Abstract
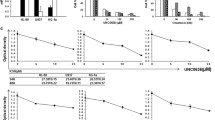
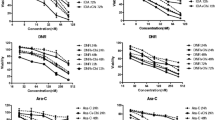
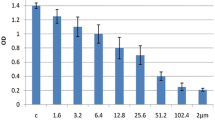
Restoration of cellular apoptotic pathways plays a crucial role in cancer therapy strategies. In a broad spectrum of anticancer drugs, epigenetic effectors are in the center of interest mostly because of potential reversibility of their action. Methylation status of the cells is influenced by methyltransferase inhibitor 2-deoxy-5′-azacytidine (decitabine, DAC), but higher concentrations of this agent cause a DNA-damage. In our study, tumor supressor p53-apoptotic pathway was activated in decitabine-induced cell death. Expression of p53-inducible BH3-only apoptotic proteins Puma and Noxa was elevated and large activation of executive caspases was observed. The extent of acetylation in the cell is affected by histonedeacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). Combination of SAHA with decitabine brought synergistic effect on apoptosis triggering in CML-T1 cell line, but apoptosis as well as necrosis occured also in normal peripheral blood lymphocytes. Therefore, promising potential of such combined therapy calls for more detailed investigation of unwanted effects in normal cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jain N, Rossi A, Garcia-Manero G (2009) Epigenetic therapy of leukemia: an update. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:72–80
Daskalakis M, Blagitko-Dorfs N, Hackanson B (2010) Decitabine. Recent Results Cancer Res 184:131–157
Garcia-Manero G (2008) Demethylating agents in myeloid malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol 20:705–710
Gurion R, Vidal L, Gafter-Gvili A, Belnik Y, Yeshurun M, Raanani P, Shpilberg O (2010) 5-Azacitidine prolongs overall survival in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome—systematic review and meta-analysis. Haematologica 95(2):303–310
Issa JP, Kantarjian HM (2009) Targeting DNA methylation. Clin Cancer Res 15:3938–3946
Amatori S, Papalini F, Lazzarini R, Donati B, Bagaloni I, Rippo MR, Procopio A, Pelicci PG, Catalano A, Fanelli M (2009) Decitabine, differently from DNMT1 silencing, exerts its antiproliferative activity through p21 upregulation in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) cells. Lung Cancer 66:184–190
Jiemjit A, Fandy TE, Carraway H, Bailey KA, Baylin S, Herman JG, Gore SD (2008) p21(WAF1/CIP1) induction by 5-azacytosine nucleosides requires DNA damage. Oncogene 27:3615–3623
Scott SA, Dong WF, Ichinohasama R, Hirsch C, Sheridan D, Sanche SE, Geyer CR, Decoteau JF (2006) 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) can relieve p21WAF1 repression in human acute myeloid leukemia by a mechanism involving release of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) without requiring p21WAF1 promoter demethylation. Leuk Res 30:69–76
Wang H, Zhao Y, Li L, McNutt MA, Wu L, Lu S, Yu Y, Zhou W, Feng J, Chai G, Yang Y, Zhu WG (2008) An ATM- and Rad3-related (ATR) signaling pathway and a phosphorylation-acetylation cascade are involved in activation of p53/p21Waf1/Cip1 in response to 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine treatment. J Biol Chem 283:2564–2574
Zheng QH, Ma LW, Zhu WG, Zhang ZY, Tong TJ (2006) p21Waf1/Cip1 plays a critical role in modulating senescence through changes of DNA methylation. J Cell Biochem 98:1230–1248
Furukawa Y, Sutheesophon K, Wada T, Nishimura M, Saito Y, Ishii H, Furukawa Y (2005) Methylation silencing of the Apaf-1 gene in acute leukemia. Mol Cancer Res 3:325–334
Shang D, Liu Y, Matsui Y, Ito N, Nishiyama H, Kamoto T, Ogawa O (2008) Demethylating agent 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine enhances susceptibility of bladder transitional cell carcinoma to Cisplatin. Urology 71:1220–1225
Yagi S, Oda-Sato E, Uehara I, Asano Y, Nakajima W, Takeshita T, Tanaka N (2008) 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine restores proapoptotic function of p53 in cancer cells resistant to p53-induced apoptosis. Cancer Invest 26:680–688
Tamm I, Wagner M, Schmelz K (2005) Decitabine activates specific caspases downstream of p73 in myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol 84(suppl 1):47–53
Lavelle D, DeSimone J, Hankewych M, Kousnetzova T, Chen YH (2003) Decitabine induces cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase via p21(WAF1) and the G2/M phase via the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Leuk Res 27:999–1007
Jabbour E, Issa JP, Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian H (2008) Evolution of decitabine development: accomplishments, ongoing investigations, and future strategies. Cancer 112:2341–2351
Qin T, Jelinek J, Si J, Shu J, Issa JP (2009) Mechanisms of resistance to 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in human cancer cell lines. Blood 113:659–667
Batty N, Malouf GG, Issa JP (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anti-neoplastic agents. Cancer Lett 280:192–200
Lee EJ, Lee BB, Kim SJ, Park YD, Park J, Kim DH (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitor scriptaid induces cell cycle arrest and epigenetic change in colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 33:767–776
