Abstract
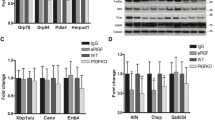
Placental growth factor (PlGF) inhibition produced promising results in reducing tumor burden in a diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of this study was to non-invasively assess the improved histology by performing a serum glycomic analysis. To elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying the observed glycomic effects, we investigated the transcription and expression of E26 transformation-specific sequence 1 (Ets-1), a transcription factor essential for the glycomic and angiogenic changes in malignant transformation, including its different phosphorylated forms that result from activation of the MAP kinase and a Ca2+-dependent pathway. In addition, three Ets-1-dependent glycosyltransferase genes, Mgat4a, Mgat4b, and Mgat5, were also evaluated. HCC was induced in mice by weekly injections with DEN for 16, 20, 25, and 30 w. In the treatment study, mice were injected with DEN for 25 w and subsequently treated with PlGF antibodies (5D11D4) for 5 w. Finally, PlGF−/− mice were injected with DEN for 20, 25, and 30 w. Serum N-glycans were analyzed with DNA sequencer-assisted fluorophore-assisted capillary electrophoresis and compared with histology. Maximum altered N-glycan phenotype was reached after 20 w of DEN-injections, i.e., when the first neoplastic lesions started to appear. 5D11D4-treatment improved the glycomic phenotype in that 7 of the 11 altered glycans tended to normalize. The PlGF−/− mice also showed a normalization trend, although not to the same extent of the treatment group. Number of Ets1, Mgat4a, Mgat4b, and Mgat5 transcripts increased considerably in DEN-injected mice, however, a non-significant decrease was observed after 5D11D4-treatment. On the protein level, 5D11D4-treatment had a prominent effect on the MAP kinase pathway with a significant p38 activation, yet independent of Ets-1 function.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nordenstedt H, White DL, El-Serag HB (2010) The changing pattern of epidemiology in Hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis 42(Suppl 3):S206–S214
Sherman M (2005) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin Liver Dis 25:143–154
Piccinino F, Sagnelli E, Pasquale G, Giusti G (1986) Complications following percutaneous liver biopsy. A multicentre retrospective study on 68,276 biopsies. J Hepatol 2:165–173
Callewaert N, Van Vlierberghe H, Van Hecke A, Laroy W, Delanghe J, Contreras R (2004) Noninvasive diagnosis of liver cirrhosis using DNA sequencer-based total serum protein glycomics. Nat Med 10:429–434
Liu XE, Desmyter L, Gao CF et al (2007) N-glycomic changes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with liver cirrhosis induced by hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 46:1426–1435
Xu J, Yun X, Jiang J et al (2010) Hepatitis B virus X protein blunts senescence-like growth arrest of human hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing Notch1 cleavage. Hepatology 52:142–154
Shim JK, Lee YC, Chung TH, Kim CH (2004) Elevated expression of bisecting N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-III gene in a human fetal hepatocyte cell line by hepatitis B virus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 19:1374–1387
Yanagi M, Aoyagi Y, Suda T, Mita Y, Asakura H (2001) N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase V as a possible aid for the evaluation of tumor invasiveness in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:1282–1289
Goldman R, Ressom HW, Varghese RS et al (2009) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma using glycomic analysis. Clin Cancer Res 15:1808–1813
Kang R, Saito H, Ihara Y et al (1996) Transcriptional regulation of the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V gene in human bile duct carcinoma cells (HuCC-T1) is mediated by Ets-1. J Biol Chem 271:26706–26712
Ko J, Miyoshi E, Noda K et al (1999) Regulation of the GnT-V promoter by transcription Ets-1 in various cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 274:22941–22948
Sato Y (2001) Role of ETS family transcription factors in vascular development and angiogenesis. Cell Struct Funct 26:19–24
Wernert N, Raes MB, Lassalle P et al (1992) c-ets1 proto-oncogene is a transcription factor expressed in endothelial cells during tumor vascularization and other forms of angiogenesis in humans. Am J Pathol 140:119–127
Yang B, Hauser C, Henkel G et al (1996) Ras-mediated phosphorylation of a conserved threonine residue enhances the transactivation activities of c-Ets-1 and c-Ets-2. Moll Cell Biol 16:538–547
Cowley D, Graves B (2000) Phosphorylation represses Ets-1 DNA binding by reinforcing autoinhibition. Genes Dev 14:366–376
Pufall M, Lee G, Nelson M et al (2005) Variable control of Ets-1 DNA binding by multiple phosphates in an unstructured region. Science 309:142–145
