Abstract
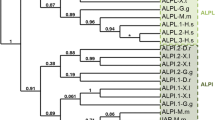
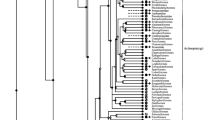
Cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR), a metabolite of NAD+, is known to function as a second messenger for intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in various vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. In this study, we isolated two Xenopus laevis cDNAs (frog cd38 and cd157 cDNAs) homologous to the one encoding the human cADPR-metabolizing enzyme CD38. Frog CD38 and CD157 are 298-amino acid proteins with 35.9 and 27.2 % identity to human CD38 and CD157, respectively. Transfection of expression vectors for frog CD38 and CD157 into COS-7 cells revealed that frog CD38 had NAD+ glycohydrolase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase (ARC), and cADPR hydrolase activities, and that frog CD157 had no enzymatic activity under physiological conditions. In addition, when recombinant CD38 and frog brain homogenate were electrophoresed on an SDS–polyacrylamide gel, ARC of the brain homogenate migrated to the same position in the gel as that of frog CD38, suggesting that frog CD38 is the major enzyme responsible for cADPR metabolism in amphibian cells. The frog cd38 gene consists of eight exons and is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues. These findings provide evidence for the existence of the CD38–cADPR signaling system in frog cells and suggest that the CD38–cADPR signaling system is conserved during vertebrate evolution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clapper DL, Walseth TF, Dargie PJ, Lee HC (1987) Pyridine nucleotide metabolites stimulate calcium release from sea urchin egg microsomes desensitized to inositol trisphosphate. J Biol Chem 262:9561–9568
Galione A, Lee HC, Busa WB (1991) Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in sea urchin egg homogenates: modulation by cyclic ADP-ribose. Science 253:1143–1146
Takasawa S, Nata K, Yonekura H, Okamoto H (1993) Cyclic ADP-ribose in insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. Science 259:370–373
Lee HC (2002) Structures, metabolism and functions. In: Lee HC (ed) Cyclic ADP-ribose and NAADP. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 1–21
Hua S-Y, Tokimasa T, Takasawa S, Furuya Y, Nohmi M, Okamoto H, Kuba K (1994) Cyclic ADP-ribose modulates Ca2+ release channels for activation by physiological Ca2+ entry in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron 12:1073–1079
Wu Y, Kuzma J, Marechal E, Graeff R, Lee HC, Foster R, Chua NH (1997) Abscisic acid signaling through cyclic ADP-ribose in plants. Science 278:2126–2130
Albrieux M, Lee HC, Villaz M (1998) Calcium signaling by cyclic ADP-ribose, NAADP, and inositol trisphosphate are involved in distinct functions in ascidian oocytes. J Biol Chem 273:14566–14574
Kuroda R, Kontam K, Kanda Y, Katada T, Nakano T, Satoh Y, Suzuki N, Kuroda H (2001) Increase of cGMP, cADP-ribose and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate preceding Ca2+ transients in fertilization of sea urchin eggs. Development 128:4405–4414
Partida-Sanchez S, Cockayne DA, Monard S, Jacobson EL, Oppenheimer N, Garvy B, Kusser K, Goodrich S, Howard M, Harmsen A, Randall TD, Lund FE (2001) Cyclic ADP-ribose production by CD38 regulates intracellular calcium release, extracellular calcium influx and chemotaxis in neutrophils and is required for bacterial clearance in vivo. Nat Med 7:1209–1216
Okamoto H, Takasawa S (2002) Recent advances in the Okamoto model: the CD38-cyclic ADP-ribose signal system and the regenerating gene protein (Reg)-Reg receptor system in p-cells. Diabetes 51:S462–S473
Glick DL, Hellmich MR, Beushausen S, Tempst P, Bayley H, Strumwasser F (1991) Primary structure of a molluscan egg-specific NADase, a second-messenger enzyme. Cell Regul 2:211–218
Lee HC, Aarhus R (1991) ADP-ribosyl cyclase: an enzyme that cyclizes NAD+ into a calcium-mobilizing metabolite. Cell Regul 2:203–209
Nata K, Sugimoto T, Tohgo A, Takamura T, Noguchi N, Matsuoka A, Nakamura T, Shikama K, Yonekura H, Takasawa S, Okamoto H (1995) The structure of the Aplysia kurodai gene encoding ADP-ribosyl cyclase, a second-messenger enzyme. Gene 158:213–218
States DJ, Walseth TF, Lee HC (1992) Similarities in amino acid sequences of Aplysia ADP-ribosyl cyclase and human lymphocyte antigen CD38. Trends Biochem Sci 17:495
Tohgo A, Takasawa S, Noguchi N, Koguma T, Nata K, Sugimoto T, Furuya Y, Yonekura H, Okamoto H (1994) Essential cysteine residues for cyclic ADP-ribose synthesis and hydrolysis by CD38. J Biol Chem 269:28555–28557
