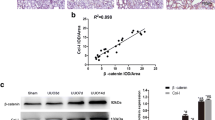
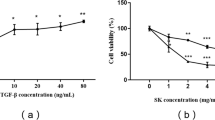
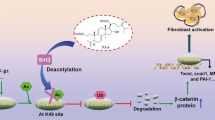
Abstract
Signaling through the Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway, especially JAK2/STAT3, is involved in renal fibrosis. Fluorofenidone (FD), a novel pyridone agent, exerts anti-fibrotic effects in vitro and in vivo. Herein, we sought to investigate whether FD demonstrates its inhibitory function through preventing JAK2/STAT3 pathway. In this study, we examined the effect of FD on activation of rat renal interstitial fibroblasts, glomerular mesangial cells (GMC), and expression of JAK2/STAT3. Moreover, we explored the histological protection effects of FD in UUO rats, db/db mice, and phosphorylation of JAK2/STAT3 cascade. Our studies found that pretreatment with FD resulted in blockade of activation of fibroblast and GMC manifested by fibronectin (FN) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) protein expression and decline of STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation induced by IL-6 or high glucose. In unilateral ureteral obstruction rats and a murine model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes (db/db mice), treatment with FD blocked the expression of FN and α-SMA, prevented renal fibrosis progression, and attenuated STAT3 activation. However, FD administration did not interfere with JAK2 activation both in vivo and in vitro. In summary, the molecular mechanism by which FD exhibits renoprotective effects appears to involve the inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeisberg M, Neilson EG (2010) Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(11):1819–1834
Harris RC, Neilson EG (2006) Toward a unified theory of renal progression. Annu Rev Med 57:365–380
Leroy V, De Seigneux S, Agassiz V, Hasler U, Rafestin-Oblin ME, Vinciguerra M, Martin PY, Feraille E (2009) Aldosterone activates NF-kappaB in the collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(1):131–144
Tu X, Chen X, Xie Y, Shi S, Wang J, Chen Y, Li J (2008) Anti-inflammatory renoprotective effect of clopidogrel and irbesartan in chronic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(1):77–83
Remuzzi G, Cattaneo D, Perico N (2008) The aggravating mechanisms of aldosterone on kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(8):1459–1462
Meng J, Zou Y, Hu C, Zhu Y, Peng Z, Hu G, Wang Z, Tao L (2012) Fluorofenidone attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice via restoring caveolin 1 expression and inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Shock 38(5):567–573
Wang LH, Liu JS, Ning WB et al (2011) Fluorofenidone attenuates diabetic nephropathy and kidney fibrosis in db/db mice. Pharmacology 88(1–2):88–99
Li BX, Tang YT, Wang W et al (2011) Fluorofenidone attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis in the rat model of obstructive nephropathy. Mol Cell Biochem 354(1–2):263–273
Yuan Q, Wang R, Peng Y et al (2011) Fluorofenidone attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-beta(1)-induced fibroblast activation. Am J Nephrol 34(2):181–194
Peng Y, Yang H, Wang N et al (2014) Fluorofenidone attenuates hepatic fibrosis by suppressing the proliferation and activation of hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 306(3):G253–G263
Peng Y, Yang H, Zhu T et al (2013) The antihepatic fibrotic effects of fluorofenidone via MAPK signalling pathways. Eur J Clin Invest 43(4):358–368
Peng ZZ, Hu GY, Shen H et al (2009) Fluorofenidone attenuates collagen I and transforming growth factor-beta1 expression through a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-dependent way in NRK-52E cells. Nephrology (Carlton) 14(6):565–572
Huang L, Zhang F, Tang Y et al (2014) Fluorofenidone attenuates inflammation by inhibiting the NF-small ka, CyrillicB pathway. Am J Med Sci 348(1):75–80
Tang Y, Li B, Wang N et al (2010) Fluorofenidone protects mice from lethal endotoxemia through the inhibition of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta release. Int Immunopharmacol 10(5):580–583
Ning WB, Hu GY, Peng ZZ, Wang L, Wang W, Chen JY, Zheng X, Li J, Tao LJ (2011) Fluorofenidone inhibits Ang II-induced apoptosis of renal tubular cells through blockage of the Fas/FasL pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 11(9):1327–1332
Wang L, Hu GY, Shen H, Peng ZZ, Ning WB, Tao LJ (2009) Fluorofenidone inhibits TGF-beta1 induced CTGF via MAPK pathways in mouse mesangial cells. Pharmazie 64(10):680–684
Yuan Q, Wang L, Zhang F et al (2011) Fluorofenidone suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the expression of connective tissue growth factor via inhibiting TGF-beta/Smads signaling in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Pharmazie 66(12):961–967
Chen CL, Loy A, Cen L et al (2007) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is involved in cell growth and survival of human rhabdomyosarcoma and osteosarcoma cells. BMC Cancer 7:111
Turkson J, Jove R (2000) STAT proteins: novel molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene 19(56):6613–6626
Stepkowski SM, Chen W, Ross JA, Nagy ZS, Kirken RA (2008) STAT3: an important regulator of multiple cytokine functions. Transplantation 85(10):1372–1377
Yamamoto T, Matsuda T, Muraguchi A, Miyazono K, Kawabata M (2001) Cross-talk between IL-6 and TGF-beta signaling in hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett 492(3):247–253
Liu XT, Wang ZX, Yang Y, Wang L, Sun RF, Zhao YM, Yu NJ (2014) Active components with inhibitory activities on IFN-gamma/STAT1 and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathways from Caulis Trachelospermi. Molecules 19(8):11560–11571
Guschin D, Rogers N, Briscoe J et al (1995) A major role for the protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 in the JAK/STAT signal transduction pathway in response to interleukin-6. EMBO J 14(7):1421–1429
