Abstract
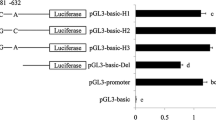
MTPAP (mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase) gene plays a role in stabilizing the level of mitochondrial mRNAs and controlling the poly(A) length of human mitochondrial mRNAs. In this study, 2,296 bp partial cDNA sequences of the porcine MTPAP gene were obtained, which contained 1,746 bp full-length coding regions flanked by a 500 bp partial 3′-UTR. The porcine MTPAP gene was assigned to SSC10q14-q16 using the radiation hybrid (IMpRH) panel and chromosome electric location methods. Q-PCR analysis showed that MTPAP was expressed in all analyzed tissues, and has higher expression in heart, liver, skeletal muscles, and fat. One single nucleotide polymorphism g.2421T>A in intron5 of MTPAP gene was identified and detected by DdeI PCR–RFLP. Association of the genotypes with economic traits showed that different genotypes were significantly associated with juiciness, individuals with genotype AT displayed a significantly higher juiciness compared to genotype TT. The C/EBPβ transcription factors was up-regulation the expression of MTPAP by analyzing a series of MTPAP promoter reporter constructs using the dual-luciferase assay system, it indicated that MTPAP gene maybe play a critical role in fat deposition regulation which is regulated by C/EBPβ transcription factor. These findings provide an important basis for further understanding of porcine MTPAP regulation and function in swine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomecki R, Dmochowska A, Gewartowski K, Dziembowski A, Stepien PP (2004) Identification of a novel human nuclear-encoded mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res 32:6001–6014
Nagaike T, Suzuki T, Katoh T, Ueda T (2005) Human mitochondrial mRNAs are stabilized with polyadenylation regulated by mitochondria-specific poly(A) polymerase and polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 280:19721–19727
Owen OE, Kalhan SC, Hanson RW (2002) The key role of anaplerosis and cataplerosis for citric acid cycle function. J Biol Chem 277:30409–30412
Reichert AS, Neupert W (2004) Mitochondriomics or what makes us breathe. Trends Genet 20:555–562
Xiao Q, Wu XL, Michal JJ, Reeves JJ, Busboom JR, Thorgaard GH, Jiang ZH (2006) A novel nuclear-encoded mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase PAPD1 is a potential candidate gene for the extreme obesity related phenotypes in mammals. Int J Biol Sci 2:171–178
Yerle M, Pinton P, Robic A, Alfonso A, Palvadeau Y, Delcros C, Hawken R, Alexander L, Beattie C, Schook L, Milan D, Gellin J (1998) Construction of a whole-genome radiation hybrid panel for high-resolution gene mapping in pigs. Cytogenet Cell Genet 82:182–188
Milan D, Hawken R, Cabau C, Leroux S, Genet C, Lahbib Y, Tosser G, Robic A, Hatey F, Alexander L, Beattie C, Schook L, Yerle M, Gellin J (2000) IMpRH server: an RH mapping server available on the web. Bioinformatics 16:558–559
Cai W, Casey DS, Dekkers JCM (2008) Selection response and genetic parameters for residual feed intake in Yorkshire swine. J Anim Sci 86:287–298
Raabe T, Murthy KG, Manley JL (1994) Poly(A) polymerase contains multiple functional domains. Mol Cell Biol 14:2946–2957
Thuresson AC, Astrom J, Astrom A, Gronvik KO, Virtanen A (1994) Multiple forms of poly(A) polymerases in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:979–983
Kyriakopoulou CB, Nordvarg H, Virtanen A (2001) A novel nuclear human poly(A) polymerase (PAP), PAP gamma. J Biol Chem 276:33504–33511
Gado K, Domjan G, Kormos L, Falus A (2002) Functional significance of genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Haematologia (Budap) 32:191–208
Hager J, Dina C, Francke S, Dubois S, Houari M, Vatin V, Vaillant E, Lorentz N, Basdevant A, Clement K, Guy-Grand B, Froguel P (1998) A genome-wide scan for human obesity genes reveals a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 10. Nat Genet 20:304–308
