Abstract
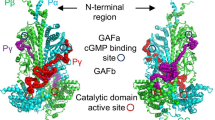
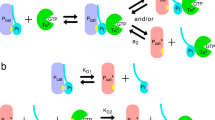
Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) in bovine rod photoreceptor outer segments (OS) comprises a catalytic subunit complex (Pαβ) and two inhibitory subunits (Pγ) and is regulated by the α subunit of transducin (Tα). Here, we show an overall mechanism for PDE regulation by identifying Pγ complexes in OS homogenates prepared with an isotonic buffer. Before Tα activation, three Pγ complexes exist in the soluble fraction. Complex a, a minor complex, contains Pαβ, Tα, and a protein named Pδ. Complex b, Pαβγγb, has a PDE activity similar to that of membranous Pαβγγ, PαβγγM, and its level, although its large portion is Pδ-free, is estimated to be 20–30% of the total Pαβγγ. Complex c, (Pγ·GDP-Tα) c2 , appears to be a dimer of Pγ·GDP-Tα. Upon Tα activation, (1) complex a stays unchanged, (2) Pαβγγb binds to membranes, (3) the level of (Pγ·GDP-Tα) c2 is reduced as its GTP-form is produced, (4) complex d, Pγ·GTP-Tαd, is formed on membranes and its substantial amount is released to the soluble fraction, and (5) membranous Pαβγγ, PαβγγM and/or Pαβγγb, becomes Pγ-depleted. These observations indicate that Pγ as a complex with GTP-Tα dissociates from Pαβγγ on membranes and is released to the soluble fraction and that Pγ-depleted PDE is the GTP-Tα-activated PDE. After GTP hydrolysis, both (Pγ·GDP-Tα) c2 and Pγ·GDP-Tαd, without liberating Pγ, deactivate Pγ-depleted PDE. The preferential order to be used for the deactivation is membranous Pγ·GDP-Tαd, solubilized Pγ·GDP-Tαd and (Pγ·GDP-Tα) c2 . Release of Pγ·GTP-Tα complexes to the soluble fraction is relevant to light adaptation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hurley JB (1987) Molecular properties of the cGMP cascade of vertebrate photoreceptors. Annu Rev Physiol 49:793–812
Yau KW, Baylor DA (1989) Cyclic GMP-activated conductance of retinal photoreceptor cells. Annu Rev Neurosci 12:289–327
Miller WH (1990) Dark mimic. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31:1664–1673
Baehr W, Devlin MJ, Applebury ML (1979) Isolation and characterization of cGMP phosphodiesterase from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem 254:11669–11677
Hurley JB, Stryer L (1982) Purification and characterization of the gamma regulatory subunit of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from retinal rod outer segments. J Biol Chem 257:11094–11099
Deterre P, Bigay J, Forquet F, Robert M, Chabre M (1988) cGMP phosphodiesterase of retinal rods is regulated by two inhibitory subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2424–2428
Fung BK, Young JH, Yamane HK, Griswold-Prenner I (1990) Subunit stoichiometry of retinal rod cGMP phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry 29:2657–2664
Miki N, Baraban JM, Keirns JJ, Boyce JJ, Bitensky MW (1975) Purification and properties of the light-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. J Biol Chem 250:6320–6327
Yamazaki M, Li N, Bondarenko VA, Yamazaki RK, Baehr W, Yamazaki A (2002) Binding of cGMP to GAF domains in amphibian rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE). Identification of GAF domains in PDE alphabeta subunits and distinct domains in the PDE gamma subunit involved in stimulation of cGMP binding to GAF domains. J Biol Chem 277:40675–40686
Charbonneau H, Prusti RK, LeTrong H, Sonnenburg WK, Mullaney PJ, Walsh KA, Beavo JA (1990) Identification of a noncatalytic cGMP-binding domain conserved in both the cGMP-stimulated and photoreceptor cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:288–292
Li TS, Volpp K, Applebury ML (1990) Bovine cone photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase structure deduced from a cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:293–297
Hamilton SE, Hurley JB (1990) A phosphodiesterase inhibitor specific to a subset of bovine retinal cones. J Biol Chem 265:11259–11264