Jackson DG, Bell JI (1990) Isolation of a cDNA encoding the human CD38 (T10) molecule, a cell surface glycoprotein with an unusual discontinuous pattern of expression during lymphocyte differentiation. J Immunol 144:2811–2815
Harada N, Santos-Argumedo L, Chang R, Grimaldi JC, Lund EF, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Heath AW, Parkhouse RME, Howard M (1993) Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel murine B cell activation marker. J Immunol 151:3111–3118
Takasawa S, Tohgo A, Noguchi N, Koguma T, Nata K, Sugimoto T, Yonekura H, Okamoto H (1993) Synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose by human leukocyte antigen CD38 and inhibition of the hydrolysis by ATP. J Biol Chem 268:26052–26054
Koguma T, Takasawa S, Tohgo A, Karasawa T, Furuya Y, Yonekura H, Okamoto H (1994) Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding rat ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase (homologue to human CD38) from islet of Langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1223:160–162
Ebihara S, Sasaki T, Hida W, Kikuchi Y, Oshiro T, Shimura S, Takasawa S, Okamoto H (1997) Role of cyclic ADP-ribose in ATP-activated potassium currents in alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem 272:16023–16029
Nata K, Takamura T, Karasawa T, Kumagai T, Hashioka W, Tohgo A, Yonekura H, Takasawa S, Nakamura S, Okamoto H (1997) Human gene encoding CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase): organization, nucleotide sequence and alternative splicing. Gene 186:285–292
Sasamori K, Sasaki T, Takasawa S, Tamada T, Nara M, Irokawa T (2004) Cyclic ADP-ribose, a putative Ca2+-mobilizing second messenger, operates in submucosal gland acinar cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L69–L78
Howard M, Grimaldi JC, Bazan IF, Lund FE, Santos-Argumedo L, Parkhouse RME, Walseth TF, Lee HC (1993) Formation and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose catalyzed by lymphocyte antigen CD38. Science 262:1056–1059
Lee HC, Zocchi E, Guida L, Franco L, Benatti U, De Flora A (1993) Production and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose at the outer surface of human erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191:639–645
Hirata Y, Kimura N, Sato K, Ohsugi Y, Takasawa S, Okamoto H, Ishikawa J, Kaisho T, Ishihara K, Hirano T (1994) ADP ribosyl cyclase activity of a novel bone marrow stromal cell surface molecule, BST-1. FEBS Lett 356:244–248
Kaisho T, Ishikawa J, Oritani K, Inazawa J, Tomizawa H, Muraoka O, Ochi T, Hirano T (1994) BST-1, a surface molecule of bone marrow stromal cell lines that facilitates pre-B-cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5325–5329
Kim H, Jacobson EL, Jacobson MK (1993) Synthesis and degradation of cyclic ADP-ribose by NAD glycohydrolases. Science 261:1330–1333
Muller-Steffner HM, Augustin A, Schuber F (1996) Mechanism of cyclization of pyridine nucleotides by bovine spleen NAD+ glycohydrolase. J Biol Chem 271:23967–23972
Sauve AA, Munshi C, Lee HC, Schramm VL (1998) The reaction mechanism for CD38. A signal intermediate is responsible for cyclization, hydrolysis, and base-exchange chemistries. Biochemistry 37:13239–13249
Schuber F, Lund FE (2004) Structure and enzymology of ADP-ribosyl cyclases: conserved enzymes that produce multiple calcium mobilizing metabolites. Curr Mol Med 4:249–261
Kukimoto I, Hoshino S, Kontani K, Inageda K, Nishina H, Takahashi K, Katda T (1996) Stimulation of ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity of the cell surface antigen CD38 by zinc ions resulting from inhibition of its NAD + glycohydrolase activity. Eur J Biochem 239:177–182
Bertheher V, Tixier JM, Muller-Steffner H, Schuber F, Deterre P (1998) Human CD38 is an authentic NAD(P)+ glycohydrolase. Biochem J 330:1383–1390
Lund FE, Moutm MJ, Muller-Steffner H, Schuber F (2005) ADP-ribosyl cyclase and GDP-ribosyl cyclase activities are not always equivalent: impact on the study of the physiological role of cyclic ADP-ribose. Anal Biochem 346:336–338
Liu Q, Kriksunov IA, Graeff R, Lee HC, Hao Q (2007) Structural basis for formation and hydrolysis of calcium messenger cyclic ADP-ribose by human CD38. J Biol Chem 282:5853–5861
Kato I, Yamamoto Y, Fujimura M, Noguchi N, Takasawa S, Okamoto H (1999) CD38 disruption impairs glucose-induced increases in cyclic ADP-ribose, [Ca2+]i, and insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 274:1869–1872
Goodrich SP, Muller-Steffner H, Osman A, Moutin M, Kusser K, Roberts A, Woodland DL, Randall TD, Kellenberger E, LoVerde PT, Schuber F, Lund FE (2005) Production of calcium-mobilizing metabolites by a novel member of the ADP-ribosyl cyclase family expressed in Schistosoma mansoni. Biochemistry 44:11082–11097
