Abstract
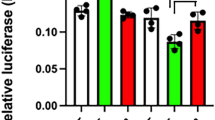
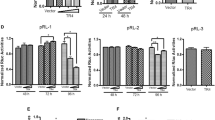
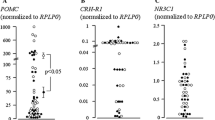
Mimecan, a secretary protein that is expressed in mouse and human pituitary corticotroph cells, is up-regulated by glucocorticoids (GC) in the corticotroph cells via classical glucocorticoid receptor (GR) pathways. In this study, we further explore the GC mechanism for mimecan expression in these cells. Five putative GR response elements (GREs) were identified in ~2 kb of the mimecan promoter by programme analysis. An EMSA assay further indicated that these putative GREs were bound by the GR. Moreover, three proximal GREs are conserved between species. Although luciferase assays showed that the −1474/+43 region of the mimecan promoter achieved the highest expression of mimecan, the −803/+43 mimecan promoter region was sufficient for the GC-mediated expression of mimecan. The mutations of three conserved GREs located in the −1474/+43 mimecan promoter region did not affect mimecan transcription, which suggests that the effects of GC on mimecan are independent of the GREs in the promoter. In addition, cycloheximide, a protein synthesis inhibitor, blocked GC-induced mimecan expression in AtT-20 cells. Taken together, these results suggest that, although there are 3–5 GREs in the mimecan promoter, GC may regulate mimecan transcription indirectly through the synthesis of intermediate proteins and not through the GREs in pituitary corticotroph cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madisen L, Neubauer M, Plowman G, Rosen D, Segarini P, Dasch J, Thompson A, Ziman J, Bentz H, Purchio AF (1990) Molecular cloning of a novel bone-forming compound: osteoinductive factor. DNA Cell Biol 9:303–309
Tasheva ES, Corpuz LM, Funderburgh JL, Conrad GW (1997) Differential splicing and alternative polyadenylation generate multiple mimecan mRNA transcripts. J Biol Chem 272:32551–32556
Funderburgh JL, Corpuz LM, Roth MR, Funderburgh ML, Tasheva ES, Conrad GW (1997) Mimecan, the 25 kDa corneal keratan sulfate proteoglycan, is a product of the gene producing osteoglycin. J Biol Chem 272:28089–28095
Ujita M, Shinomura T, Kimata K (1995) Molecular cloning of the mouse osteoglycin-encoding gene. Gene 158:237–240
Long CJ, Roth MR, Tasheva ES, Funderburgh M, Smit R, Conrad GW, Funderburgh JL (2000) Fibroblast growth factor-2 promotes keratan sulfate proteoglycan expression by keratocytes in vitro. J Biol Chem 275:13918–13923
Shanahan CM, Cary NR, Osbourn JK, Weissberg PL (1997) Identification of osteoglycin as a component of the vascular matrix. Differential expression by vascular smooth muscle cells during neointima formation and in atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:2437–2447
Tasheva ES, Maki CG, Conrad AH, Conrad GW (2001) Transcriptional activation of bovine mimecan by p53 through an intronic DNA-binding site. Biochim Biophys Acta 1517:333–338
Tasheva ES, Koester A, Paulsen AQ, GarrettAS BoyleDL, Davidson HJ, SongM FoxN, Conrad GW (2002) Mimecan/osteoglycin-deficient mice have collagen fibril abnormalities. Mol Vis 8:407–415
Tasheva ES (2002) Analysis of the promoter region of human mimecan gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1575:123–129
Tasheva ES, Conrad GW (2003) The UV responsive elements in the human mimecan promoter: a functional characterization. Mol Vis 9:1–9
TashevaES ConradGW (2003) Interferon-gamma regulation of the human mimecan promoter. Mol Vis 9:277–287
Chrousos GP, Gold PW (1992) The concepts of stress and stress system disorders. Overview of physical and behavioral homeostasis. JAMA 267:1244–1252
Chrousos GP (1995) The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N Engl J Med 332:1351–1362
Strawhecker JM, Betz NA, Neades RY, Houser W, Pelling JC (1989) Binding of the 97 kDa glucocorticoid receptor to the 5′ upstream flanking region of the mouse c-Ha-ras oncogene. Oncogene 4:1317–1322
Drouin J, Sun YL, Tremblay S, Lavender P, Schmidt TJ, de Lean A, Nemer M (1992) Homodimer formation is rate-limiting for high affinity DNA binding by glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Endocrinol 6:1299–1309
Hu RM, Han ZG, Song HD, Peng YD, Huang QH, Ren SX, Gu YJ, Huang CH, Li YB, Jiang CL, Fu G, Zhang QH, Gu BW, Dai M, Mao YF, Gao GF, Rong R, Ye M, Zhou J, Xu SH, Gu J, Shi JX, Jin WR, Zhang CK, Wu TM, Huang GY, Chen Z, Chen MD, Chen JL (2000) Gene expression profiling in the human hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and full-length cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9543–9548
Hu SM, Li F, Yu HM, Li RY, Ma QY, Ye TJ, Lu ZY, Chen JL, Song HD (2005) The mimecan gene expressed in human pituitary and regulated by pituitary transcription factor-1 as a marker for diagnosing pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:6657–6664
Ma QY, Zuo CL, Ma JH, Zhang XN, Ru Y, Li P, Pan CM, Liu Z, Cao HM, Chen MD, Song HD (2010) Glucocorticoid up-regulates mimecan expression in corticotroph cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 321:239–244
Lee HC, Shibata H, Ogawa S, Maki K, Ikuta K (2005) Transcriptional regulation of the mouse IL-7 receptor alpha promoter by glucocorticoid receptor. J Immunol 174:7800–7806
Bamberger CM, Schulte HM, Chrousos GP (1996) Molecular determinants of glucocorticoid receptor function and tissue sensitivity to glucocorticoids. Endocr Rev 17:245–261
Kumar R, Thompson EB (2005) Gene regulation by the glucocorticoid receptor: structure:function relationship. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 94:383–394
Iozzo RV (1999) The biology of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. Functional network of interactive proteins. J Biol Chem 274:18843–18846
Kresse H, Schonherr E (2001) Proteoglycans of the extracellular matrix and growth control. J Cell Physiol 189:266–274
Ameye L, Young MF (2002) Mice deficient in small leucine-rich proteoglycans: novel in vivo models for osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, muscular dystrophy, and corneal diseases. Glycobiology 12:107R–116R
Acknowledgement
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30871206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiao-Na Zhang and Li-Qiong Xue contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.N., Xue, L.Q., Jiang, H. et al. The mechanism of mimecan transcription induced by glucocorticoid in pituitary corticotroph cells. Mol Cell Biochem 360, 321–328 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1071-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1071-3