Yamazaki A, Moskvin O, Yamazaki RK (2002) Phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 of the regulatory subunit (Pγ) of retinal cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE6): its implications in phototransduction. Adv Exp Med Biol 514:131–153
Bondarenko VA, Desai M, Dua S, Yamazaki M, Amin RH, Yousif KK, Kinumi T, Ohashi M, Komori N, Matsumoto H, Jackson KW, Hayashi F, Usukura J, Lipkin VM, Yamazaki A (1997) Residues within the polycationic region of cGMP phosphodiesterase gamma subunit crucial for the interaction with transducin alpha subunit. Identification by endogenous ADP- ribosylation and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 272:15856–15864
Yamazaki A, Yamazaki M, Tsuboi S, Kishigami A, Umbarger KO, Hutson LD, Madland WT, Hayashi F (1993) Regulation of G protein function by an effector in GTP-dependent signal transduction. An inhibitory subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibits GTP hydrolysis by transducin in vertebrate rod photoreceptors. J Biol Chem 268:8899–8907
Liu W, Clark WA, Sharma P, Northup JK (1998) Mechanism of allosteric regulation of the rod cGMP phosphodiesterase activity by the helical domain of transducin alpha subunit. J Biol Chem 273:34284–34292
Clerc A, Bennett N (1992) Activated cGMP phosphodiesterase of retinal rods. A complex with transducin alpha subunit. J Biol Chem 267:6620–6627
Bennett N, Clerc A (1992) cGMP phosphodiesterase dependent light-induced scattering changes in suspensions of retinal disc membranes. Biochemistry 31:1858–1866
Catty P, Pfister C, Bruckert F, Deterre P (1992) The cGMP phosphodiesterase-transducin complex of retinal rods. Membrane binding and subunits interactions. J Biol Chem 267:19489–19493
Erickson JW, Cerione RA (1993) Regulation of the cGMP phosphodiesterase in bovine rod outer segments. Use of resonance energy transfer to distinguish between associative and dissociative activation mechanisms. J Biol Chem 268:3328–3333
Berger AL, Cerione RA, Erickson JW (1997) Real time conformational changes in the retinal phosphodiesterase gamma subunit monitored by resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem 272:2714–2721
Lugnier C (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) superfamily: a new target for the development of specific therapeutic agents. Pharmacol Ther 109:366–398
Ionita MA, Pittler SJ (2007) Focus on molecules: rod cGMP phosphodiesterase type 6. Exp Eye Res 109:1–2
Wensel TG (2008) Signal transducing membrane complexes of photoreceptor outer segments. Vis Res 48:2052–2061
Yamazaki A, Stein PJ, Chernoff N, Bitensky MW (1983) Activation mechanism of rod outer segment cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase. Release of inhibitor by the GTP/GTP- binding protein. J Biol Chem 258:8188–8194
Yamazaki A, Hayashi F, Tatsumi M, Bitensky MW, George JS (1990) Interactions between the subunits of transducin and cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase in Rana catesbeiana rod photoreceptors. J Biol Chem 265:11539–11548
Deterre P, Bigay J, Robert M, Pfister C, Kühn H, Chabre M (1986) Activation of retinal rod cyclic GMP-phosphodiesterase by transducin: characterization of the complex formed by phosphodiesterase inhibitor and transducin alpha-subunit. Proteins 1:188–193
Matsuura I, Bondarenko VA, Maeda T, Kachi S, Yamazaki M, Usukura J, Hayashi F, Yamazaki A (2000) Phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 of the regulatory subunit of retinal cGMP phosphodiesterase. I. Identification of the kinase and its role in the turnoff of phosphodiesterase in vitro. J Biol Chem 275:32950–32957
Hayashi F, Matsuura I, Kachi S, Maeda T, Yamamoto M, Fujii Y, Liu H, Yamazaki M, Usukura J, Yamazaki A (2000) Phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 of the regulatory subunit of retinal cGMP phosphodiesterase. II. Its role in the turnoff of phosphodiesterase in vivo. J Biol Chem 275:32958–32965