Lim CP, Phan TT, Lim IJ, Cao X (2009) Cytokine profiling and Stat3 phosphorylation in epithelial-mesenchymal interactions between keloid keratinocytes and fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol 129(4):851–861
Watanabe S, Mu W, Kahn A, Jing N, Li JH, Lan HY, Nakagawa T, Ohashi R, Johnson RJ (2004) Role of JAK/STAT pathway in IL-6-induced activation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Nephrol 24(4):387–392
Nightingale J, Patel S, Suzuki N et al (2004) Oncostatin M, a cytokine released by activated mononuclear cells, induces epithelial cell-myofibroblast transdifferentiation via Jak/Stat pathway activation. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(1):21–32
Wang X, Shaw S, Amiri F, Eaton DC, Marrero MB (2002) Inhibition of the Jak/STAT signaling pathway prevents the high glucose-induced increase in tgf-beta and fibronectin synthesis in mesangial cells. Diabetes 51(12):3505–3509
Amiri F, Shaw S, Wang X, Tang J, Waller JL, Eaton DC, Marrero MB (2002) Angiotensin II activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in mesangial cells is altered by high glucose. Kidney Int 61(5):1605–1616
Ogata H, Chinen T, Yoshida T, Kinjyo I, Takaesu G, Shiraishi H, Iida M, Kobayashi T, Yoshimura A (2006) Loss of SOCS3 in the liver promotes fibrosis by enhancing STAT3-mediated TGF-beta1 production. Oncogene 25(17):2520–2530
Samavati L, Rastogi R, Du W, Huttemann M, Fite A, Franchi L (2009) STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol Immunol 46(8–9):1867–1877
Kuratsune M, Masaki T, Hirai T, Kiribayashi K, Yokoyama Y, Arakawa T, Yorioka N, Kohno N (2007) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 involvement in the development of renal interstitial fibrosis after unilateral ureteral obstruction. Nephrology (Carlton) 12(6):565–571
Pang M, Ma L, Gong R et al (2010) A novel STAT3 inhibitor, S3I-201, attenuates renal interstitial fibroblast activation and interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 78(3):257–268
Berthier CC, Zhang H, Schin M et al (2009) Enhanced expression of Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway members in human diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 58(2):469–477
Lu TC, Wang ZH, Feng X et al (2009) Knockdown of Stat3 activity in vivo prevents diabetic glomerulopathy. Kidney Int 76(1):63–71
Lan HY, Mu W, Tomita N, Huang XR, Li JH, Zhu HJ, Morishita R, Johnson RJ (2003) Inhibition of renal fibrosis by gene transfer of inducible Smad7 using ultrasound-microbubble system in rat UUO model. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(6):1535–1548
Lin SL, Chen RH, Chen YM, Chiang WC, Lai CF, Wu KD, Tsai TJ (2005) Pentoxifylline attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis by blocking Smad3/4-activated transcription and profibrogenic effects of connective tissue growth factor. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(9):2702–2713
Radford MJ, Donadio JJ, Bergstralh EJ, Grande JP (1997) Predicting renal outcome in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 8(2):199–207
Striker LJ, Doi T, Elliot S, Striker GE (1989) The contribution of glomerular mesangial cells to progressive glomerulosclerosis. Semin Nephrol 9(4):318–328
Nechemia-Arbely Y, Barkan D, Pizov G, Shriki A, Rose-John S, Galun E, Axelrod JH (2008) IL-6/IL-6R axis plays a critical role in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(6):1106–1115
Peters M, Muller AM, Rose-John S (1998) Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptor: direct stimulation of gp130 and hematopoiesis. Blood 92(10):3495–3504
Koike K, Ueda S, Yamagishi S, Yasukawa H, Kaida Y, Yokoro M, Fukami K, Yoshimura A, Okuda S (2014) Protective role of JAK/STAT signaling against renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Clin Immunol 150(1):78–87
Herrmann JE, Imura T, Song B et al (2008) STAT3 is a critical regulator of astrogliosis and scar formation after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 28(28):7231–7243
Ortiz-Munoz G, Lopez-Parra V, Lopez-Franco O et al (2010) Suppressors of cytokine signaling abrogate diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(5):763–772
Mauer SM, Steffes MW, Ellis EN, Sutherland DE, Brown DM, Goetz FC (1984) Structural–functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest 74(4):1143–1155
Fioretto P, Mauer M (2007) Histopathology of diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27(2):195–207
Bader R, Bader H, Grund KE, Mackensen-Haen S, Christ H, Bohle A (1980) Structure and function of the kidney in diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Correlations between morphological and functional parameters. Pathol Res Pract 167(2–4):204–216
Banes-Berceli AK, Shaw S, Ma G, Brands M, Eaton DC, Stern DM, Fulton D, Caldwell RW, Marrero MB (2006) Effect of simvastatin on high glucose- and angiotensin II-induced activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291(1):F116–F121
Ha H, Lee HB (2000) Reactive oxygen species as glucose signaling molecules in mesangial cells cultured under high glucose. Kidney Int Suppl 77:S19–S25
Haneda M, Kikkawa R, Sugimoto T, Koya D, Araki S, Togawa M, Shigeta Y (1995) Abnormalities in protein kinase C and MAP kinase cascade in mesangial cells cultured under high glucose conditions. J Diabetes Complicat 9(4):246–248
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Doctoral Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 20120162130001), by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81273575) to Dr Li-Jian Tao, and by the National Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Grant No. 81300610) to Dr Qiong-jing Yuan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Liu, Cy., Lu, Mm. et al. Fluorofenidone protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biochem 407, 77–87 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2456-5