Maglione D, Guerriero V, Viglietto G, Dellibovi P, Persico M (1991) Isolation of a human placenta cDNA coding for a protein related to the vascular permeability factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9267–9271
Fischer C, Jonckx B, Mazzone M et al (2007) Anti-PlGF inhibits growth of VEGF(R)-inhibitor-resistant tumors without affecting healthy vessels. Cell 131:463–475
Van de Veire S, Stalmans I, Heindryckx F et al (2010) Further pharmacological and genetic evidence for the efficacy of PlGF inhibition in cancer and eye disease. Cell 141:178–190
Tang Z, Varghese R, Bekesova S et al (2010) Identification of N-glycan serum markers associated with hepatocellular carcinoma from mass spectrometry data. J Proteome Res 9:104–112
Heindryckx F, Mertens K, Charette N et al (2010) Kinetics of angiogenic changes in a new mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer 9:219–232
Laroy W, Contreras R, Callewaert N (2006) Glycome mapping on DNA sequencing equipment. Nat Protoc 1:397–405
Blomme B, Van Steenkiste C, Callewaert N, Van Vlierberghe H (2011) Alterations of serum protein N-glycosylation in two models of chronic liver disease are hepatocyte and not B cell driven. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:G833–G842
Blomme B, Van Steenkiste C, Vanhuysse J, Colle I, Callewaert N, Van Vlierberghe H (2010) Impact of elevation of total bilirubin level and etiology of the liver disease on serum N-glycosylation patterns in mice and humans. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G615–G624
Klein A, Carre Y, Louvet A, Michalski JC, Morelle W (2010) Immunoglobulins are the major glycoproteins involved in the modifications of total serum N-glycome in cirrhotic patients. Proteomics Clin Appl 4:379–393
Vanderschaeghe D, Laroy W, Sablon E et al (2009) GlycoFibroTest is a highly performant liver fibrosis biomarker derived from DNA sequencer-based serum protein glycomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:986–994
Liu XE, Dewaele S, Vanhooren V et al (2010) Alteration of N-glycome in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice: a non-invasive monitoring tool for liver cancer. Liver Int 30:1221–1228
Ito Y, Miyoshi E, Takeda T et al (2000) Expression and possible role of ets-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 114:719–725
Vanderschaeghe D, Szekrényes A, Wenz C et al (2010) High-throughput profiling of the serum N-glycome on capillary electrophoresis microfluidics systems: towards clinical implication of the GlycoHepatoTest. Anal Chem 82:7408–7415
Takamatsu S, Antonopoulos A, Ohtsubo K et al (2010) Physiological and glycomic characterization of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IVa and -IVb double deficient mice. Glycobiology 20:485–497
Mendoza R, Moody E, Enriquez M, Mejia S, Thordarson G (2011) Tumorigenicity of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells lacking the p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Endocrinol 208:11–19
Hsu Y, Meng X, Ou L, Ip M (2010) Activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase-p38 MAP kinase pathway mediates apoptosis induced by conjugated linoleic acid in p53-mutant mouse mammary tumor cells. Cell Signal 22:590–599
Hui L, Bakiri L, Stepniak E, Wagner E (2007) P38 alpha: a suppressor of cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle 6:2429–2433
Hui L, Bakiri L, Mairhorfer A et al (2007) P38 alpha suppresses normal and cancer cell proliferation by antagonizing the JNK-c-Jun pathway. Nat Genet 39:741–749
McMullen M, Bryant P, Glembotski C, Vincent P, Pumiglia K (2005) Activation of p38 has opposing effects on the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 280:20995–21003
Issbrücker K, Marti H, Hippenstiel S (2003) p38 MAP kinase—a molecular switch between VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. FASEB J 17:262–264
Luttun A, Brusselmans K, Fukao H et al (2002) Loss of placental growth factor protects mice against vascular permeability in pathological conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:428–434
Vetter M, Blumenthal S, Lindemann R (2005) Ets1 is an effector of protein kinase Cα in cancer cells. Oncogene 24:650–661
Acknowledgments
BB receives a scholarship GOA BOFF07/GOA/017 of the University Ghent Research Fund (BOF). HVV is Senior Clinical Investigator of the Research Foundation (FWO). FH is funded by a FWO grant (Aspirant FWO, FWO09/ASP/161).
Conflict of interest
JM Stassen is a shareholder and Head of pre-clinical R&D of ThromboGenics NV and named in a patent related to data reported in this article which may result in payment of royalties. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blomme, B., Heindryckx, F., Stassen, J.M. et al. Serum protein N-glycan alterations of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice and their evolution after inhibition of the placental growth factor. Mol Cell Biochem 372, 199–210 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1461-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1461-1