Li Q, Bartlett DL, Gorry MC, O’Malley ME, Guo ZS (2009) Three epigenetic drugs up-regulate homeobox gene Rhox5 in cancer cells through overlapping and distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 76(5):1072–1081
Kumagai T, Wakimoto N, Yin D, Gery S, Kawamata N, Takai N, Komatsu N, Chumakov A, Imai Y, Koeffler HP (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (Vorinostat, SAHA) profoundly inhibits the growth of human pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Cancer 121:656–665
Jiang X, Tsang YH, Yu Q (2007) c-Myc overexpression sensitizes Bim-mediated Bax activation for apoptosis induced by histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) through regulating Bcl-2/Bcl-xL expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:1016–1025
Heider U, von Metzler I, Kaiser M, Rosche M, Sterz J, Rotzer S, Rademacher J, Jakob C, Fleissner C, Kuckelkorn U, Kloetzel PM, Sezer O (2008) Synergistic interaction of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in mantle cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 80:133–142
Lobjois V, Frongia C, Jozan S, Truchet I, Valette A (2009) Cell cycle and apoptotic effects of SAHA are regulated by the cellular microenvironment in HCT116 multicellular tumour spheroids. Eur J Cancer 45:2402–2411
Seo SK, Jin HO, Lee HC, Woo SH, Kim ES, Yoo DH, Lee SJ, An S, Rhee CH, Hong SI, Choe TB, Park IC (2008) Combined effects of sulindac and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid on apoptosis induction in human lung cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 73:1005–1012
Kuzelova K, Pluskalova M, Brodska B, Otevrelova P, Elknerova K, Grebenova D, Hrkal Z (2010) Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) at subtoxic concentrations increases the adhesivity of human leukemic cells to fibronectin. J Cell Biochem 109:184–195
Wozniak MB, Villuendas R, Bischoff JR, Aparicio CB, Martinez Leal JF, de La Cueva P, Rodriguez ME, Herreros B, Martin-Perez D, Longo MI, Herrera M, Piris MA, Ortiz-Romero PL (2010) Vorinostat interferes with the signaling transduction pathway of T-cell receptor and synergizes with phosphoinositide-3 kinase inhibitors in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 95:613–621
Brodska B, Otevrelova P, Kalousek I (2009) Variations in c-Myc and p21WAF1 expression protect normal peripheral blood lymphocytes against BimEL-mediated cell death. Cell Biochem Funct 27:167–175
Bonazzi VF, Irwin D, Hayward NK (2009) Identification of candidate tumor suppressor genes inactivated by promoter methylation in melanoma. Genes Chromosom Cancer 48:10–21
Carambula SF, Oliveira LJ, Hansen PJ (2009) Repression of induced apoptosis in the 2-cell bovine embryo involves DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:418–421
Chai G, Li L, Zhou W, Wu L, Zhao Y, Wang D, Lu S, Yu Y, Wang H, McNutt MA, Hu YG, Chen Y, Yang Y, Wu X, Otterson GA, Zhu WG (2008) HDAC inhibitors act with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine to inhibit cell proliferation by suppressing removal of incorporated abases in lung cancer cells. PLoS One 3:e2445
Ecke I, Petry F, Rosenberger A, Tauber S, Monkemeyer S, Hess I, Dullin C, Kimmina S, Pirngruber J, Johnsen SA, Uhmann A, Nitzki F, Wojnowski L, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Witt O, Hahn H (2009) Antitumor effects of a combined 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine and valproic acid treatment on rhabdomyosarcoma and medulloblastoma in Ptch mutant mice. Cancer Res 69:887–895
De Bruyne E, Bos TJ, Schuit F, Van Valckenborgh E, Menu E, Thorrez L, Atadja P, Jernberg-Wiklund H, Vanderkerken K (2010) IGF-1 suppresses Bim expression in multiple myeloma via epigenetic and posttranslational mechanisms. Blood 115:2430–2440
Gore SD (2009) In vitro basis for treatment with hypomethylating agents and histone deacetylase inhibitors: can epigenetic changes be used to monitor treatment? Leuk Res 33(Suppl 2):S2–S6
Cho HJ, Kim SY, Kim KH, Kang WK, Kim JI, Oh ST, Kim JS, An CH (2009) The combination effect of sodium butyrate and 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine on radiosensitivity in RKO colorectal cancer and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. World J Surg Oncol 7:49
Steele N, Finn P, Brown R, Plumb JA (2009) Combined inhibition of DNA methylation and histone acetylation enhances gene re-expression and drug sensitivity in vivo. Br J Cancer 100:758–763
Kalousek I, Brodska B, Otevrelova P, Roselova P (2007) Actinomycin D upregulates proapoptotic protein Puma and downregulates Bcl-2 mRNA in normal peripheral blood lymphocytes. Anticancer Drugs 18:763–772
Gillissen B, Essmann F, Hemmati PG, Richter A, Richter A, Oztop I, Chinnadurai G, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2007) Mcl-1 determines the Bax dependency of Nbk/Bik-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 179:701–715
Gallenne T, Gautier F, Oliver L, Hervouet E, Noel B, Hickman JA, Geneste O, Cartron PF, Vallette FM, Manon S, Juin P (2009) Bax activation by the BH3-only protein Puma promotes cell dependence on antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members. J Cell Biol 185:279–290
