Abstract
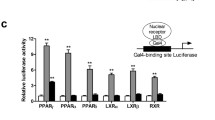
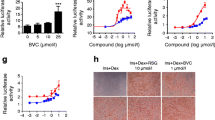
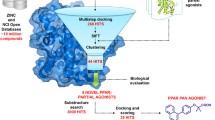
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are the transcriptional factor that regulate glucose and lipid homeostasis and widely well-known as molecular targets for improvement of metabolic disorder. Because major transcriptional activity of PPARs depends on their proper ligands, the studies for PPAR ligands have been continuously developed. We previously reported the simple enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) systems to screen PPAR ligands and a chemical library including flavonoid derivatives have applied to these systems. In this study, we introduce two compounds (KU16476 and KU28843) identified as PPARγ partial agonists by a screening ELISA for PPARγ ligand. KU16476 and KU28843 significantly increased binding between PPARγ and SRC-1 in a simple ELISA system. Co-activator recruiting-induced abilities of two compounds were less than that of indomethacin, a well-known PPARγ agonist. To determine whether these compounds would be PPARγ partial agonists, each candidate with indomethacin were applied to a simple ELISA based on binding between PPARγ and SRC-1. Cotreatment with indomethacin significantly increased binding between PPARγ and SRC-1 than treatment of indomethacin or candidate alone. Two compounds had no considerable cytotoxicities, induced partial adipogenesis, and accumulated lipid droplets in 3T3-L1 fibroblast. Also, these two compounds enhanced expression of PPARγ-mediated genes such as aP2 and UCP-2. By docking study, we confirmed that two compounds bound well to the active site of PPARγ with hydrophobic interactions. We suggest that two compounds identified by a simple ELISA system can be PPARγ partial agonists. These PPARγ partial agonists and these studies to find out novel PPARγ agonists may contribute to drug development against metabolic disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferated-activator receptor gamma
- TZDs:
-
Thiazolidinediones
- LBD:
-
Ligand-binding domain
- SRC-1:
-
Steroid receptor coactivator-1
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- PPRE:
-
Peroxisome proliferator response element
- aP2:
-
Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein
- SRB:
-
Sulforhodamine B
References
Giguere V (1999) Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev 20(5):689–725
Lowell BB (1999) PPARgamma: an essential regulator of adipogenesis and modulator of fat cell function. Cell 99(3):239–242
Desvergne B, Wahli W (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20(5):649–688
Willson TM, Lambert MH, Kliewer SA (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and metabolic disease. Annu Rev Biochem 70:341–367. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.341
Lehmann JM, Lenhard JM, Oliver BB, Ringold GM, Kliewer SA (1997) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem 272(6):3406–3410
Houseknecht KL, Cole BM, Steele PJ (2002) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and its ligands: a review. Domest Anim Endocrinol 22(1):1–23
Tontonoz P, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Erdjument-Bromage H, Lui M, Hu E, Tempst P, Spiegelman BM (1994) Adipocyte-specific transcription factor ARF6 is a heterodimeric complex of two nuclear hormone receptors, PPAR gamma and RXR alpha. Nucleic Acids Res 22(25):5628–5634
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Spiegelman BM (1994) mPPAR gamma 2: tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev 8(10):1224–1234
Nolte RT, Wisely GB, Westin S, Cobb JE, Lambert MH, Kurokawa R, Rosenfeld MG, Willson TM, Glass CK, Milburn MV (1998) Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature 395(6698):137–143. doi:10.1038/25931
Heery DM, Kalkhoven E, Hoare S, Parker MG (1997) A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 387(6634):733–736. doi:10.1038/42750
Cho MC, Lee K, Paik SG, Yoon DY (2008) Peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor (PPAR) modulators and metabolic disorders. PPAR Res 2008:679137. doi:10.1155/2008/679137
Cho MC, Lee WS, Hong JT, Park SW, Moon DC, Paik SG, Yoon DY (2005) 5-(3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylidene) thiazolidine-2,4-dione modulates peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: roles as a PPARgamma ligand. Mol Cell Endocrinol 242(1–2):96–102. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.08.005
Lee HS, Cho MC, Baek TW, Choe YK, Kim JW, Hong JT, Myung PK, Paik SG, Yoon DY (2005) Epitope analysis of PPARgamma monoclonal antibody Pgamma48.34A and its application for screening PPARgamma ligands. J Immunol Methods 296(1-2):125–134. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2004.11.011
Cho MC, Yoon HE, Kang JW, Park SW, Yang Y, Hong JT, Song EY, Paik SG, Kim SH, Yoon DY (2006) A simple method to screen ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta. Eur J Pharm Sci 29(5):355–360. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2006.07.003
Lee JY, Kim Y (2005) Comparative homology modeling and ligand docking study of human catechol-O-methyltransfease for antiparkinson drug desing. Bull Korean Chem Soc 26:1695–1700
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662
Cho MC, Lee S, Choi HS, Yang Y, Tae Hong J, Kim SJ, Yoon DY (2009) Optimization of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to screen ligand of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 31(3):459–467. doi:10.1080/08923970902785246
Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (2000) The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 14(2):121–141
Yu S, Reddy JK (2007) Transcription coactivators for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771(8):936–951. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.01.008
