Abstract
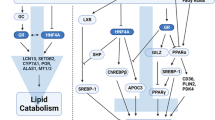
Hind limb-suspended rats represent a sedentary-hyperinsulinemic model with a liver dyslipidemia mainly related to changes in sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) expression and activity. To assess the effects of dietary fatty acids on hepatic lipid homeostasis, the hepatic expression and activity of PPARα, SREBP-1, and hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α (HNF-4α) were investigated in this animal model. In control and sedentary rats, diets enriched with saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) enhanced the expression of the PPARα target genes carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 and acyl-CoA oxidase, the highest effect being exerted by ω-3. The same diets reduced SREBP-1 mRNA and target lipogenic gene expression, as indicated by the reduction in fatty acid synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase mRNA content. Effects were greater in sedentary rat liver than in controls on the same diet. Only the ω-3 enriched diet decreased liver triglyceride content as well as plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels in sedentary rats. This effect may be mainly related to the enhanced mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation genes expression. On the other hand, saturated fatty acid-enriched diet induced an increase in liver triglyceride content and enhanced plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels, both in control and immobilized rats. This detrimental effect may be ascribed to the induced HNF-4α binding activity on ApoCIII promoter and to the enhanced ApoCIII mRNA levels both in control and in sedentary rat livers. In conclusion, we can speculate that dietary saturated fats, acting at apolipoprotein transcriptional level, may impact on the close relationship existing among high ApoCIII plasma level, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SREBP-1:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1
- ACC:
-
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- FAS:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- PPARα:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α
- CPT-1:
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1
- ACO:
-
Acyl-CoA oxidase
- HNF-4α:
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α
- ApoCIII:
-
Apolipoprotein CIII
References
Reaven GM (2005) The insulin resistance syndrome: definition and dietary approaches to treatment. Annu Rev Nutr 25:391–406 (Review)
Ford ES, Li C (2006) Physical activity or fitness and the metabolic syndrome. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 4:897–915 (Review)
Haag M, Dippenaar NG (2005) Dietary fats, fatty acids and insulin resistance: short review of a multifaceted connection. Med Sci Monit 11:RA359–RA367
Muller-Wieland D, Kotzka J (2005) Correction of insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Handb Exp Pharmacol 170:591–617
Reilly MP, Rader DJ (2003) The metabolic syndrome: more than the sum of its parts? Circulation 108:1546–1551 Review
Vecchini A, Ceccarelli V, Orvietani P, Caligiana P, Susta F, Binaglia L, Nocentini G, Riccardi C, Di Nardo P (2003) Enhanced expression of hepatic lipogenic enzymes in an animal model of sedentariness. J Lipid Res 44:696–704
Jump DB (2002) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and regulation of gene transcription. Curr Opin Lipidol 13:155–164 Review
Schoonians K, Staels B, Auwerx J (1996) Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in mediating the effects of fibrates and fatty acids on gene expression. J Lipid Res 37:907–925
Xu J, Nakamura MT, Cho HP, Clarke SD (1999) Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 expression is suppressed by dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids. A mechanism for the coordinate suppression of lipogenic genes by polyunsaturated fats. J Biol Chem 274:23577–23583
Hertz R, Magenheim J, Berman I, Bar-Tana J (1998) Fatty acyl-CoA thioesters are ligands of hepatic nuclear factor-4alpha. Nature 392:512–516
Hayhurst GP, Lee YH, Lambert G, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (2001) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (nuclear receptor 2A1) is essential for maintenance of hepatic gene expression and lipid homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol 21:1393–1403
Grundy SM, Denke MA (1990) Dietary influences on serum lipids and lipoproteins. J Lipid Res 31:1149–1172
Dhe-Paganon S, Duda K, Iwamoto M, Chi YI, Shoelson SE (2002) Crystal structure of the HNF4-alpha ligand binding domain in complex with endogenous fatty acid ligand. J Biol Chem 41:37973–37976
Wisely GB, Miller AB, Davis RG, Thornquest AD Jr, Johnson R, Spitzer T, Sefler A, Shearer B, Moore JT, Miller AB, Willson TM, Williams SP (2002) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 is a transcription factor that constitutively binds fatty acids. Structure 10:1225–1234
Yuan X, Ta TC, Lin M, Evans JR, Dong Y, Bolotin E, Sherman MA, Forman BM, Sladek FM (2009) Identification of an endogenous ligand bound to a native orphan nuclear receptor. PLoS One 4:e5609
Maeda N, Li H, Lee D, Oliver P, Quarfordt SH, Osada J (1994) Targeted disruption of the apolipoprotein C-III gene in mice results in hypotriglyceridemia and protection from postprandial hypertriglyceridemia. J Biol Chem 269:23610–23616
Ito Y, Azrolan N, O’Connel A, Walsh A, Breslow JL (1990) Hypertriglyceridemia as a result of human apo CIII gene expression in transgenic mice. Science 49:790–793
Stuart CA, Kidder LS, Pietrzyk RA, Klein GL, Simmons DJ (1993) Rat tail suspension causes a decline in insulin receptors. J Exp Toxicol Pathol 45:291–295
Nakamura K, Handa S (1984) Coomassie brilliant blue staining of lipids on thin-layer plates. Anal Biochem 142:406–410
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chirgwin JM, Przybyla AE, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18:5294–5299
