Abstract
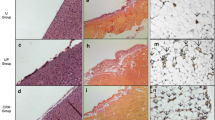
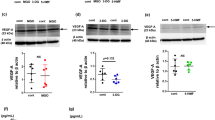
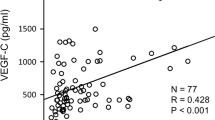
The effect of peritoneal dialysis (PD) with high-glucose dialysis fluid on the VEGF family, tristetraprolin (TTP), angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis was investigated. Forty male SD rats were randomised into five groups: normal group, sham operation group, uraemia group, PD 2-week group and PD4-week group. After 4 weeks of PD, microvessel density (MVD) and lymphatic vessel density (LVD) were measured. The expressions of both the VEGF family and TTP were detected. Compared with the normal group, the mRNA expression levels of the VEGF family were significantly increased in the uraemia group (P < 0.05), and also in the PD 2-week group and PD4-week group (P < 0.05) compared with uraemia group. The mRNAs of VEGF-A and VEGF-C in 4-week PD group likewise were significantly increased compared with the 2-week PD group. However, the mRNA expression of TTP was significantly decreased in the uraemia group compared with the normal group (P < 0.05), and also in the PD group compared with the uraemia group (P < 0.05). Compared with the normal group, the protein expressions of TTP were significantly decreased in the uraemia group (P < 0.05), and also in the PD group compared with the uraemia group (P < 0.05). Compared with the normal group, the MVD and LVD counts were gradually increased in the PD group, which was associated with PD time. In addition, the expression of TTP gradually decreased over PD time. High-glucose PD fluid and uraemic circumstance resulted in the abnormal expression of TTP and the VEGF family in a PD time-dependent manner; this may lead to UFF through angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy H, Bhardwaj S, Yla-Herttuala S (2006) Biology of vascular endothelial growth factors. FEBS Lett 580:2879–2887
Karnezis T, Shayan R, Caesar C et al (2012) VEGF-D promotes tumor metastasis by regulating prostaglandins produced by the collecting lymphatic endothelium. Cancer Cell 21(2):181–195
Zweers MM, Struijk DG, Smit W, Krediet RT (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor in peritoneal dialysis: a longitudinal follow-up. J Lab Clin Med 137:125–132
De Vriese AS, Tilton RG, Stephan CC, Lameire NH (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor is essential for hyperglycemia-induced structural and functional alterations of the peritoneal membrane. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1734–1741
Io H, Hamada C, Ro Y, Ito Y, Hirahara I, Tomino Y (2004) Morphologic changes of peritoneum and expression of VEGF in encapsulated peritoneal sclerosis rat models. Kidney Int 65(1927–1936):22
Carballo E, Lai WS, Blackshear PJ (1998) Feedback inhibition of macrophage tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by tristetraprolin. Science 281:1001–1005
Carballo E, Lai WS, Blackshear PJ (2000) Evidence that tristetraprolin is a physiological regulator of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor messenger RNA deadenylation and stability. Blood 95:1891–1899
Lai WS, Carballo E, Strum JR, Kennington EA, Phillips RS, Blackshear PJ (1999) Evidence that tristetraprolin binds to AU-rich elements and promotes the deadenylation and destabilization of tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA. Mol Cell Biol 19:4311–4323
Lai WS, Parker JS, Grissom SF, Stumpo DJ, Blackshear PJ (2006) Novel mRNA targets for tristetraprolin (TTP) identified by global analysis of stabilized transcripts in TTP-deficient fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 26:9196–9208
Blackshear PJ (2002) Tristetraprolin and other CCCH tandem zinc-finger proteins in the regulation of mRNA turnover. Biochem Soc Trans 30(Pt 6):945–952
Ogilvie RL, Abelson M, Hau HH, Vlasova I, Blackshear PJ, Bohjanen PR (2005) Tristetraprolin down-regulates IL-2 gene expression through AU-rich element-mediated mRNA decay. J Immunol 174:953–961
Ogilvie RL, Sternjohn JR, Rattenbacher B, Vlasova IA, Williams DA, Hau HH, Blackshear PJ, Bohjanen PR (2009) Tristetraprolin mediates interferon-gamma mRNA decay. J Biol Chem 284:11216–11223
Bakheet T, Frevel M, Williams BR, Greer W, Khabar KS (2001) ARED: human AU-rich element-containing mRNA database reveals an unexpectedly diverse functional repertoire of encoded proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 29:246–254
Lai WS, Blackshear PJ (2001) Interactions of CCCH zinc finger proteins with mRNA: tristetraprolin-mediated AU-rich elementdependent mRNA degradation can occur in the absence of a poly(A) tail. J Biol Chem 276:23144–23154
Sawaoka H, Dixon DA, Oates JA, Boutaud O (2003) Tristetraprolin binds to the 30-untranslated region of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA. A polyadenylation variant in a cancer cell line lacks the binding site. J Biol Chem 278:13928–13935
Dixon DA (2004) Dysregulated post-transcriptional control of COX-2 gene expression in cancer. Curr Pharm Des 10:635–646
Weidner N (1995) Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol 147(1):9–19
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR et al (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis-correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324(1):1–8
