Abstract
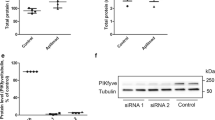
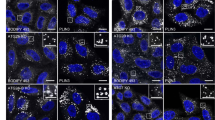
CI-976 is a lysophospholipid acyltransferase antagonist that is known to affect secretory and endocytic membrane-trafficking pathways likely by increasing the lysophospholipid content in membranes. Our previous study suggested that lysophospholipids formed through the action of an intracellular phospholipase A1, KIAA0725p (also known as DDHD2 and iPLA1γ), may be important for the association of this enzyme with membranes. In this study, we examined the effect of CI-976 on the membrane association of KIAA0725p. While in HeLa cells KIAA0725p is localized in the Golgi and cytosol, in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), it was found to be principally localized in the cytosol with some on post-endoplasmic reticulum compartments including the cis-Golgi. Treatment of MEFs with CI-976 induced the redistribution of KIAA0725p to membrane tubules, which were in vicinity to fragmented mitochondria. These tubules were not decorated with canonical organelle markers including Golgi proteins. A human KIAA0725p mutant, which exhibits decreased membrane-binding ability, was also redistributed to membrane structures upon CI-976 treatment. Our data suggest that the association of KIAA0725p with membranes is regulated by lipid metabolism, and that CI-976 may create unique membrane structures that can be marked by KIAA0725p.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown WJ, Chambers K, Doody A (2003) Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymes in membrane trafficking: mediators of membrane shape and function. Traffic 4:214–221
Bechler ME, de Figueiredo P, Brown WJ (2012) A PLA1-2 punch regulates the Golgi complex. Trends Cell Biol 22:116–124
Zimmerberg J, Kozlov MM (2006) How proteins produce cellular membrane curvature. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:9–19
Woolf TF, Bjorge SM, Black AE, Holmes A, Chang T (1991) Metabolism of the acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor 2,2-dimethyl-N-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)dodecanamide in rat and monkey. Omega-/beta-oxidation pathway. Drug Metab Dispos 19:696–702
Drecktrah D, Chambers K, Racoosin EL, Cluett EB, Gucwa A, Jackson B, Brown WJ (2003) Inhibition of a Golgi complex lysophospholipid acyltransferase induces membrane tubule formation and retrograde trafficking. Mol Biol Cell 14:3459–3469
Chambers K, Brown WJ (2004) Characterization of a novel CI-976-sensitive lysophospholipid acyltransferase that is associated with the Golgi complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:681–686
Chambers K, Judson B, Brown WJ (2005) A unique lysophospholipid acyltransferase (LPAT) antagonist, CI-976, affects secretory and endocytic membrane trafficking pathways. J Cell Sci 118:3061–3071
Schmidt JA, Brown WJ (2009) Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase 3 regulates Golgi complex structure and function. J Cell Biol 186:211–218
Tani K, Kogure T, Inoue H (2012) The intracellular phospholipase A1 protein family. Biomol Concepts 3:471–478
Nakajima K, Sonoda H, Mizoguchi T, Aoki J, Arai H, Nagahama M, Tagaya M, Tani K (2002) A novel phospholipase A1 with sequence homology to a mammalian Sec23p-interacting protein, p125. J Biol Chem 277:11329–11335
Morikawa RK, Aoki J, Kano F, Murata M, Yamamoto A, Tsujimoto M, Arai H (2009) Intracellular phospholipase A1γ (iPLA1γ) is a novel factor involved in coat protein complex I- and Rab6-independent retrograde transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem 284:26620–26630
Sato S, Inoue H, Kogure T, Tagaya M, Tani K (2010) Golgi-localized KIAA0725p regulates membrane trafficking from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane in mammalian cells. FEBS Lett 584:4389–4395
Inoue H, Baba T, Sato S, Ohtsuki R, Takemori A, Watanabe T, Tagaya M, Tani K (2012) Roles of SAM and DDHD domains in mammalian intracellular phospholipase A1 KIAA0725p. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823:930–939
Iinuma T, Shiga A, Nakamoto K, O’Brien MB, Aridor M, Arimitsu N, Tagaya M, Tani K (2007) Mammalian Sec16/p250 plays a role in membrane traffic from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 282:17632–17639
Wakana Y, Takai S, Nakajima K, Tani K, Yamamoto A, Watson P, Stephens DJ, Hauri HP, Tagaya M (2008) Bap31 is an itinerant protein that moves between the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and a juxtanuclear compartment related to ER-associated degradation. Mol Biol Cell 19:1825–1836
Nakamura N, Rabouille C, Watson R, Nilsson T, Hui N, Slusarewicz P, Kreis TE, Warren G (1995) Characterization of a cis-Golgi matrix protein, GM130. J Cell Biol 131:1715–1726
Robinson MS (1990) Cloning and expression of γ-adaptin, a component of clathrin-coated vesicles associated with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 111:2319–2326