Tontonoz P, Kim JB, Graves RA, Spiegelman BM (1993) ADD1 a novel helix–loop–helix transcription factor associated with adipocyte determination differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 13:4753–4759
Amy CM, Witkowski A, Naggert J, Williams B, Randhawa Z, Smith S (1989) Molecular cloning and sequencing of cDNAs encoding the entire rat fatty acid synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3114–3118
Lopez-Casillas F, Bai DH, Luo XC, Kong IS, Hermodson MA, Kim KH (1988) Structure of the coding sequence and primary amino acid sequence of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5784–5788
Gottlicher M, Widmark E, Li Q, Gustafsson JA (1992) Fatty acids activate a chimera of the clofibric acid-activated receptor, the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4653–4657
Miyazawa S, Hayashi H, Hijikata M, Ishii N, Furuta S, Kagamiyama H, Osumi T, Hashimoto T (1987) Complete nucleotide sequence of cDNA and predicted amino acid sequence of rat acyl-CoA oxidase. J Biol Chem 262:8131–8137
Esser V, Britton CH, Weis BC, Foster DW, McGarry JD (1993) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of a cDNA encoding rat liver carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Direct evidence that a single polypeptide is involved in inhibitor interaction and catalytic function. J Biol Chem 268:5817–5822
Sladek FM, Zhong WM, Lai E, Darnell JE Jr (1990) Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev 4:2353–2365
Shimokata K, Yamada Y, Kondo T, Ichihara S, Izawa H, Nagata K, Murohara T, Ohno M, Yokota M (2004) Association of gene polymorphisms with coronary artery disease in individuals with or without nonfamilial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 172:167–173
Sheng ZZ, Otani H, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1995) Independent regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins 1 and 2 in hamster liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:935–938
Kim JB, Sarraf P, Wright M, Yan KM, Mueller E, Solanes G, Lowell BB, Spiegelman BM (1998) Nutritional and insulin regulation of fatty acid synthetase and leptin gene expression through ADD1/SREBP1. J Clin Invest 101:1–9
Spath GF, Weiss MC (1997) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 expression overcomes repression of the hepatic phenotype in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 17:1913–1922
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GM (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Horrocks LA (1968) The alk-1-enyl group content of mammalian myelin phosphoglycerides by quantitative two dimensional thin layer chromatography. J Lipid Res 9:469–472
Li T, Jahan A, Chiang JY (2006) Bile acids and cytokines inhibit the human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene via the JNK/c-jun pathway in human liver cells. Hepatology 43:1202–1210
Browning LM, Krebs JD, Moore CS, Mishra GD, O’Connell MA, Jebb SA (2007) The impact of long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on inflammation, insulin sensitivity and CVD risk in a group of overweight women with an inflammatory phenotype. Diabetes Obes Metab 9:70–80
Nettleton JA, Katz R (2005) n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in type 2 diabetes: a review. J Am Diet Assoc 105:428–440
Pachikian BD, Neyrinck AM, Cani PD, Portois L, Deldicque L, De Backer FC, Bindels LB, Sohet FM, Malaisse WJ, Francaux M, Carpentier YA, Delzenne NM (2008) Hepatic steatosis in n-3 fatty acid depleted mice: focus on metabolic alterations related to tissue fatty acid composition. BMC Physiol 8:21
Davidson MH (2006) Mechanisms for the hypotriglyceridemic effect of marine omega-3 fatty acids. Am J Cardiol 98:27i–33i
Clarke SD (2001) Nonalcholic stestosis and steatohepatitis. I. Molecular mechanism for polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G865–G869
Lavrentiadou SN, Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M, Kardassis D, Zannis VI (1999) Binding specificity and modulation of the human ApoCIII promoter activity by heterodimers of ligand-dependent nuclear receptors. Biochemistry 38:964–975
Lee SJ, Campos H, Moye LA, Sacks FM (2003) LDL containing apolipoprotein CIII is an independent risk factor for coronary events in diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:853–858
Kawakami A, Yoshida M (2009) Apolipoprotein CIII links dyslipidemia with atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 16:6–11 (Review)
Sacks FM, Katan M (2002) Randomized clinical trials on the effects of dietary fat and carbohydrate on plasma lipoproteins and cardiovascular disease. Am J Med 113:13S–24S
Spady DK, Woollett LA, Dietschy JM (1993) Regulation of plasma LDL-cholesterol levels by dietary cholesterol and fatty acids. Annu Rev Nutr 13:355–381
Mensink RP, Zock PL, Kester AD, Katan MB (2003) Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: a meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 77:1146–1155
Hegsted DM, Gotsis A, Stare FJ, Worcester J (1959) Interrelations between the kind and amount of dietary fat and dietary cholesterol in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Am J Clin Nutr 7:5–12
Keys A, Mickelsen O, Miller EO, Chapman CB (1950) The relation in man between cholesterol levels in the diet and in the blood. Science 112:79–81
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Geraldine Boyd for revising the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from the Italian Space Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceccarelli, V., Nocentini, G., Riccardi, C. et al. Effect of dietary saturated fatty acids on HNF-4α DNA binding activity and ApoCIII mRNA in sedentary rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 347, 29–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0609-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0609-0