Stacker SA, Williams RA, Achen MG (2004) Lymphangiogenic growth factors as markers of tumor metastasis. APMIS 112:539–549
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG et al (2001) Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 7(2):192–198
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor-c-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J 20(4):672–682
Karpanen T, Alitalo K (2001) Lymphatic vessels as targets of tumor therapy. J Exp Med 194(6):F37–F42
Liu T, Owen W, Yu YM et al (2000) Arginine, eitndline, and nilrie oxide melabolisin in end stage renal disease patients. Clin Invest 105(9):l217–l225
Ferrier ML, Combet S, van Landschoot M et al (2001) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase reverses changes in peritoneal permeability in a rat model of acute peritonitis. Kidney Int 60(6):2343–2350
Devuyst O, Combet S, Cnops Y (2001) Regulation of NO synthase isoforms in the peritoneum: implications for ultrafiltration failure in peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 16(3):675–678
Heimburger O, Waniewski J, Werynski A (1990) Peritoneal transport in CAPD patients with permanent loss of ultrafiltration capacity Lindholm. Kidney Int. 38:495–506
Imholz AL, Koomen GC, Struijk DG (1993) Effect of dialysate osmolarity on the transport of low-molecular weight solutes and proteins during CAPD. Kidney Int. 43:1339–1346
Ho-dac-Pannekeet MM, Atasever B, Struijk DG (1997) Analysis of ultrafiltration failure in peritoneal dialysis patients by means of standard peritoneal permeability analysis. Dial Int. 17:144–150
Krediet RT (1999) The peritoneal membrane in chronic peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int 55:341–356
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM (1983) Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219:983–985
Connolly DT, Olander JV, Heuvelman D (1989) Human vascular permeability factor. Isolation from U937 cells. Biol. Chem. 264:20017–20024
Hood JD, Meininger CJ, Ziche M, Granger HJ (1998) VEGF upregulates ecNOS message, protein, and NO production in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol 274:H1054–H1058
Ferrara N, Davis Smyth T (1997) The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev 18:4–25
Devuyst O, Combet S, Pouthier D, Miyata T, Balligand JL, Glyoxalffin EJ (1998) Am. Soc. Nephrol. 9:191A
Niwa H, Takeda A, Wakai M (1998) Accelerated Formation of N ϵ-(carboxymethyl) Lysine, an advanced glycation end product, by glyoxal and 3-deoxyglucosone in cultured rat sensory neurons G. Sobue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 248:93–97
Akhand AA, Kato M, Suzuki H (1999) Carbonyl compounds cross-link cellular proteins and activate protein-tyrosine kinase p60(c-Src) Cell. Biochem 72:1–7
Miyata T, Inagi R, Asahi K, Yamada Y, Horie K, Sakai H, Uchida K, Kurokawa K (1998) Generation of protein carbonyls by glycoxidation and lipoxidation reactions with autoxidation products of ascorbic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acids. FEBS Lett 437:24–28
Miyata T, Ueda Y, Yamada Y (1998) Accumulation of carbonyls accelerates the formation of pentosidine, an advanced glycation end product: carbonyl stress in uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2349–2356
Carballo E, Cao H, Lai WS, Kennington EA, Campbell D, Blackshear PJ (2001) Decreased sensitivity of tristetraprolin-deficient cells to p38 inhibitors suggests the involvement of tristetraprolin in the p38 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 276:42580–42587
Mahtani KR, Brook M, Dean JL (2001) Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 controls the expression and posttranslational modification of tristetraprolin, a regulator of tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol 21:6461–6469
Johnson BA, Stehn JR, Yaffe MB, Blackwell TK (2002) Cytoplasmic localization of tristetraprolin involves 14-3-3-dependent and independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 277:18029–18036
Chrestensen CA, Schroeder MJ, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Pelo JW, Worthington MT, Sturgill TW (2004) MAPKAP kinase 2 phosphorylates tristetraprolin on in vivo sites including Ser178, a site required for 14-3-3 binding. J Biol Chem 279:10176–10184
Stoecklin G, Stubbs T, Kedersha N, Wax S, Rigby WF, Blackwell TK, Anderson P (2004) MK2-induced tristetraprolin:14-3-3 complexes prevent stress granule association and ARE-mRNA decay. EMBO J 23:1313–1324
Tsiani E, Lekas P, Fantus IG (2002) High glucose-enhanced activation of mesangial cell p38 MAPK by ET-1, ANG-2, and platelet-derived growth factor. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282:E161–E169
Jeon YJ, Kim BH, Kim S, Oh I, Lee S, Shin J, Kim TY (2013) Rhododendrin ameliorates skin inflammation through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK, and PI3 K/Akt signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 714:7–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Gao, H., Jin, Y. et al. The abnormal expressions of tristetraprolin and the VEGF family in uraemic rats with peritoneal dialysis. Mol Cell Biochem 392, 229–238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2033-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2033-3