Abstract
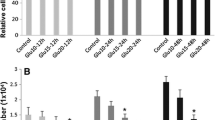
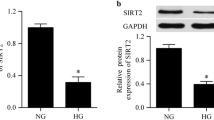
Our previous study found that blocking nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling could protect human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) from apoptosis and proliferation inhibition due to high glucose (HG). Intermittent HG makes glucose toxicity more significant. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of NF-κB pathway on HUVECs induced by intermittent HG (a daily alternating 5.5 or 30.5 mmol/l glucose). A recombinant adenovirus containing a RNAi cassette targeting the NF-κB/p65 gene was produced, and its silencing effect on p65 gene was detected by Western blot analysis in HUVECs cultured with intermittent HG. The subsequent effect on proliferation of HUVECs in the indicated conditions was measured by the AlamarBlue assay. The Bcl-2 expression was also detected by Western blot. The results showed that the expression of p65 protein could be inhibited efficiently by the RNAi adenovirus. Intermittent HG also induced the translocation of NF-κB in HUVECs. Inhibition of NF-κB with the RNAi adenovirus could prevent the effects. At the 6th day after HUVECs were exposed to intermittent HG, the proliferation of HUVECs with Ad-1566 was significantly higher than that of HUVECs with Ad-DEST (P < 0.01). Knockdown of NF-κB/p65 up-regulated the Bcl-2 expression of HUVECs under intermittent HG conditions (P < 0.01). These findings concluded that the NF-κB/p65-targeting RNAi adenovirus is an important tool, which can efficiently inhibit the expression of p65 gene in HUVECs. Intermittent HG reduces HUVECs proliferation with a concomitant increase in apoptosis. Knockdown of NF-κB/p65 partly protected HUVECs from proliferation inhibition and may reduce apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen G, Qiao Y, Lin X et al (2007) Construction of the NF-κB/p65 specific RNAi adenovirus vector and its inhibition effects on p65 expression. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 23:363–367
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG et al (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52:2745–2756
Chen G, Shen X, Yao J, Chen F et al (2009) Ablation of NF-kappaB expression by small interference RNA prevents the dysfunction of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by high glucose. Endocrine 35(1):63–74
Nakagami H, Morishita R, Yamamoto K et al (2001) Phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase downstream of Bax-caspase-3 pathway leads to cell death induced by high d-glucose in human endothelial cells. Diabetes 50:1472–1481
Risso A, Mercuri F, Quagliaro L et al (2001) Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281:924–930
Mertens HJ, Heineman MJ, Evers JL (2002) The expression of apoptosis-related proteins Bcl-2 and Ki67 in endometrium of ovulatory menstrual cycles. Gynecol Obstet Invest 53(4):224–230
Li H, Telemaque S, Millcr RE et al (2005) High glucose inhibits apoptosis induced by serum deprivation in vascular smooth muscle cells via upregulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl. Diabetes 54(2):540–545
Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R et al (2003) Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis related to oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: the role of protein kinase C and NAD(P)H-oxidase activation. Diabetes 52(11):2795–2804
Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R et al (2005) Intermittent high glucose enhances ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture: The distinct role of protein kinase C and mitochondrial superoxide production. Atherosclerosis 183:259–267
Piconi L, Quagliaro L, Assaloni R et al (2006) Constant and intermittent high glucose enhances endothelial cell apoptosis through mitochondrial superoxide overproduction. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 22(3):198–203
Piconi L, Corgnali M, Da Ros R et al (2008) The protective effect of rosuvastatin in human umbilical endothelial cells exposed to constant or intermittent high glucose. J Diabetes Complicat 22(1):38–45
McConkey DJ, Nicotera P, Orrenius S (1994) Signalling and chromatin fragmentation in thymocyte apoptosis. Immunol Rev 142:343–363
Beg AA, Baldwin AS (1993) The Ikappa B proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors. Genes Dev 7(11):2064–2070
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant C071002, 2008F3026, and 2009Y0011 for natural science foundation from Fujian province of China and grant from the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China (WKJ 2005-2-021).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first four authors contributed to the study equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Chen, Y., Chen, H. et al. The effect of NF-κB pathway on proliferation and apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by intermittent high glucose. Mol Cell Biochem 347, 127–133 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0620-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0620-5