Thyberg J, Moskalewski S (1985) Microtubules and the organization of the Golgi complex. Exp Cell Res 159:1–16
Cole NB, Sciaky N, Marotta A, Song J, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1996) Golgi dispersal during microtubule disruption: regeneration of Golgi stacks at peripheral endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Mol Biol Cell 7:631–650
Zanetti G, Pahuja KB, Studer S, Shim S, Schekman R (2011) COPII and the regulation of protein sorting in mammals. Nat Cell Biol 14:20–28
Linstedt AD, Mehta A, Suhan J, Reggio H, Hauri HP (1997) Sequence and overexpression of GPP130/GIMPc: evidence for saturable pH-sensitive targeting of a type II early Golgi membrane protein. Mol Biol Cell 8:1073–1087
Saraste J, Svensson K (1991) Distribution of the intermediate elements operating in ER to Golgi transport. J Cell Sci 100:415–430
Klumperman J, Schweizer A, Clausen H, Tang BL, Hong W, Oorschot V, Hauri HP (1998) The recycling pathway of protein ERGIC-53 and dynamics of the ER–Golgi intermediate compartment. J Cell Sci 111:3411–3425
Brown WJ, Plutner H, Drecktrah D, Judson BL, Balch WE (2008) The lysophospholipid acyltransferase antagonist CI-976 inhibits a late step in COPII vesicle budding. Traffic 9:786–797
Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P (1983) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol 97:329–339
Kreykenbohm V, Wenzel D, Antonin W, Atlachkine V, von Mollard GF (2002) The SNAREs vti1a and vti1b have distinct localization and SNARE complex partners. Eur J Cell Biol 81:273–280
Chen JW, Murphy TL, Willingham MC, Pastan I, August JT (1985) Identification of two lysosomal membrane glycoproteins. J Cell Biol 101:85–95
Raturi A, Simmen T (2013) Where the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondrion tie the knot: the mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM). Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:213–224
Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto A, Furuno A, Hatsuzawa K, Tani K, Himeno M, Tagaya M (1997) Possible involvement of heterotrimeric G proteins in the organization of the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 272:25260–25266
Drecktrah D, de Figueiredo P, Mason RM, Brown WJ (1998) Retrograde trafficking of both Golgi complex and TGN markers to the ER induced by nordihydroguaiaretic acid and cyclofenil diphenol. J Cell Sci 111:951–965
Fujiwara T, Takami N, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y (1998) Nordihydroguaiaretic acid blocks protein transport in the secretory pathway causing redistribution of Golgi proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 273:3068–3075
Fujiwara T, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y (1998) Dynamic recycling of ERGIC53 between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex is disrupted by nordihydroguaiaretic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 253:869–876
Fujiwara T, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y (2003) Direct interaction of the Golgi membrane with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane caused by nordihydroguaiaretic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:927–933
Arasaki K, Tani K, Yoshimori T, Stephens DJ, Tagaya M (2007) Nordihydroguaiaretic acid affects multiple dynein–dynactin functions in interphase and mitotic cells. Mol Pharmacol 71:454–460
Schroer TA (2004) Dynactin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:759–779
Famulski JK, Vos LJ, Rattner JB, Chan GK (2011) Dynein/dynactin-mediated transport of kinetochore components off kinetochores and onto spindle poles induced by nordihydroguaiaretic acid. PLoS ONE 6:e16494
Tirnauer JS, Bierer BE (2000) EB1 proteins regulate microtubule dynamics, cell polarity, and chromosome stability. J Cell Biol 149:761–766
Youle RJ, van der Bliek AM (2012) Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science 337:1062–1065
Huang H, Frohman MA (2009) Lipid signaling on the mitochondrial surface. Biochim Biophys Acta 179:839–844
Choi SY, Huang P, Jenkins GM, Chan DC, Schiller J, Frohman MA (2006) A common lipid links Mfn-mediated mitochondrial fusion and SNARE-regulated exocytosis. Nat Cell Biol 8:1255–1262
Huang H, Gao Q, Peng X, Choi SY, Sarma K, Ren H, Morris AJ, Frohman MA (2011) piRNA-associated germline nuage formation and spermatogenesis require MitoPLD profusogenic mitochondrial-surface lipid signaling. Dev Cell 20:376–387
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, 20570190, to KT from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan. We thank Ms. Y. Mizuya for her assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, T., Yamamoto, A., Tagaya, M. et al. A lysophospholipid acyltransferase antagonist, CI-976, creates novel membrane tubules marked by intracellular phospholipase A1 KIAA0725p. Mol Cell Biochem 376, 151–161 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1563-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1563-4