Abstract
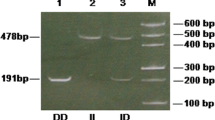
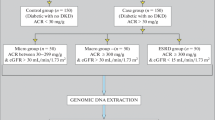
Bahrain has one of the highest incidence rates of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Development of diabetic nephropathy (DN) as a complication was noticed in some patients while absent in others. This interesting observation raises the role of certain genetic risk factors for the development of DN. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism was found to be associated with T2DM. While some patients have predisposition to DN in the population, others have negative association. The present case–control association study was designed to investigate the association of ACE I/D polymorphism in T2DM patients in Bahrain especially in those who developed DN. A total of 360 T2DM patients (110 with DN and 250 without DN) and 360 healthy (non-diabetic) age-matched subjects were recruited for this study for comparison. The presence (insertion)/absence (deletion) (I/D) polymorphism of a 287-bp Alu1 element inside intron 16 of the ACE gene was investigated using PCR-gel electrophoresis. The results show that the distribution of the homozygote DD genotype of the ACE gene was high among Bahraini T2DM patients compared to the healthy non-diabetic subjects. In addition, the distribution of the deletion (D) allele was high among Bahraini T2DM patients with DN when compared to the healthy non-diabetic subjects. However, there was no significant difference in the distribution of ACE I/D allele and genotypes between DN patients when compared to those T2DM patients without DN. The results obtained in this study are in closely agreement with some previous reports which show a strong association of ACE polymorphism with T2DM patients, yet not a risk factor for development of DN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
King H, Rewers M (1993) Global estimates for prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in adults. WHO Ad Hoc Diabetes Reporting Group. Diabetes Care 16:157–177
Wild R, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27:1047–1053
World Health Organization. Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia. Report of a WHO consultation (2006) World Health Org, Geneva
Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P (1997) The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med 14:S1–S85
Najjar S (2002) Regulation of insulin action by CEACAM1. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:240–245
McLarty DG, Swai AB, Kitange HM, Masuki G, Mtinangi BL, Kilima PM, Makene WJ, Chuwa LM, Alberti KG (1989) Prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in rural Tanzania. Lancet 1:871–875
Froguel P, Velho G (2001) Genetic determinants of type 2 diabetes. Recent Prog Horm Res 56:91–105
Kussman MJ, Goldstein H, Gleason RE (1976) The clinical course of diabetic nephropathy. JAMA 236:1861–1863
White KE, Bilous RW (2000) Type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy show structural–functional relationships that are similar to type 1 disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1667–1673
Mogensen CE, Christensen CK (1984) Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent patients. N Engl J Med 311:89–93
Woeste G, Wullstein C, Zapletal C, Hauser IA, Gossmann J, Geiger H, Bechstein WO (2006) Evaluation of type 1 diabetics for simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation with regard to cardiovascular risk. Transplant Proc 38:747–750
National Kidney Foundation (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1–266
Ritz E, Orth SR (1999) Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 341:1127–1133
Yang WC, Hwang SJ, Taiwan Society of Nephrology (2008) Incidence, prevalence and mortality trends of dialysis end-stage renal disease in Taiwan from 1990 to 2001: the impact of national health insurance. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3977–3982
Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR, UKPDS Group (2003) Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int 63:225–232
Sarnak MJ, Levey AS (2000) Cardiovascular disease and chronic renal disease: a new paradigm. Am J Kidney Dis 35:S117–S131
Park HC, Choi SR, Kim BS, Lee TH, Kang BS, Choi KH, Lee HY, Han DS, Ha SK (2005) Polymorphism of the ACE Gene in dialysis patients overexpression of DD genotype in type 2 diabetic end-stage renal failure patients. Yonsei Med J 46:779–787
Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F (1990) An insertion deletion polymorphism in angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Invest 86:1343–1346
Tiret L, Rigat B, Visvikis S, Breda C, Corvol P, Cambien F, Soubrier F (1992) Evidence from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. Am J Hum Genet 51:197–205
Arzu Ergen H, Hatemi H, Agachan B, Camlica H, Isbir T (2004) Angiotensin-I converting enzyme gene polymorphism in Turkish type 2 diabetic patients. Exp Mol Med 36:345–350
Obineche EN, Frossard PM, Bokhari AM (2001) An association study of five genetic loci and left ventricular hypertrophy amongst Gulf Arabs. Hypertens Res 24:635–639
Agerholm-Larsen B, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjaerg-Hansen A (2000) ACE gene polymorphism in cardiovascular disease: meta-analyses of small and large studies in Whites. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:484–492
Zee RY, Ridker PM, Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH, Lindpaintner K (1999) Prospective evaluation of the angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and the risk of stroke. Circulation 99:340–343
Ramachandran V, Ismail P, Stanslas J, Shamsudin N, Moin S, Mohd Jas R (2008) Association of insertion/deletion polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene with essential hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Malaysian subjects. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 9:208–214
Gesang L, Liu G, Cen W, Qiu C, Zhuoma C, Zhuang L, Ren D, Pincuo Z, Chan Y (2002) Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism and its association with essential hypertension in a Tibetan population. Hypertens Res 25:481–485