Arshavsky V, Bownds MD (1992) Regulation of deactivation of photoreceptor G protein by its target enzyme and cGMP. Nature 357:416–417
Pages F, Deterre P, Pfister C (1992) Enhanced GTPase activity of transducin when bound to cGMP phosphodiesterase in bovine retinal rods. J Biol Chem 267:22018–22021
Pages F, Deterre P, Pfister C (1993) Enhancement by phosphodiesterase subunits of the rate of GTP hydrolysis by transducin in bovine retinal rods. Essential role of the phosphodiesterase catalytic core. J Biol Chem 268:26358–26364
Angleson JK, Wensel TG (1994) Enhancement of rod outer segment GTPase accelerating protein activity by the inhibitory subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 269:16290–16296
Slep KC, Kercher MA, He W, Cowan CW, Wensel TG, Sigler PB (2001) Structural determinants for regulation of phosphodiesterase by a G protein at 2.0 A. Nature 409:1071–1077
Wensel TG, Stryer L (1990) Activation mechanism of retinal rod cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase probed by fluorescein-labeled inhibitory subunit. Biochemistry 29:2155–2161
Wensel TG, Stryer L (1986) Reciprocal control of retinal rod cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase by its gamma subunit and transducin. Proteins 1:90–99
Fung BK, Griswold-Prenner I (1989) G protein-effector coupling: binding of rod phosphodiesterase inhibitory subunit to transducin. Biochemistry 28:3133–3137
Sitaramayya A, Harkness J, Parks JH, Gonzalez-Oliva C, Liebman PA (1986) Kinetic studies suggest that light-activated cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase is a complex with G- protein subunits. Biochemistry 25:651–656
Gray-Keller MP, Biernbaum MS, Bownds MD (1990) Transducin activation in electropermeabilized frog rod outer segments is highly amplified, and a portion equivalent to phosphodiesterase remains membrane-bound. J Biol Chem 265:15323–15332
Liebman PA, Parker KR, Dratz EA (1987) The molecular mechanism of visual excitation and its relation to the structure and composition of the rod outer segment. Annu Rev Physiol 49:765–791
Yamazaki A, Tatsumi M, Bondarenko VA, Kurono S, Komori N, Matsumoto H, Matsuura I, Hayashi F, Yamazaki RK, Usukura J (2009) Mechanism for the regulation of mammalian cGMP phosphodiesterase6. 2: Isolation and characterization of the transducin-activated form. Mol Cell Biochem. doi:10.1007/s11010-010-0404-y
Kajimura N, Yamazaki M, Morikawa K, Yamazaki A, Mayanagi K (2002) Three- dimensional structure of non-activated cGMP phosphodiesterase 6 and comparison of its image with those of activated forms. J Struct Biol 139:27–38
Otto-Bruc A, Antonny B, Vuong TM, Chardin P, Chabre M (1993) Interaction between the retinal cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor and transducin. Kinetics and affinity studies. Biochemistry 32:8636–8645
Piriev NI, Yamashita C, Samuel G, Farber DB (1993) Rod photoreceptor cGMP- phosphodiesterase: analysis of alpha and beta subunits expressed in human kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9340–9344
Qin N, Baehr W (1994) Expression and mutagenesis of mouse rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 269:3265–3271
Granovsky AE, Natochin M, McEntaffer RL, Haik TL, Francis SH, Corbin JD, Artemyev NO (1998) Probing domain functions of chimeric PDE6alpha’/PDE5 cGMP-phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 273:24485–24490
Fung BK, Nash CR (1983) Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. II. Evidence for distinct binding sites and conformational changes revealed by limited proteolysis with trypsin. J Biol Chem 258:10503–10510
Malinski JA, Wensel TG (1992) Membrane stimulation of cGMP phosphodiesterase activation by transducin: comparison of phospholipid bilayers to rod outer segment membranes. Biochemistry 31:9502–9512
Melia TJ, Malinski JA, He F, Wensel TG (2000) Enhancement of phototransduction protein interactions by lipid surfaces. J Biol Chem 275:3535–3542
