells, associates with multiple integrins and modulates cell function. J Cell Sci 112:833–844
Zhang XA, Kazarov AR, Yang X et al (2002) Function of the tetraspanin CD151-alpha6beta1 integrin complexduring cellular morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 13:1–11
Tokuhara T, Hasegawa H, Hattori N et al (2001) Clinical significance of CD151 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7:4109–4114
Hui Zhu G, Huang C, Jun-Qiu Zh et al (2011) Expression and prognostic significance of CD151, c-Met, and integrin alpha3/alpha6 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 56:1090–1098. doi:10.1007/s10620-010-1416-x
Hashida H, Takabayashi A, Tokuhara T et al (2003) Clinical significance of transmembrane 4 superfamily in colon cancer. Br J Cancer 89:158–167
Ke AW, Shi GM, Zhou J et al (2009) Role of overexpression of CD151 and/or c-Met in predicting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49:491–503. doi:10.1002/hep.22639
Shigemasa S, Tatsuya M, Naritaka T et al (2011) Prognostic significance of CD151 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with aggressive cell proliferation and invasiveness. Ann Surg Oncol 18:888–893. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-1387-3
Voss MA, Gordon N, Maloney S et al (2011) Tetraspanin CD151 is a novel prognostic marker in poor outcome endometrial cancer. Br J Cancer 104:1611–1618. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011
Baldwin LA, Hoff JT et al (2014) CD151-α3β1 integrin complexes suppress ovarian tumor growth by repressing slug-mediated EMT and canonical Wnt signaling. Oncotarget 5: 12203–12217
Mosig RA, Lin L, Senturk E et al (2012) Application of RNA-Seq transcriptome analysis: CD151 is an invasion/migration target in all stages of epithelial ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res 5:1–9. doi:10.1186/1757-2215-5-4
Petrocca F, Lieberman J (2011) Promise and chal-lenge of RNA interference-based therapy for cancer. J Clin Oncol 29:747–754. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.27.6287
Li Z, Tian T, Xiaopeng H et al (2014) Targeting Six1 by lentivirus-mediated RNA interference inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and invasion. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:631–639
Manjunath N, Wu H, Subramanya S, Shankar P (2009) Lentiviral delivery of short hairpin RNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:732–745. doi:10.1016/j.addr
Roselli S, Kahl RGS, Copeland BT et al (2014) Deletion of Cd151 reduces mammary tumorigenesis in the MMTV/PyMT mouse model. BMC Cancer 14:509–519. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-509
Yang XH, Richardson AL, Torres-Arzayus MI et al (2008) CD151 accelerates breast cancer by regulating A6 integrin function, signaling, and molecular organization. Cancer Res 68:3204–3212. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
Hashmi AA, Edhi MM, Naqvi H et al (2014) Clinicopathologic features of triple negative breast cancers: an experience from Pakistan. Diagn Pathol 9:43–52. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-9-43
Kwon MJ, Park S, Choi JY et al (2012) Clinical significance of CD151 overexpression in subtypes of invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer 106:923–930. doi:10.1038/bjc
Copeland BT, Bowman MJ, Ashman LK (2013) Genetic ablation of the tetraspanin CD151 reduces spontaneous metastatic spread of prostate cancer in the TRAMP model. Mol Cancer Res 11:95–105. doi:10.1158/1541-7786
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2011) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J 278:16–27. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07919.x
Hong IK, Jin YJ, Byun HJ et al (2006) Homophilic interactions of tetraspanin CD151 upregulate motility and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression of human melanoma cells through adhesion-dependent c-Jun activation signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 281:24279–24292
Hasegawa M, Furuya M, Kasuya Y et al (2007) CD151 dynamics in carcinoma–stroma interaction: integrin expression, adhesion strength and proteolytic activity. Lab Invest 87:882–892
Park HI, Ni J, Gerkema FE, Liu D, Belozerov VE, Sang QX (2000) Identification and characterization of human endometase (Matrix metalloproteinase-26) from endometrial tumor. J Biol Chem 275:20540–20544
Qiu W, Bai SX, Zhao M et al (2005) Spatio-temporal expression of matrix metalloproteinase-26 in human placental trophoblasts and fetal red cells during normal placentation. Biol Reprod 72:954–959
Uria JA, Lopez-Otin C (2000) Matrilysin-2, a new matrix metalloproteinase expressed in human tumors and showing the minimal domain organization required for secretion, latency, and activity. Cancer Res 60:4745–4751
Xu T, Zhou M, Peng L et al (2014) Upregulation of CD147 promotes cell invasion, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and activates MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:7432–7441
Iacono KT, Brown AL, Greene MI, Saouaf SJ (2007) CD147 immunoglobulin superfamily receptor function and role in pathology. Exp Mol Pathol 83:283–295
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (81172499), the project of Heilongjiang Education Department(11511453,12521626), The Science and Technology Development Fund of Jilin Province (20076023), and the platform foundation from Jilin University (450060445657).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., wang, S., Wang, L. et al. Targeting CD151 by lentivirus-mediated RNA interference inhibits luminal and basal-like breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Mol Cell Biochem 407, 111–121 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2459-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2459-2