Abstract
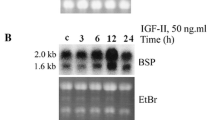
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 (IGFBP-6) is a member of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein family, which has both Insulin-like growth factor-dependent and independent effects on cell growth. In previous studies, we have shown that recombinant IGFBP-6 could be translocated into the cell nucleus. But the effect in the nucleus of IGFBP-6 is not clear. In the present study, we use multiple methodologies including Glutathione S-transferase pull-down assay, co-immunoprecipitation, fluorescence resonance energy transfer to demonstrate that IGFBP-6 can directly interact with thyroid hormone receptor alpha 1 (TRα1) in vitro and in vivo. We also demonstrate that the DNA-binding domains and Ligand-binding domains of TRα1 and N-terminal domains and C-terminal domains of IGFBP-6 are involved in the interaction. This interaction also can block the formation of TR: retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Furthermore, immunofluorescence co-localization studies show IGFBP-6 and TRα1 could co-localize in the nucleus of the cells. Reporter gene experiment shows that IGFBP-6 negatively regulates the growth hormone promoter activity induced by ligand activated TRα1. Moreover, real-time RT-PCR demonstrates that IGFBP-6 could inhibit the osteocalcin mRNA transcription induced by Triiodothyronine (3,3′,5-Triiodo-L-thyronine, T3) in osteoblastic cells. Finally, alkaline phosphatase activity was significantly decreased in osteoblastic cells when the cells were transfected with IGFBP-6 in the presence of T3. In conclusion, these studies provide evidence that overexpression of IGFBP-6 suppresses osteoblastic differentiation regulated by TR in the present of T3.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassett JH, Williams GR (2003) The molecular actions of thyroid hormone in bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab 14:356–364
Harvey CB, O’Shea PJ, Scott AJ, Robson H, Siebler T, Shalet SM, Samarut J, Chassande O, Williams GR (2002) Molecular mechanisms of thyroid hormone effects on bone growth and function. Mol Genet Metab 75:17–30
Bassett JH, Williams AJ, Murphy E, Boyde A, Howell PG, Swinhoe R, Archanco M, Flamant F, Samarut J, Costagliola S, Vassart G, Weiss RE, Refetoff S, Williams GR (2008) A lack of thyroid hormones rather than excess thyrotropin causes abnormal skeletal development in hypothyroidism. Mol Endocrinol 22:501–512
Shao YY, Wang L, Ballock RT (2006) Thyroid hormone and the growth plate. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 7:265–271
Klaushofer K, Varga F, Glantschnig H, Fratzl-Zelman N, Czerwenka E, Leis HJ, Koller K, Peterlik M (1995) The regulatory role of thyroid hormones in bone cell growth and differentiation. J Nutr 125(Supplement 7):1996S–2003S
Murphy E, Williams GR (2004) The thyroid and the skeleton. Clin Endocrinol 61:285–298
Gogakos AI, Duncan Bassett JH, Williams GR (2010) Thyroid and bone. Arch Biochem Biophys 503:129–136
Bassett J, Williams G (2008) Critical role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in bone. Bone 43:418–426
Yen PM (2001) Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev 81:1097–1142
Shi YB (2009) Dual functions of thyroid hormone receptors in vertebrate development: the roles of histone-modifying cofactor complexes. Thyroid 19:987–999
Oetting A, Yen PM (2007) New insights into thyroid hormone action. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 21:193–208
Cheng SY (2000) Multiple mechanisms for regulation of the transcriptional activity of thyroid hormone receptors. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 1:9–18
Capelo LP, Beber EH, Fonseca TL, Gouveia CH (2009) The monocarboxylate transporter 8 and L-type amino acid transporters 1 and 2 are expressed in mouse skeletons and in osteoblastic MC3T3–E1 cells. Thyroid 19:171–180
Perks CM, McCaig C, Holly JM (2000) Differential insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent interactions of IGF binding protein-3 and IGF binding protein-5 on apoptosis in human breast cancer cells involvement of the mitochondria. J Cell Biochem 80:248–258
Kamanga-Sollo E, Pampusch MS, White ME, Hathaway MR, Dayton WR (2005) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 and IGFBP-5 mediate TGF-beta- and myostatin-induced suppression of proliferation in porcine embryonic myogenic cell cultures. Exp Cell Res 311:167–176
Bach LA (2005) IGFBP-6 five years on; not so ‘forgotten’? Growth Horm IGF Res 15:185–192
Iosef C, Gkourasas T, Jia CY, Li SS, Han VK (2008) A functional nuclear localization signal in insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 mediates its nuclear import. Endocrinology 149:1214–1226