Hinney A, Ziegler A, Oeffner F, Wedewardt C, Vogel M, Wulftange H, Geller F, Stubing K, Siegfried W, Goldschmidt HP, Remschmidt H, Hebebrand J (2000) Independent confirmation of a major locus for obesity on chromosome 10. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2962–2965
Price RA, Li WD, Bernstein A, Crystal A, Golding EM, Weisberg SJ, Zuckerman WA (2001) A locus affecting obesity in human chromosome region 10p12. Diabetologia 44:363–366
Boutin P, Dina C, Vasseur F, Dubois S, Corset L, Seron K, Bekris L, Cabellon J, Neve B, Vasseur-Delannoy V, Chikri M, Charles MA, Clement K, Lernmark A, Froguel P (2003) GAD2 on chromosome 10p12 is a candidate gene for human obesity. PLoS Biol 1:E68
Eikelenboom G, Hoving-Bolink AH, Van Der Waal PG (1996) The eating quality of pork. 2. The influence of intramuscular fat. Fleischwirtschaft 76:517–518
Wood JD, Brown SN, Nute GR, Whittington FM, Perry AM, Johnson SP, Enser MB (1996) Effects of breed, feed level and conditioning time on the tenderness of pork. Meat Sci 44:105–112
Park B, Cho S, Kim J, Yoo Y, Lee J, Ahn Ch, Kim Y, Yun S (2001) Carcass composition and meat quality by intramuscular fat contents in Longissimus dorsi of Hanwoo. In: Materials of 47th international congress of meat science and technology, August 26th–31st 2001, Kraków, pp 116–118
Hocquette JF, Gondret F, Baéza E, Médale F, Jurie C, Pethick DW (2010) Intramuscular fat content in meat-producing animals: development genetic and nutritional control and identification of putative markers. Animal 4(2):303–319
Enfält AC, Lundström K, Hansson I, Lundeheim N, Nyström PE (1997) Effects of outdoor rearing and sire breed (Duroc or Yorkshire) on carcass composition and sensory and technological meat quality. Meat Sci 45:1–15
Bredahl L, Grunert KG, Fertin C (1998) Relating consumer perceptions of pork quality to physical product characteristics. Food Qual Prefer 4:273–281
Resurreccion AVA (2004) Sensory aspects of consumer choices for meat and meat products. Meat Sci 66:11–20
Fernandez X, Monin G, Talmant A, Mourot J, Lebret B (1999) Influence of intramuscular fat content on the quality of pig meat—1. Composition of the lipid fraction and sensory characteristics of m. longissimus lumborum. Meat Sci 53:59–65
Tomasz D, Tomasz B, Jerzy D (2005) Quality of pork with a different intramuscular fat (IMF) content. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 1:31–36
Darlington GJ, Ross SE, MacDougald OA (1998) The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 273:30057–30060
Poli V (1998) The role of C/EBP isoforms in the control of inflammatory and native immunity functions. J Biol Chem 273:29279–29282
Farmer SR (2006) Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab 4:263–273
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA (2006) Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Natl Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:885–896
Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD (2003) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is required for mitotic clonal expansion during adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:850–855
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the numbers of Dr Rothschild’s Lab for their assistance on this research and Dr. Martine Yerle for providing the RH panel (INRA, Castanet-Tolosan, France). The study was supported by the National Transgenic Key Program (2009ZX08012-015B) and Scientific Innovation of University Students Foundation (SRF, A08041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xuelei Han and Tengfei Jiang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Jiang, T., Yu, L. et al. Molecular characterization of the porcine MTPAP gene associated with meat quality traits: chromosome localization, expression distribution, and transcriptional regulation. Mol Cell Biochem 364, 173–180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1216-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1216-4