Kuhn I, Kellenberger E, Rognan D, Lund FE, Muller-Steffner H, Schuber F (2006) Redesign of Schistosoma mansoni NAD + catabolizing enzyme: active site H103W mutation restores ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity. Biochemistry 45:11867–11878
Churamam D, Boulware MJ, Geach TJ, Martin ACR, Moy GW, Su YH, Vacquier VD, Marchant JS, Dale L, Patel S (2007) Molecular characterization of a novel intracellular ADP-ribosyl cyclase. PLoS One 2:e797
Davis LC, Morgan AJ, Ruas M, Wong JL, Graef RM, Poustka AJ, Lee HC, Wessel GM, Parrington J, Galione A (2008) Ca2+ signaling occurs via second messenger release from intraorganelle synthesis sites. Curr Biol 18:1612–1618
Okamoto H, Takasawa S, Tohgo A, Nata K, Kato I, Noguchi N (1997) Synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose by human leukocyte antigen CD38: Inhibition of hydrolysis by ATP and physiological significance. Methods Enzymol 280:306–318
Karasawa T, Takasawa S, Yamakawa K, Yonekura H, Okamoto H, Nakamura S (1995) NAD+-glycohydrolase from Streptococcus pyogenes shows cyclic ADP-ribose forming activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 130:201–204
Graeff RM, Walseth TF, Hill HK, Lee HC (1996) Fluorescent analogs of cyclic ADP-ribose: synthesis, spectral characterization, and use. Biochemistry 35:379–386
Lee HC, Graeff RM, Munshi CB, Walseth TF, Aarhus R (1997) Large-scale purification of Aplysia ADP-ribosyl cyclase and measurement of its activity by fluorometric assay. Methods Enzymol 280:331–340
Ziegler M, Jorcke D, Schweiger M (1997) Identification of bovine liver mitochondrial NAD+ glycohydrolase as ADP-ribosyl cyclase. Biochem J 326:401–405
Takasawa S, Akiyama T, Nata K, Kuroki M, Tohgo A, Noguchi N, Kobayashi S, Kato I, Katada T, Okamoto H (1998) Cyclic ADP-ribose and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate as alternate second messengers for intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in normal and diabetic p-cells. J Biol Chem 273:2497–2500
Nakazawa T, Takasawa S, Noguchi N, Nata K, Tohgo A, Mori M, Nakagawara K, Akiyama T, Ikeda T, Yamauchi A, Takahashi I, Yoshikawa T, Okamoto H (2005) Genomic organization, chromosomal localization, and promoter of human gene for FK506-binding protein 12.6. Gene 360:55–64
Itoh M, Ishihara K, Tomizawa H, Tanaka H, Kobune Y, Ishikawa J, Kaisho T, Hirano T (1994) Molecular cloning of murine BST-1 having homology with CD38 and Aplysia ADP-ribosyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 203:1309–1317
Furuya Y, Takasawa S, Yonekura H, Tanaka T, Takahara J, Okamoto H (1995) Cloning of a cDNA encoding rat bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (BST-1) from the islets of Langerhans. Gene 165:329–330
Munshi C, Thiel DJ, Mathews II, Aarhus R, Walseth TF, Lee HC (1999) Characterization of the active site of ADP-ribosyl cyclase. J Biol Chem 274:30770–30777
Munshi C, Aarhus R, Greaff R, Walseth TF, Levitt D, Lee HC (2000) Identification of the enzymatic active site of CD38 by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 275:21566–21571
Okamoto H, Takasawa S (2001) CD38. In: Creighton TE (ed) Encyclopedia of molecular medicine. Wiley, New York, pp 601–604
Muraoka O, Tanaka H, Itoh M, Ishihara K, Hirano T (1996) Genomic structure of human BST-1. Immunol Lett 54:1–4
McNagny KM, Cazenave PA, Cooper MD (1988) A cell surface glycoprotein that marks early B lineage cells and mature myeloid lineage cells in mice. J Immunol 141:2551–2556
Alessio M, Roggero S, Funaro A, De Monte LB, Peruzzi L, Geuna M, Malavasi F (1990) CD38 molecule: structural and biochemical analysis on human T lymphocytes, thymocytes, and plasma cells. J Immunol 145:878–884
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Brent Bell for valuable assistance in preparing the manuscript for publication and to Yuya Shichinohe for skillful technical assistance. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan and was submitted by T. I. in partial fulfilment of the degree of Doctor of Medical Science at Tohoku University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, T., Takasawa, S., Noguchi, N. et al. Identification of a major enzyme for the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose in amphibian cells and evolutional conservation of the enzyme from human to invertebrate. Mol Cell Biochem 366, 69–80 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1284-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1284-0