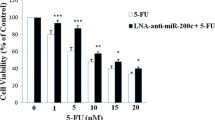
Abstract
Chemotherapy remains the core of anticancer treatment. However, despite the tremendous strides made in the development of targeted anticancer therapies, emergence of resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs is still a major obstacle in the successful management of resistant tumors. Therefore, profound investigation into the in-depth molecular mechanisms of drug resistance is essential and may hopefully translate into effective therapies that can flip the switch from drug resistance to susceptibility. To develop novel-targeted therapy holds promise for conquering chemotherapy resistance, one of the major hurdles in current colon cancer treatment. Previous studies indicate that CD147 is involved in the progression of chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer and ovarian cancer cells and its expression is negative regulated by miR-492 in muscles cells. In the present study, we found that lower level of miR-492 is accompanied with increased expression of CD147 in Oxaliplatin-resistant colon cancer cell line LS174T/L-OHP as compared with its parental cell line LS174T. Exogenous expression of miR-492 in LS174T/L-OHP could sensitize its reaction on the treatment of Oxaliplatin, which is coincided with its directly reducing the expression of CD147. Furthermore, we found that knockdown of CD147 in LS174T/L-OHP could also sensitize its reaction of the treatment with Oxaliplatin. Besides, intratumoral delivering of miR-492 could also restore Oxaliplatin treatment response in Oxaliplatin-resistant xenografts in vivo. These findings provide direct evidences that the miR-492/CD147 axis might play an essential role in the Oxaliplatin resistance of colon cancer cells, suggesting that the miR-492/CD147 signaling cohort could be served as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of chemotherapy resistant in colon cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stordal B, Pavlakis N et al (2010) Oxaliplatin for the treatment of cisplatin-resistant cancer: a systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev 33:347–357
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I et al (2009) Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:663–671
Esperance SL, Popa I et al (2006) Gene expression profiling of paired ovarian tumors obtained prior to and following adjuvant chemotherapy: molecular signatures of chemoresistant tumors. Int J Oncol 29:5–24
Ieta K, Tanaka F et al (2008) Biological and genetic characteristics of tumor-initiating cells in colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 15:638–648
Iacono KT, Brown AL et al (2007) CD147 immunoglobulin superfamily receptor function and role in pathology. Exp Mol Pathol 83:283–295
Zheng HC, Takahashi H et al (2006) Upregulated EMMPRIN/CD147 might contribute to growth and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma: a good marker for local invasion and prognosis. Br J Cancer 95:1371–1378
Xiong L, Edwards CK et al (2014) The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature. Int J Mol Sci 15:17411–17441
Zou W, Yang H et al (2007) Inhibition of CD147 gene expression via RNA interference reduces tumor cell invasion, tumorigenicity and increases chemosensitivity to paclitaxel in HO-8910 pm cells. Cancer Lett 248:211–218
Hao JL, Madigan MC et al (2012) In vitro and in vivo prostate cancer metastasis and chemoresistance can be modulated by expression of either CD44 or CD147. PLoS One 7:1–14
Calin GA, Croce CM et al (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866
Lu R, Ji ZL et al (2014) miR-145 functions as tumor suppressor and targets two oncogenes, ANGPT2 and NEDD9, in renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140:387–397
von Frowein J, Pagel P et al (2011) MicroRNA-492 is processed from the keratin 19 gene and up-regulated in metastatic hepatoblastoma. Hepatology 53:833–842
Xia L, Zhang D et al (2008) miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 123:372–379
Kupcinskas J, Bruzaite I et al (2014) Lack of association between miR-27a, miR-146a, miR-196a-2, miR-492 and miR-608 gene polymorphisms and colorectal cancer. Sci Rep 4:1–6
Wu LS, Tang LM et al (2012) Resveratrol inhibits CD147 expression via miR-492 upregulation and promotes apoptosis in malignant melanoma cells. In: Proceedings of the second eastern Asia dermatology congress (EADC2012), vol 125, pp 3–12
Wu LS, Li FF et al (2011) A miRNA-492 binding-site polymorphism in BSG (basigin) confers risk to psoriasis in central south Chinese population. Hum Genet 130:749–757
Jemal A, Center MM et al (2010) Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 19:1893–1907
Montero J, Morales A et al (2008) Mitochondrial cholesterol contributes to chemotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 68:5246–5256
Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H et al (2006) Emmprin (basigin/CD147): matrix metalloproteinase modulator and multifunctional cell recognition molecule that plays a critical role in cancer progression. Pathol Int 56:359–367
Sun J, Hemle ME (2001) Regulation of MMP-1and MMP-2 production through CD147/extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer interactions. Cancer Res 61:2276–2281
Chen X, Lin J et al (2006) A small interfering CD147-targeting RNA inhibited the proliferation, invasiveness, and metastatic activity of malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 66:11323–11330
Chen PN, Chu SC et al (2006) Mulberry anthocyanins, cyanidin 3-rutinoside and cyanidin 3-glucoside, exhibited an inhibitory effect on the migration and invasion of a human lung cancer cell line. Cancer Lett 235:248–259
Chu K, Cornetta KG et al (2008) Efficient and stable gene expression into human osteoclasts using an HIV-1-based lentiviral vector. DNA Cell Biol 27:315–320
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Shandong Provincial Foundation for Natural Sciences (ZR2011HM07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lipan Peng and Tongxing Cui have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Zhu, H., Wang, J. et al. MiR-492 is functionally involved in Oxaliplatin resistance in colon cancer cells LS174T via its regulating the expression of CD147. Mol Cell Biochem 405, 73–79 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2397-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2397-z