Abstract
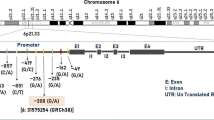
Migraine is a complex neurological disorder with a clear neurogenic inflammatory component apparently including enhanced nitric oxide (NO) formation. Excessive NO amounts possibly contributing to migraine are derived from increased expression and activity of inducible NO synthase (iNOS). We tested the hypothesis that two functional, clinically relevant iNOS genetic polymorphisms (C−1026A—rs2779249 and G2087A—rs2297518) are associated with migraine with or without aura. We studied 142 healthy women without migraine (control group) and 200 women with migraine divided into two groups: 148 with migraine without aura (MWA) and 52 with aura (MA). Genotypes were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction using the Taqman® allele discrimination assays. The PHASE 2.1 software was used to estimate the haplotypes. The A allele for the G2087A polymorphism was more commonly found in the MA group than in the MWA group (28 vs. 18%; P < 0.05). No other significant differences in the alleles or genotypes distributions were found (P > 0.05). The haplotype combining both A alleles for the two polymorphisms was more commonly found in the MA group than in the control group or in the MWA group (19 vs. 10 or 8%; P = 0.0245 or 0.0027, respectively). Our findings indicate that the G2087A and the C−1026A polymorphism in the iNOS gene affect the susceptibility to migraine with aura when their effects are combined within haplotypes, whereas the G2087A affects the susceptibility to aura in migraine patients. These finding may have therapeutic implications when examining the effects of selective iNOS inhibitors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen R, Stovner LJ (2008) Epidemiology and comorbidity of headache. Lancet Neurol 7(4):354–361
Pietrobon D, Striessnig J (2003) Neurobiology of migraine. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(5):386–398
Bigal ME, Kurth T, Santanello N, Buse D, Golden W, Robbins M, Lipton RB (2010) Migraine and cardiovascular disease: a population-based study. Neurology 74(8):628–635
Dalkara T, Nozari A, Moskowitz MA (2010) Migraine aura pathophysiology: the role of blood vessels and microembolisation. Lancet Neurol 9(3):309–317
Kurth T, Schurks M, Logroscino G, Buring JE (2009) Migraine frequency and risk of cardiovascular disease in women. Neurology 73(8):581–588
Goncalves FM, Martins-Oliveira A, Speciali JG, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Luizon MR, Dach F, Tanus-Santos JE (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor genetic polymorphisms and haplotypes in women with migraine. DNA Cell Biol 29(7):357–362
Martins-Oliveira A, Speciali JG, Dach F, Marcaccini AM, Goncalves FM, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2009) Different circulating metalloproteinases profiles in women with migraine with and without aura. Clin Chim Acta 408(1–2):60–64
Goncalves FM, Martins-Oliveira A, Speciali JG, Luizon MR, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Silva PS, Dach F, Tanus-Santos JE (2011) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase haplotypes associated with aura in patients with migraine. DNA Cell Biol 30(6):363–369
Stam AH, van den Maagdenberg AM, Haan J, Terwindt GM, Ferrari MD (2008) Genetics of migraine: an update with special attention to genetic comorbidity. Curr Opin Neurol 21(3):288–293
Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD (2002) Migraine–current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med 346(4):257–270
Olesen J (2008) The role of nitric oxide (NO) in migraine, tension-type headache and cluster headache. Pharmacol Ther 120(2):157–171
Olesen J (2010) Nitric oxide-related drug targets in headache. Neurotherapeutics 7(2):183–190
Sarchielli P, Floridi A, Mancini ML, Rossi C, Coppola F, Baldi A, Pini LA, Calabresi P (2006) NF-kappaB activity and iNOS expression in monocytes from internal jugular blood of migraine without aura patients during attacks. Cephalalgia 26(9):1071–1079
Moncada S, Higgs A (1993) The l-arginine–nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med 329(27):2002–2012