Whitman SP, Hackanson B, Liyanarachchi S, Liu S, Rush LJ, Maharry K, Margeson D, Davuluri R, Wen J, Witte T, Yu L, Liu C, Bloomfield CD, Marcucci G, Plass C, Caligiuri MA (2008) DNA hypermethylation and epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor gene, SLC5A8, in acute myeloid leukemia with the MLL partial tandem duplication. Blood 112:2013–2016
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Komatsu N, Koeffler HP, Yokoyama A (2009) Blockade of MEK signaling potentiates 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine-induced apoptosis and upregulation of p21(waf1) in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Int J Cancer 125:1168–1176
Almond JB, Cohen GM (2002) The proteasome: a novel target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 16:433–443
Zhao Y, Lu S, Wu L, Chai G, Wang H, Chen Y, Sun J, Yu Y, Zhou W, Zheng Q, Wu M, Otterson GA, Zhu WG (2006) Acetylation of p53 at lysine 373/382 by the histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide induces expression of p21(Waf1/Cip1). Mol Cell Biol 26:2782–2790
Yamaguchi H, Woods NT, Piluso LG, Lee HH, Chen J, Bhalla KN, Monteiro A, Liu X, Hung MC, Wang HG (2009) p53 acetylation is crucial for its transcription-independent proapoptotic functions. J Biol Chem 284:11171–11183
Tang YA, Wen WL, Chang JW, Wei TT, Tan YH, Salunke S, Chen CT, Chen CS, Wang YC (2010) A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor exhibits antitumor activity via apoptosis induction, F-actin disruption and gene acetylation in lung cancer. PLoS One 5:e12417
Ito A, Lai CH, Zhao X, Saito S, Hamilton MH, Appella E, Yao TP (2001) p300/CBP-mediated p53 acetylation is commonly induced by p53-activating agents and inhibited by MDM2. EMBO J 20:1331–1340
Carlisi D, Vassallo B, Lauricella M, Emanuele S, D’Anneo A, Di Leonardo E, Di Fazio P, Vento R, Tesoriere G (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce in human hepatoma HepG2 cells acetylation of p53 and histones in correlation with apoptotic effects. Int J Oncol 32:177–184
Kantarjian HM, Issa JP (2005) Decitabine dosing schedules. Semin Hematol 42:S17–S22
Kiziltepe T, Hideshima T, Catley L, Raje N, Yasui H, Shiraishi N, Okawa Y, Ikeda H, Vallet S, Pozzi S, Ishitsuka K, Ocio EM, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2007) 5-Azacytidine, a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, induces ATR-mediated DNA double-strand break responses, apoptosis, and synergistic cytotoxicity with doxorubicin and bortezomib against multiple myeloma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1718–1727
Palii SS, Van Emburgh BO, Sankpal UT, Brown KD, Robertson KD (2008) DNA methylation inhibitor 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine induces reversible genome-wide DNA damage that is distinctly influenced by DNA methyltransferases 1 and 3B. Mol Cell Biol 28:752–771
Garrison SP, Jeffers JR, Yang C, Nilsson JA, Hall MA, Rehg JE, Yue W, Yu J, Zhang L, Onciu M, Sample JT, Cleveland JL, Zambetti GP (2008) Selection against PUMA gene expression in Myc-driven B-cell lymphomagenesis. Mol Cell Biol 28:5391–5402
Hoglund A, Nilsson LM, Forshell LP, Maclean KH, Nilsson JA (2009) Myc sensitizes p53-deficient cancer cells to the DNA-damaging effects of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor decitabine. Blood 113:4281–4288
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P, Craig RW (1993) MCL1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:3516–3520
Michels J, Johnson PW, Packham G (2005) Mcl-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:267–271
Akgul C (2009) Mcl-1 is a potential therapeutic target in multiple types of cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1326–1336
Mandelin AM 2nd, Pope RM (2007) Myeloid cell leukemia-1 as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11:363–373
Warr MR, Shore GC (2008) Unique biology of Mcl-1: therapeutic opportunities in cancer. Curr Mol Med 8:138–147
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman PM, Day CL, Adams JM, Huang DC (2005) Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 17:393–403
Willis SN, Adams JM (2005) Life in the balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:617–625
Yang Y, Zhao S, Song J (2004) Caspase-dependent apoptosis and -independent poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage induced by transforming growth factor beta1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(2):223–234
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant NS-9374-6 from the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic and the grant No 301/09/1026 from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1259-1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brodská, B., Otevřelová, P. & Holoubek, A. Decitabine-induced apoptosis is derived by Puma and Noxa induction in chronic myeloid leukemia cell line as well as in PBL and is potentiated by SAHA. Mol Cell Biochem 350, 71–80 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0683-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0683-3