Ortega-Pierres LE, Gómez García A, Rodríguez-Ayala E, Figueroa-Núñez B, Farias-Rodríguez VM, Higareda-Mendoza AE, Pardo-Galván MA, Cortés-García JC, López-Meza JE, Alvarez-Aguilar C (2007) Angiotensin-1 converting enzyme insertion/deletion gene polymorphism in a Mexican population with diabetic nephropathy. Med Clin (Barc) 129:6–10
Movva S, Alluri RV, Komandur S, Vattam K, Eppa K, Mukkavali KK, Mubigonda S, Saharia S, Shastry JC, Hasan Q (2007) Relationship of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism with nephropathy associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. J Diabetes Complicat 21:237–241
Viswanathan V, Zhu Y, Bala K, Dunn S, Snehalatha C, Ramachandran A, Jayaraman M, Sharma K (2001) Association between ACE gene polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy in South Indian patients. JOP 2:83–87
Fujisawa T, Ikegami H, Kawaguchi Y, Hamada Y, Ueda H, Shintani M, Fukuda M, Ogihara T (1998) Meta-analysis of association of insertion/deletion polymorphism of angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene with diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy. Diabetologia 41:47–53
Marre M, Jeunemaitre X, Gallois Y, Rodier M, Chatellier G, Sert C, Dusselier L, Kahal Z, Chaillous L, Halimi S, Muller A, Sackmann H, Bauduceau B, Bled F, Passa P, Alhenc-Gelas F (1997) Contribution of genetic polymorphism in the renin-angiotensin system to the development of renal complications in insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest 99:1585–1595
Yoshida H, Kuriyama S, Atsumi Y, Tomonari H, Mitarai T, Hamaguchi A, Kubo H, Kawaguchi Y, Kon V, Matsuoka K, Ichikawa I, Sakai O (1996) Angiotensin I converting enzyme gene polymorphism in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 50:657–664
Al-Mahroos F, McKeigue PM (1998) High prevalence of diabetes in Bahrainis. Associations with ethnicity and raised plasma cholesterol. Diabetes Care 21:936–942
Esteghamati A, Gouya MM, Abbasi M, Delavari A, Alikhani S, Alaedini F, Safaie A, Forouzanfar M, Gregg EW (2008) Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in the adult population of Iran: National Survey of Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Diseases of Iran. Diabetes Care 31:96–98
Rigat B, Hubert C, Corvol P, Soubrier F (1992) PCR detection of the insertion/deletion polymorphism of the human angiotensin converting enzyme gene (DCP1) (dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase 1). Nucleic Acids Res 20:1433 (an abstract)
Lindpaintner K, Pfeffer MA, Kreutz R, Stampfer MJ, Grodstein F, LaMotte F, Buring J, Hennekens CH (1995) A prospective evaluation of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme gene polymorphism and the risk of ischemic heart disease. N Engl J Med 332:706–711
Shanmugan V, Sell KW, Saha BK (1993) Mistyping ACE heterozygotes. PCR Methods Appl 3:120–121
Kumar PJ, Clark ML (2007) Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine disorders. In: Kumar PJ, Clark ML (eds) Textbook of clinical medicine chapter 19, 7th edn. Saunders, London, pp 1069–1121
Stephens JW, Dhamrait SS, Cooper JA, Acharya J, Miller GJ, Hurel SJ, Humphries SE (2005) The D allele of the ACE I/D common gene variant is associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Caucasian subjects. Mol Genet Metab 84:83–89
Degirmenci I, Kebapci N, Basaran A, Efe B, Gunes HV, Akalin A, Kurt H, Urhan M, Demirustu C (2005) Frequency of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism in Turkish type 2 diabetic patients. Int J Clin Pract 59:1137–1142
Lee YJ, Tsai JC (2002) ACE gene insertion/deletion polymorphism associated with 1998 World Health Organization definition of metabolic syndrome in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 25:1002–1008
Feng Y, Niu T, Xu X, Chen C, Li Q, Qian R, Wang G, Xu X (2002) Insertion/deletion polymorphism of the ACE gene is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 51:1986–1988
Hsieh MC, Lin SR, Hsieh TJ, Hsu CH, Chen HC, Shin SJ, Tsai JH (2000) Increased frequency of angiotensin-converting enzyme DD genotype in patients with type 2 diabetes in Taiwan. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:1008–1013
Chuang LM, Chiu KC, Chiang FT, Lee KC, Wu HP, Lin BJ, Tai TY (1997) Insertion/deletion polymorphism of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene in patients with hypertension, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and coronary heart disease in Taiwan. Metabolism 46:1211–1214
Nitiyanant W, Sriussadaporn S, Ploybutr S, Watanakejorn P, Tunlakit M, Bejrachandra S (1997) Angiotensin converting enzyme gene polymorphism in healthy Thais and patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Med Assoc Thai 80:747–752
Schmidt S, Strojek K, Grzeszczak W, Bergis K, Ritz E (1997) Excess of DD homozygotes in haemodialysed patients with type II diabetes. The Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:427–429
Ha SK, Park HC, Park HS, Kang BS, Lee TH, Hwang HJ, Kim SJ, Kim DH, Kang SW, Choi KH, Lee HY, Han DS (2003) ACE gene polymorphism and progression of diabetic nephropathy in Korean type 2 diabetic patients: effect of ACE gene DD on the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 41:943–949
Kunz R, Bork JP, Fritsche L, Ringel J, Sharma AM (1998) Association between the angiotensin-converting enzyme -insertion/deletion polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy: a methodologic appraisal and systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1653–1663
Tarnow L (1996) Genetic pattern in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:410–412
Fava S, Azzopardi J, Ellard S, Hattersley AT (2001) ACE gene polymorphism as a prognostic indicator in patients with type 2 diabetes and established renal disease. Diabetes Care 24:2115–2120
Acknowledgments
Special thanks for Colonel Dr. Abdulla Darweesh Chairman of Department of Pathology in BDF Hospital & Major Khalid Matar, Chief of Medical Technologists for giving the opportunity to collect blood samples, for the current study, from the BDF Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Harbi, E.M., Farid, E.M., Gumaa, K.A. et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms and T2DM in a case–control association study of the Bahraini population. Mol Cell Biochem 350, 119–125 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0688-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0688-y