Yamazaki A, Bitensky MW, Casnellie JE (1988) Photoaffinity labeling of high-affinity cGMP-specific noncatalytic binding sites on cGMP phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. Methods Enzymol 159:730–736
Yamazaki A, Yamazaki M, Yamazaki RK, Usukura J (2006) Illuminated rhodopsin is required for strong activation of retinal guanylate cyclase by guanylate cyclase-activating proteins. Biochemistry 45:1899–1909
Florio SK, Prusti RK, Beavo JA (1996) Solubilization of membrane-bound rod phosphodiesterase by the rod phosphodiesterase recombinant delta subunit. J Biol Chem 271:24036–24047
Yamazaki A, Tatsumi M, Bitensky MW (1988) Purification of rod outer segment GTP- binding protein subunit and cGMP phosphodiesterase by single-step column chromatography. Methods Enzymol 159:702–710
Li N, Baehr W (1998) Expression and characterization of human PDEdelta and its Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog CEdelta. FEBS Lett 440:454–457
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Yamazaki A, Tatsumi M, Torney DC, Bitensky MW (1987) The GTP-binding protein of rod outer segments. I. Role of each subunit in the GTP hydrolytic cycle. J Biol Chem 262:9316–9323
Fairbanks G, Steck TL, Wallach DF (1971) Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry 10:2606–2617
Gillespie PG, Prusti RK, Apel ED, Beavo JA (1989) A soluble form of bovine rod photoreceptor phosphodiesterase has a novel 15-kDa subunit. J Biol Chem 264:12187–12193
Norton WA, Hosier S, Terew JM, Li N, Dhingra A, Vardi N, Baehr W, Cote RH (2005) Evaluation of the 17 kDa prenyl-binding protein as a regulatory protein for phototransduction in retinal photoreceptors. J Biol Chem 280:1248–1256
Clack JW, Oakley B II, Stein PJ (1983) Injection of GTP-binding protein or cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase hyperpolarizes retinal rods. Nature 305:59–61
Kondo H, Miller WH (1988) Rod light adaptation may be mediated by acceleration of the phosphodiesterase-guanylate cyclase cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1322–1326
Lamb TD, Mattews HR (1988) Incorporation of analogues of GTP and GDP into rod photoreceptors isolated from the tiger salamander. J Physiol (London) 407:463–487
Erickson MA, Robinson P, Lisman J (1992) Deactivation of visual transduction without guanosine triphosphate hydrolysis by G protein. Science 257:1255–1258
Hu G, Zhang Z, Wensel TG (2003) Activation of RGS9–1GTPase acceleration by its membrane anchor, R9AP. J Biol Chem 278:14550–14554
Astakhova LA, Firsov ML, Gorvardovskii VI (2008) Kinetics of turn-offs of frog rod phototransduction cascade. J Gen Physiol 132:587–604
Woodruff ML, Janish KM, Peshenko IV, Dizhoor AM, Tsang SH, Fain GL (2008) Modulation of phosphodiesterase6 turnoff during background illumination in mouse rod photoreceptors. J Neurosci 28:2064–2074
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Richard Needleman, Mr. Masaomi Matsumoto, and Ms. Marta Matsumoto for critical reading of the manuscript. We also thank Drs. N. Li and W. Baehr (University of Utah) for providing of the plasmid for expression of recombinant Pδ. This work was supported in part by National Institute of Health Grants EY07546, EY09631, and EY13877, Jules and Doris Stein Professorship and an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness, Grants-in Aids for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the promotion of Science 18310088 and 18370062, and Iketani Foundation for science and Engineering 0191093-A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamazaki, A., Bondarenko, V.A., Matsuura, I. et al. Mechanism for the regulation of mammalian cGMP phosphodiesterase6. 1: Identification of its inhibitory subunit complexes and their roles. Mol Cell Biochem 339, 215–233 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0387-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0387-8