Abstract
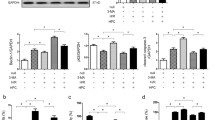
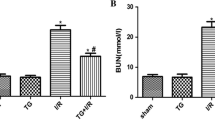
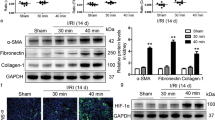
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) could ameliorate renal ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI), but the underlying mechanism remains elusive. In the current study, we aim to investigate the possible role of prolyl hydroxylases inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG) in inducing delayed preconditioning-like effects against IRI. Mice were divided into four groups (n = 6): sham group; IRI group; DMOG group: pretreated with DMOG 24 h before IRI; and GW274150 + DMOG group: pretreated with DMOG followed by iNOS inhibitor GW274150 treatment 24 h before IRI. The results showed that the protein level of HIF-1a and the expression of its targets inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), erythropoietin, and heme oxygenase-1 were obviously increased after administration of DMOG. Histological analysis of renal function showed improvement in tubulointerstitial injury due to ischemia by delayed preconditioning with DMOG. GW274150 antagonized the delayed renal protection afforded by DMOG as reflected by deteriorated renal dysfunction, aggravated histological injury, increased renal cell apoptosis, and increased vimentin expression in the kidney. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that DMOG pretreatment induces delayed renal protection against IRI in mice and the beneficial effects are mitigated by pharmacological inhibition of iNOS, suggesting that the protective effects derived from HIF-1 activation via DMOG in the kidney are partially mediated by iNOS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basile DP, Donohoe D, Roethe K, Osborn JL (2001) Renal ischemic injury results in permanent damage to peritubular capillaries and influences long-term function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F887–F899
Reutzel-Selke A, Pratschke J, Martins PN, Denecke C, Jurisch A, Kotsch K, Pascher A, Neuhaus P, Tullius SG (2008) Ischemic preconditioning produces systemic protective and adoptively transferable effects. Kidney Int 74:622–630
Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney ischemic preconditioning. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11:43–48
Wang GL, Semenza GL (1993) General involvement of hypoxia inducible factor 1 in transcription response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4304–4308
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS, Kaelin WG Jr (2001) HIF targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implication for O2 sensing. Science 292:464–468
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian Y, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, Kriegsheim Av, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 94:468–472
Bruick RM SLA (2001) A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294:1337–1340
Semenza GL (2000) Surviving ischemia: adaptive responses mediated by hypoxia inducible factor 1. J Clin Invest 106:809–812
Haase VH (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factors in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F271–F281
Rosenberger C, Rosen S, Shina A, Frei U, Eckardt KU, Flippin LA, Arend M, Klaus SJ, Heyman SN (2008) Activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates hypoxic distal tubular injury in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3472–3478
Ockaili R, Natarajan R, Salloum F, Fisher BJ, Jones D, Fowler AA 3rd, Kukreja RC (2005) HIF-1 activation attenuates postischemic myocardial injury: role for heme oxygenase-1 in modulating microvascular chemokine generation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H542–H548
Harten SK, Ashcroft M, Maxwell PH (2010) Prolyl hydroxylase domain inhibitors: a route to HIF activation and neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 12:459–480
Jablonski P, Howden BO, Rae DA, Birrell CS, Marshall VC, Tange J (1983) An experimental model for assessment of renal recovery from warm ischemia. Transplantation 35:198–204
Witzgall R, Brown D, Schwarz C, Bonventre JV (1994) Localization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, vimentin, c-Fos, and clusterin in the postischemic kidney: evidence for a heterogenous genetic response among nephron segments, and a large pool of mitotically active and dedifferentiated cells. J Clin Invest 93:2175–2188
Rosenberger C, Rosen S, Heyman SN (2006) Renal parenchymal oxygenation and hypoxia adaptation in acute kidney injury. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33:980–988
Joo JD, Kim M, D’Agati VD, Lee HT (2006) Ischemic preconditioning provides both acute and delayed protection against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:3115–3123
Yang CC, Lin LC, Wu MS, Chien CT, Lai MK (2009) Repetitive hypoxic preconditioning attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion induced oxidative injury via upregulating HIF-1 alpha-dependent bcl-2 signaling. Transplantation 88:1251–1260
Hill P, Shukla D, Tran MG, Aragones J, Cook HT, Carmeliet P, Maxwell PH (2008) Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor hydroxylases protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:39–46