Berger JP, Akiyama TE, Meinke PT (2005) PPARs: therapeutic targets for metabolic disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(5):244–251. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2005.03.003
Knouff C, Auwerx J (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma calls for activation in moderation: lessons from genetics and pharmacology. Endocr Rev 25(6):899–918. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0036
Zoete V, Grosdidier A, Michielin O (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor structures: ligand specificity, molecular switch and interactions with regulators. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771(8):915–925. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.01.007
Kuhn B, Hilpert H, Benz J, Binggeli A, Grether U, Humm R, Marki HP, Meyer M, Mohr P (2006) Structure-based design of indole propionic acids as novel PPARalpha/gamma co-agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16(15):4016–4020. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.05.007
Lewis SN, Bassaganya-Riera J, Bevan DR (2010) Virtual screening as a technique for PPAR modulator discovery. PPAR Res 2010:861238. doi:10.1155/2010/861238
Liu LS, Tanaka H, Ishii S, Eckel J (1998) The new antidiabetic drug MCC-555 acutely sensitizes insulin signaling in isolated cardiomyocytes. Endocrinology 139(11):4531–4539
Reginato MJ, Bailey ST, Krakow SL, Minami C, Ishii S, Tanaka H, Lazar MA (1998) A potent antidiabetic thiazolidinedione with unique peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-activating properties. J Biol Chem 273(49):32679–32684
Benson SC, Pershadsingh HA, Ho CI, Chittiboyina A, Desai P, Pravenec M, Qi N, Wang J, Avery MA, Kurtz TW (2004) Identification of telmisartan as a unique angiotensin II receptor antagonist with selective PPARgamma-modulating activity. Hypertension 43(5):993–1002. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000123072.34629.57
Schupp M, Clemenz M, Gineste R, Witt H, Janke J, Helleboid S, Hennuyer N, Ruiz P, Unger T, Staels B, Kintscher U (2005) Molecular characterization of new selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulators with angiotensin receptor blocking activity. Diabetes 54(12):3442–3452
Allen T, Zhang F, Moodie SA, Clemens LE, Smith A, Gregoire F, Bell A, Muscat GE, Gustafson TA (2006) Halofenate is a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator with antidiabetic activity. Diabetes 55(9):2523–2533. doi:10.2337/db06-0618
Zhang F, Lavan BE, Gregoire FM (2007) Selective modulators of PPAR-gamma activity: molecular aspects related to obesity and side-effects. PPAR Res 2007:32696. doi:10.1155/2007/32696
Fujimura T, Sakuma H, Konishi S, Oe T, Hosogai N, Kimura C, Aramori I, Mutoh S (2005) FK614, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator, induces differential transactivation through a unique ligand-specific interaction with transcriptional coactivators. J Pharmacol Sci 99(4):342–352
Minoura H, Takeshita S, Ita M, Hirosumi J, Mabuchi M, Kawamura I, Nakajima S, Nakayama O, Kayakiri H, Oku T, Ohkubo-Suzuki A, Fukagawa M, Kojo H, Hanioka K, Yamasaki N, Imoto T, Kobayashi Y, Mutoh S (2004) Pharmacological characteristics of a novel nonthiazolidinedione insulin sensitizer, FK614. Eur J Pharmacol 494(2–3):273–281. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.04.038
Gross B, Staels B (2007) PPAR agonists: multimodal drugs for the treatment of type-2 diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 21(4):687–710. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2007.09.004
Acton JJ III, Akiyama TE, Chang CH, Colwell L, Debenham S, Doebber T, Einstein M, Liu K, McCann ME, Moller DE, Muise ES, Tan Y, Thompson JR, Wong KK, Wu M, Xu L, Meinke PT, Berger JP, Wood HB (2009) Discovery of (2R)-2-(3-{3-[(4-methoxyphenyl)carbonyl]-2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H- indol-1-yl}phenoxy)butanoic acid (MK-0533): a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with a reduced potential to increase plasma and extracellular fluid volume. J Med Chem 52(13):3846–3854. doi:10.1021/jm900097m
Henriksen K, Byrjalsen I, Nielsen RH, Madsen AN, Larsen LK, Christiansen C, Beck-Nielsen H, Karsdal MA (2009) A comparison of glycemic control, water retention, and musculoskeletal effects of balaglitazone and pioglitazone in diet-induced obese rats. Eur J Pharmacol 616(1–3):340–345. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.06.051
Xu HE, Lambert MH, Montana VG, Plunket KD, Moore LB, Collins JL, Oplinger JA, Kliewer SA, Gampe RT Jr, McKee DD, Moore JT, Willson TM (2001) Structural determinants of ligand binding selectivity between the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(24):13919–13924. doi:10.1073/pnas.241410198
Dubuquoy L, Rousseaux C, Thuru X, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Romano O, Chavatte P, Chamaillard M, Desreumaux P (2006) PPARgamma as a new therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 55(9):1341–1349. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.093484
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Korea Research Foundation grant funded by the Korean government (2010-0019306, 2009-0072028). D.Y is partially supported from Priority Research Centers Program (2009-0093824) and J.H. is partially supported by through the NRF (R13-2008-001-00000-00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Min-Chul Cho and Dong-Hun Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, MC., Lee, DH., Kim, E.J. et al. Novel PPARγ partial agonists with weak activity and no cytotoxicity; identified by a simple PPARγ ligand screening system. Mol Cell Biochem 358, 75–83 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0923-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0923-1