Strohbach C, Kleinman S, Linkhart T, Amaar Y, Chen ST, Mohan S, Strong D (2008) Potential involvement of the interaction between insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-6 and LIM mineralization protein (LMP)-1 in regulating osteoblast differentiation. J Cell Biochem 104:1890–1905
Efendiev R, Cinelli AR, Leibiger IB, Bertorello AM, Pedemonte CH (2006) FRET analysis reveals a critical conformational change within the Na, K-ATPase α1 subunit N-terminus during GPCR-dependent endocytosis. FEBS Lett 580:5067–5070
Gordon GW, Berry G, Liang XH, Levine B, Herman B (1998) Quantitative fluorescence resonance energy transfer measurements using fluorescence microscopy. Biophys J 74:2702–2713
Schedlich LJ, Muthukaruppan A, O’Han MK, Baxter RC (2007) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 interacts with the vitamin D receptor and modulates the vitamin D response in osteoblasts. Mol Endocrinol 21:2378–2390
Schedlich LJ, O’Han MK, Leong GM, Baxter RC (2004) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 prevents retinoid receptor heterodimerization: implications for retinoic acid-sensitivity in human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Common 314:83–88
Kumar R, Thompson EB (1999) The structure of the nuclear hormone receptors. Steroids 64:310–319
Schedlich LJ, Graham LD, O’Han MK, Muthukaruppan A, Yan X, Firth SM, Baxter RC (2007) Molecular basis of the interaction between IGFBP-3 and retinoid X receptor: role in modulation of RAR-signaling. Arch Biochem Biophys 465:359–369
Dye BT (2005) Flow cytometric analysis of CFP–YFP FRET as a marker for in vivo protein–protein interaction. Clin Appl Immu Rev 5:307–324
Bassett J, Williams G (2008) Critical role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in bone. Bone 43:418–426
Huang W, Carlsen B, Rudkin GH, Shah N, Chung C, Ishida K, Yamaguchi DT, Miller TA (2001) Effect of serial passage on gene expression in MC3T3–E1 preosteoblastic cells: a microarray study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:1120–1126
Govoni KE, Amaar YG, Kramer A, Winter E, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2006) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, four and a half lim-2, and a disintegrin and metalloprotease-9 expression in osteoblasts. Growth Horm IGF Res 16:49–56
Mukherjee A, Rotwein P (2007) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 in osteogenesis: facilitator or inhibitor? Growth Horm IGF Res 17:179–185
Chihara K, Sugimoto T (1997) The action of GH/IGF-I/IGFBP in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Horm Res 48(Suppl 5):45–49
Mukherjee A, Rotwein P (2008) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 inhibits osteoblast differentiation and skeletal growth by blocking insulin-like growth factor actions. Mol Endocrinol 22:1238–1250
Durant D, Pereira RM, Canalis E (2004) Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 decreases osteoblastic function in vitro. Bone 35:1256–1262
Asai S, Cao X, Yamauchi M, Funahashi K, Ishiguro N, Kambe F (2009) Thyroid hormone non-genomically suppresses Src thereby stimulating osteocalcin expression in primary mouse calvarial osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:92–96
Kasono K, Sato K, Han D, Fujii Y, Tsushima T, Shizume K (1988) Stimulation of alkaline phosphatase activity by thyroid hormone in mouse osteoblast-like cells (MC3T3–E1): a possible mechanism of hyperalkaline phosphatasia in hyperthyroidism. Bone Miner 4:355–363
Varga F, Rumpler M, Luegmayr E, Fratzl-Zelman N, Glantschnig H, Klaushofer K (1997) Triiodothyronine, a regulator of osteoblastic differentiation: depression of histone H4, attenuation of c-fos/c-jun, and induction of osteocalcin expression. Calcif Tissue Int 61:404–411
Chambery D, De Galle B, Ehrenborg E, Babajko S (2000) Multi-hormonal regulation of IGFBP-6 expression in human neuroblastoma cell. Growth Horm IGF Res 10:349–359
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. David J. Mangelsdorf (Howard Hughes Medical Institute, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Department of Pharmacology) for giving us pGEX-2T-hRXRa. The authors also thank Prof. Norman Eberhardt (Mayo Clinic, Department of Medicine/Division of Endocrinology) and Dr. Peter A. Cattini (Department of Physiology, University of Manitoba) for giving them pGL3-GH promoter plasmid and other GH relative luciferase reporter plasmids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Ma, XL., Wang, X. et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 interacts with the thyroid hormone receptor α1 and modulates the thyroid hormone-response in osteoblastic differentiation. Mol Cell Biochem 361, 197–208 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1104-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1104-y