Natarajan R, Salloum FN, Fisher BJ, Ownby ED, Kukreja RC, Fowler AA 3rd (2007) Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 via prolyl-4 hydoxylase-2 gene silencing attenuates acute inflammatory responses in postischemic myocardium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1571–H1580
Natarajan R, Salloum FN, Fisher BJ, Kukreja RC, Fowler AA 3rd (2006) Hypoxia inducible factor-1 activation by prolyl 4-hydroxylase-2 gene silencing attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Circ Res 98:133–140
Ockaili R, Natarajan R, Salloum F, Fisher BJ, Jones D, Fowler AA 3rd, Kukreja RC (2005) HIF-1 activation attenuates postischemic myocardial injury: role for heme oxygenase-1 in modulating microvascular chemokine generation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H542–H548
Sasabe E, Tatemoto Y, Li D, Yamamoto T, Osaki T (2005) Mechanism of HIF-1alpha-dependent suppression of hypoxia-induced apoptosis in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci 96:394–402
Liu XB, Wang JA, Ogle ME, Wei L (2009) Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine enhances mesenchymal stem cell survival. J Cell Biochem 106:903–911
Yang CW, Li C, Jung JY, Shin SJ, Choi BS, Lim SW, Sun BK, Kim YS, Kim J, Chang YS, Bang BK (2003) Preconditioning with erythropoietin protects against subsequent ischemia reperfusion injury in rat kidney. FASEB J 17:1754–1755
Wagner M, Cadetg P, Ruf R, Mazzucchelli L, Ferrari P, Redaelli CA (2003) Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis and improves survival in rat renal allografts. Kidney Int 63:1564–1573
Cuzzocrea S, Chatterjee PK, Mazzon E, Dugo L, De Sarro A, Van de Loo FA, Caputi AP, Thiemermann C (2002) Role of induced nitric oxide in the initiation of the inflammatory response after postischemic injury. Shock 18:169–176
Alderton WK, Angell AD, Craig C, Dawson J, Garvey E, Moncada S, Monkhouse J, Rees D, Russell LJ, Russell RJ, Schwartz S, Waslidge N, Knowles RG (2005) GW274150 and GW273629 are potent and highly selective inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 145:301–312
Sakamoto K, Yonoki Y, Kubota Y, Kuwagata M, Saito M, Nakahara T, Ishii K (2006) Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors abolished histological protection by late ischemic preconditioning in rat retina. Exp Eye Res 82:512–518
Shinmura K, Xuan YT, Tang XL, Kuwagata M, Saito M, Nakahara T, Ishii K (2002) Inducible nitric oxide synthase modulates cyclooxygenase-2 activity in the heart of conscious rabbits during the late phase of ischemic preconditioning. Circ Res 90:602–608
Cho S, Park EM, Zhou P, Frys K, Ross ME, Iadecola C (2005) Obligatory role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in ischemic preconditioning. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:493–501
Park KM, Byun JY, Kramers C, Kim JI, Huang PL, Bonventre JV (2003) Inducible nitric-oxide synthase is an important contributor to prolonged protective effects of ischemic preconditioning in the mouse kidney. J Biol Chem 278:27256–27266
Wakeno-Takahashi M, Otani H, Nakao S, Imamura H, Shingu K (2005) Isoflurane induces second window of preconditioning through up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H2585–H2591
Zhao T, Xi L, Chelliah J, Levasseur JE, Kukreja RC (2000) Inducible nitric oxide synthase mediates delayed myocardial protection induced by activation of adenosine A(1) receptors: evidence from gene-knockout mice. Circulation 102:902–907
Xi L, Taher M, Yin C, Salloum F, Kukreja RC (2004) Cobalt chloride induces delayed cardiac preconditioning in mice through selective activation of HIF-1α and AP-1 and iNOS signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H2369–H2375
Yu L, Gengaro PE, Niederberger M, Burke TJ, Schrier RW (1994) Nitric oxide: a mediator in rat tubular hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1691–1695
Bertuglia S (2008) Intermittent hypoxia modulates nitric oxide-dependent vasodilation and capillary perfusion during ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H1914–H1922
Lopez-Neblina F, Paez AJ, Toledo-Pereyra LH (1995) Modulation of neutrophil infiltration through nitric oxide in the ischemic rat kidney. Transplant Proc 27:1883–1885
Goligorsky MS, Brodsky SV, Noiri E (2002) Nitric oxide in acute renal failure: NOS versus NOS. Kidney Int 61:855–861
Pannu R, Singh I (2006) Pharmacological strategies for the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase: neurodegenerative versus neuroprotective mechanisms. Neurochem Int 49:170–182
Kimura H, Weisz A, Kurashima Y, Hashimoto K, Ogura T, D’Acquisto F, Addeo R, Makuuchi M, Esumi H (2000) Hypoxia response element of the human vascular endothelial growth factor gene mediates transcriptional regulation by nitric oxide: control of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity by nitric oxide. Blood 95:189–197
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Project of Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai, China (No. 09410705800).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, XL., Yan, ZW., Sheng, WW. et al. Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 ameliorates postischemic renal injury via inducible nitric oxide synthase. Mol Cell Biochem 358, 287–295 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0979-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0979-y