Lea RA, Curtain RP, Shepherd AG, Brimage PJ, Griffiths LR (2001) No evidence for involvement of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene in susceptibility to typical migraine. Am J Med Genet 105(1):110–113
Jia S, Ni J, Chen S, Jiang Y, Dong W, Gao Y (2011) Association of the pentanucleotide repeat polymorphism in NOS2 promoter region with susceptibility to migraine in a Chinese population. DNA Cell Biol 30(2):117–122
Amaral LM, Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Luizon MR, Cavalli RC, Duarte G, Tanus-Santos JE (2011) Maternal iNOS genetic polymorphisms and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. J Hum Hypertens. doi:10.1038/jhh.2011.65
Li W, Liu H, Fu L, Li D, Zhao Y (2010) Identification of Yin Yang 1-interacting partners at −1026C/A in the human iNOS promoter. Arch Biochem Biophys 498(2):119–126
Fu L, Zhao Y, Lu J, Shi J, Li C, Liu H, Li Y (2009) Functional single nucleotide polymorphism-1026C/A of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene with increased YY1-binding affinity is associated with hypertension in a Chinese Han population. J Hypertens 27(5):991–1000
Wang SS, Davis S, Cerhan JR, Hartge P, Severson RK, Cozen W, Lan Q, Welch R, Chanock SJ, Rothman N (2006) Polymorphisms in oxidative stress genes and risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Carcinogenesis 27(9):1828–1834
Lee KM, Kang D, Park SK, Berndt SI, Reding D, Chatterjee N, Chanock S, Huang WY, Hayes RB (2009) Nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms and prostate cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 30(4):621–625
Sandrim VC, Palei AC, Cavalli RC, Araujo FM, Ramos ES, Duarte G, Tanus-Santos JE (2008) eNOS haplotypes associated with gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. Pharmacogenomics 9(10):1467–1473
Sandrim VC, Palei AC, Luizon MR, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Cavalli RC, Tanus-Santos JE (2010) eNOS haplotypes affect the responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in preeclampsia but not in gestational hypertension. Pharmacogenomics J 10(1):40–45
Sandrim VC, Palei AC, Sertorio JT, Cavalli RC, Duarte G, Tanus-Santos JE (2010) Effects of eNOS polymorphisms on nitric oxide formation in healthy pregnancy and in pre-eclampsia. Mol Hum Reprod 16(7):506–510
HCSotIH Society (2004) The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 24(Suppl 1):9–160
Lacchini R, Metzger IF, Luizon M, Ishizawa M, Tanus-Santos JE (2010) Interethnic differences in the distribution of matrix metalloproteinases genetic polymorphisms are consistent with interethnic differences in disease prevalence. DNA Cell Biol 29(11):649–655
Metzger IF, Sandrim VC, Tanus-Santos JE (2012) Endogenous nitric oxide formation correlates negatively with circulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 levels in black subjects. Mol Cell Biochem 360(1–2):393–399
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68(4):978–989
Johannesen J, Pie A, Pociot F, Kristiansen OP, Karlsen AE, Nerup J (2001) Linkage of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene to type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(6):2792–2796
Lassen LH, Ashina M, Christiansen I, Ulrich V, Grover R, Donaldson J, Olesen J (1998) Nitric oxide synthase inhibition: a new principle in the treatment of migraine attacks. Cephalalgia 18(1):27–32
Hoivik HO, Laurijssens BE, Harnisch LO, Twomey CK, Dixon RM, Kirkham AJ, Williams PM, Wentz AL, Lunnon MW (2010) Lack of efficacy of the selective iNOS inhibitor GW274150 in prophylaxis of migraine headache. Cephalalgia 30(12):1458–1467
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico and Coordenadoria de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de O. S. Mansur, T., Gonçalves, F.M., Martins-Oliveira, A. et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase haplotype associated with migraine and aura. Mol Cell Biochem 364, 303–308 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1231-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1231-0