Abstract
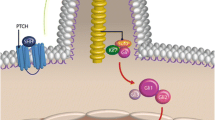
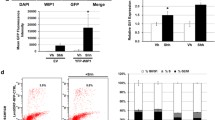
Accumulated evidence suggests a major role for the activation of the Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway in the development of neural crest stem cells that give rise to the sympathetic nervous system. We therefore investigated the involvement of SHH signaling in the pathogenesis of neuroblastoma (NB), a common childhood malignant tumor of the sympathetic nervous system. Inhibition of SHH signaling by cyclopamine induced apoptosis and blocked proliferation in all major types of NB cells, and abrogated the tumorigenicity of NB cells. Our study has revealed a molecular mechanism for the persistent activation of the SHH pathway which promotes the development of NB, and suggests a new approach for the treatment of this childhood malignant tumor.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SHH:
-
Sonic Hedgehog
- NB:
-
Neuroblastoma
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- Toma:
-
Tomatidine
- Cyclo:
-
Cyclopamine
- BrdU:
-
5-Bromo-2_-deoxyuridine
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- 7-AAD:
-
7-Aminoactinomycin D
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
References
Fietz MJ, Concordet JP, Barbosa R, Johnson R, Krauss S, McMahon AP, Tabin C, Ingham PW (1994) The Hedgehog gene family in Drosophila and vertebrate development. Development (Suppl) 120:43–51
Hooper JE, Scott MP (2005) Communicating with Hedgehogs. Natl Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(4):306–317
Riobo NA, Manning DR (2007) Pathways of signal transduction employed by vertebrate Hedgehogs. Biochem J 403(3):369–379
Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ (2006) Targeting the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(12):1026–1033
Brodeur GM (2003) Neuroblastoma: biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer 3(3):203–216
Wu SM, Choo AB, Yap MG, Chan KK (2010) Role of Sonic Hedgehog signaling and the expression of its components in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res 4(1):38–49
Le Douarin NM, Calloni GW, Dupin E (2008) The stem cells of the neural crest. Cell Cycle 7(8):1013–1019
Ahlgren SC, Bronner-Fraser M (1999) Inhibition of Sonic Hedgehog signaling in vivo results in craniofacial neural crest cell death. Curr Biol 9(22):1304–1314
Fu M, Lui VC, Sham MH, Pachnis V, Tam PK (2004) Sonic Hedgehog regulates the proliferation, differentiation, and migration of enteric neural crest cells in gut. J Cell Biol 166(5):673–684
Jeong J, Mao J, Tenzen T, Kottmann AH, McMahon AP (2004) Hedgehog signaling in the neural crest cells regulates the patterning and growth of facial primordia. Genes Dev 18(8):937–951
Williams Z, Tse V, Hou L, Xu L, Silverberg GD (2000) Sonic Hedgehog promotes proliferation and tyrosine hydroxylase induction of postnatal sympathetic cells in vitro. Neuroreport 11(15):3315–3319
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK, Beachy PA (2002) Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev 16(21):2743–2748
Cooper MK, Porter JA, Young KE, Beachy PA (1998) Teratogen-mediated inhibition of target tissue response to Shh signaling. Science 280(5369):1603–1607
Incardona JP, Gaffield W, Kapur RP, Roelink H (1998) The teratogenic Veratrum alkaloid cyclopamine inhibits Sonic Hedgehog signal transduction. Development 125(18):3553–3562
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL (2001) Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 414(6859):105–111
Jordan CT, Guzman ML, Noble M (2006) Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med 355(12):1253–1261
Bar EE, Chaudhry A, Lin A, Fan X, Schreck K, Matsui W, Piccirillo S, Vescovi AL, DiMeco F, Olivi A, Eberhart CG (2007) Cyclopamine-mediated Hedgehog pathway inhibition depletes stem-like cancer cells in glioblastoma. Stem Cells 25(10):2524–2533
Liu S, Dontu G, Mantle ID, Patel S, Ahn NS, Jackson KW, Suri P, Wicha MS (2006) Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res 66(12):6063–6071
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang B, Beachy PA, Baylin SB (2003) Hedgehog signalling within airway epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature 422(6929):313–317
Bar EE, Chaudhry A, Farah MH, Eberhart CG (2007) Hedgehog signaling promotes medulloblastoma survival via Bc/II. Am J Pathol 170(1):347–355
Kenney AM, Rowitch DH (2000) Sonic Hedgehog promotes G(1) cyclin expression and sustained cell cycle progression in mammalian neuronal precursors. Mol Cell Biol 20(23):9055–9067
Gartel AL, Serfas MS, Tyner AL (1996) p21–negative regulator of the cell cycle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 213(2):138–149
Saqui-Salces M, Merchant JL (2010) Hedgehog signaling and gastrointestinal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803(7):786–795
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for Dr. Han-fei Ding and Dr. Qingyou Xia for their invaluable support. This study were supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012cb114603), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31172268, 30872649/C1608, 81172413), and the Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ (No. cstc 2011jjA8007).
Conflicts of interest
The authors are not employed by any commercial companies that may influence during the performance of this study
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Wang, X., Wan, J. et al. Sonic Hedgehog pathway is essential for neuroblastoma cell proliferation and tumor growth. Mol Cell Biochem 364, 235–241 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1222-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1222-6