Abstract
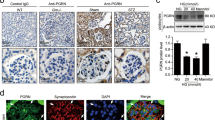
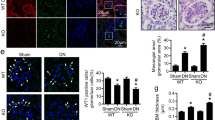
Podocyte injury may contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy (DN), but the underlying mechanism of hyperglycemia induced podocyte damage is not fully understood. The Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 is associated to the slit diaphragm proteins and the actin cytoskeleton in podocyte. Here, we studied IQGAP1 expression alterations in human DN biopsies and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-dependent pathways of IQGAP1 expression in podocyte under high glucose (HG) media. In vivo, analysis of renal biopsies from patients with DN revealed a significant reduction in IQGAP1 expression compared to controls. In vitro, IQGAP1 mRNA and protein expression were observed to decline under HG media at 48 h. But phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was activated under HG media at 24 h and 48 h. However, HG-induced downregulation of IQGAP1 protein was attenuated by specific ERK1/2 activation inhibitor PD98059. Taken together, these results highlight the importance of IQGAP1 in DN, and suggest that IQGAP1 expression in podocyte under HG media is modulated by the ERK1/2 pathway, which may lead to the future development of therapies targeting IQGAP1 dysfunction in podocytes in DN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Remuzzi G, Macia M, Ruggenenti P (2006) Prevention and treatment of diabetic renal disease in type 2 diabetes: the BENEDICT study. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:S90–97
Wolf G, Chen S, Ziyadeh FN (2005) From the periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of disease: podocyte injury comes of age indiabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 54:1626–1634
Ha TS (2006) High glucose and advanced glycosylated end-products affect the expression of alpha-actinin-4 in glomerular epithelial cells. Nephrology (Carlton) 11:435–441
Doublier S, Salvidio G, Lupia E, Ruotsalainen V, Verzola D, Deferrari G, Camussi G (2003) Nephrin expression is reduced in human diabetic nephropathy: evidence for a distinct role for glycated albumin and angiotensin II. Diabetes 52:1023–1030
Liu XL, Kilpeläinen P, Hellman U, Sun Y, Wartiovaara J, Morgunova E, Pikkarainen T, Yan K, Jonsson AP, Tryggvason K (2005) Characterization of the interactions of the nephrin intracellular domain. FEBS J 272:228–243
Rigothier C, Auguste P, Welsh GI, Lepreux S, Deminière C, Mathieson PW, Saleem MA, Ripoche J, Combe C (2012) IQGAP1 interacts with components of the slit diaphragm complex in podocytes and is involved in podocyte migration and permeability in vitro. PLoS One 7:e37695
Saleem MA, O’Hare MJ, Reiser J, Coward RJ, Inward CD, Farren T, Xing CY, Ni L, Mathieson PW, Mundel P (2002) A conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating nephrin and podocin expression. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:630–638
Kim EY, Dryer SE (2011) Effects of insulin and high glucose on mobilization of slo1 BKCa channels in podocytes. J Cell Physiol 226:2307–2315
Yamaoka-Tojo M, Ushio-Fukai M, Hilenski L, Dikalov SI, Chen YE, Tojo T, Fukai T, Fujimoto M, Patrushev NA, Wang N, Kontos CD, Bloom GS, Alexander RW (2004) IQGAP1, novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding protein, is involved in reactive oxygen species-dependent endothelial migration and proliferation. Circ Res 95:276–283
Lai LW, Yong KC, Lien YH (2008) Site-specific expression of IQGAP1, a key mediator of cytoskeleton, in mouse renal tubules. J Histochem Cytochem 56:659–666
Brinkkoetter PT, Olivier P, Wu JS, Henderson S, Krofft RD, Pippin JW, Hockenbery D, Roberts JM, Shankland SJ (2009) Cyclin I activates Cdk5 and regulates expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in postmitotic mouse cells. J Clin Invest 119:3089–3101
Toyoda M, Suzuki D, Honma M, Uehara G, Sakai T, Umezono T, Sakai H (2004) High expression of PKC-MAPK pathway mRNAs correlates with glomerular lesions in human diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 66:1107–1114
Hoshi S, Nomoto K, Kuromitsu J, Tomari S, Nagata M (2002) High glucose induced VEGF expression via PKC and ERK in glomerular podocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:177–184
Bai Y, Wang L, Li Y, Liu S, Li J, Wang H, Huang H (2006) High ambient glucose levels modulates the production of MMP-9 and alpha5 (IV) collagen by cultured podocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 17:57–68
Cheng X, Gao W, Dang Y, Liu X, Li Y, Peng X, Ye X (2013) Both ERK/MAPK and TGF-Beta/Smad signaling pathways play a role in the kidney fibrosis of diabetic mice accelerated by blood glucose fluctuation. J Diabetes Res 2013:463740
Jameson KL, Mazur PK, Zehnder AM, Zhang J, Zarnegar B, Sage J, Khavari PA (2013) IQGAP1 scaffold-kinase interaction blockade selectively targets RAS-MAP kinase-driven tumors. Nat Med 19:626–630
Roy M, Li Z, Sacks DB (2004) IQGAP1 binds ERK2 and modulates its activity. J Biol Chem 279:17329–17337
Sbroggiò M, Bertero A, Velasco S, Fusella F, De Blasio E, Bahou WF, Silengo L, Turco E, Brancaccio M, Tarone G (2011) ERK1/2 activation in heart is controlled by melusin, focal adhesion kinase and the scaffold protein IQGAP1. J Cell Sci 124:3515–3524
Li S, Wang Q, Chakladar A, Bronson RT, Bernards A (2000) Gastric hyperplasia in mice lacking the putative Cdc42 effector IQGAP1. Mol Cell Biol 20:697–701
Sanchez-Laorden B, Viros A, Marais R (2013) Mind the IQGAP. Cancer Cell 23:715–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Yao, C., Bian, A. et al. The Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 is downregulated in human diabetic nephropathy and associated with ERK1/2 pathway activation. Mol Cell Biochem 391, 21–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-1982-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-1982-x