Abstract
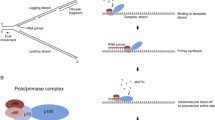
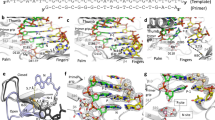
Fingers domain of HIV-1 RT is one of the constituents of the dNTP-binding pocket that is involved in binding of both dNTP and the template-primer. In the ternary complex of HIV-1 RT, two residues Trp-24 and Phe-61 located on the β1 and β3, respectively, are seen interacting with N + 1 to N + 3 nucleotides in the template overhang. We generated nonconservative and conservative mutant derivatives of these residues and examined their impact on the template-primer binding and polymerase function of the enzyme. We noted that W24A, F61A, and F61Y and the double mutant (W24A/F61A) were significantly affected in their ability to bind template-primer and also to catalyze the polymerase reaction while W24F remained unaffected. Using a specially designed template-primer with photoactivatable bromo-dU base in the duplex region at the penultimate position to the primer terminus, we demonstrated that F61A, W24A, F61Y as well as the double mutant were also affected in their cross-linking ability with the duplex region of the template-primer. We also isolated the E–TP covalent complexes of these mutants and examined their ability to catalyze single dNTP incorporation onto the immobilized primer terminus. The E–TP covalent complexes from W24F mutant displayed wild-type activity while those from W24A, F61A, F61Y, and the double mutant (W24A/F61A) were significantly impaired in their ability to catalyze dNTP incorporation onto the immobilized primer terminus. This unusual observation indicated that amino acid residues involved in the positioning of the template overhang may also influence the binding and orientation of the duplex region of the template-primer. Molecular modeling studies based on our biochemical results suggested that conformation of both W24 and F61 are interdependent on their interactions with each other, which together are required for proper positioning of the +1 template nucleotide in the binary and ternary complexes.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HIV-1:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- RT:
-
Reverse transcriptase
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- dNTP:
-
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
- ddNTP:
-
Dideoxy-nucleoside triphosphate
- TP:
-
Template-primer
- U5-PBS RNA template:
-
HIV-1 genomic RNA template corresponding to the primer binding sequence region
- U5-PBS DNA template:
-
HIV-1 genomic DNA template corresponding to the primer binding sequence region
- E–DNA:
-
Enzyme bound with DNA template-primer in the binary complex
- E–DNA–dNTP:
-
Enzyme bound with DNA template-primer and dNTP in the ternary complex
References
Sarafianos SG, Marchand B, Das K, Himmel DM, Parniak MA, Hughes SH, Arnold E (2009) Structure and function of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: molecular mechanisms of polymerization and inhibition. J Mol Biol 385:693–713
Telesnitsky A, Goff SP (1997) Reverse transcriptase and generation of retroviral DNA. In: Coffin JH, Hughes SH, Varmus HE (eds) Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY
Basavapathruni A, Anderson KS (2007) Reverse transcription of the HIV-1 pandemic. FASEB J 21:3795–3808
Katz RA, Skalka AM (1994) The retroviral enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 63:133–173
Schatz O, Mous J, Le Grice SF (1990) HIV-1 RT-associated ribonuclease H displays both endonuclease and 3′–5′ exonuclease activity. EMBO J 9:1171–1176
Beard WA, Wilson SH (1993) Kinetic analysis of template-primer interactions with recombinant forms of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry 32:9745–9753
Wang J, Smerdon SJ, Jager J, Kohlstaedt LA, Rice PA, Friedman JM, Steitz TA (1994) Structural basis of asymmetry in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7242–7246
Kohlstaedt LA, Wang J, Friedman JM, Rice PA, Steitz TA (1992) Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science 256:1783–1790
Kaushik N, Rege N, Yadav PN, Sarafianos SG, Modak MJ, Pandey VN (1996) Biochemical analysis of catalytically crucial aspartate mutants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry 35:11536–11546
Dash C, Fisher TS, Prasad VR, Le Grice SF (2006) Examining interactions of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with single-stranded template nucleotides by nucleoside analog interference. J Biol Chem 281:27873–27881
Powell MD, Beard WA, Bebenek K, Howard KJ, Le Grice SF, Darden TA, Kunkel TA, Wilson SH, Levin JG (1999) Residues in the alphaH and alphaI helices of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase thumb subdomain required for the specificity of RNase H-catalyzed removal of the polypurine tract primer. J Biol Chem 274:19885–19893
Hermann T, Meier T, Gotte M, Heumann H (1994) The ‘helix clamp’ in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: a new nucleic acid binding motif common in nucleic acid polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4625–4633
Hermann T, Heumann H (1996) Strained template under the thumbs. How reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 moves along its template. Eur J Biochem 242:98–103
Hsiou Y, Ding J, Das K, Clark AD Jr, Hughes SH, Arnold E (1996) Structure of unliganded HIV-1 reverse transcriptase at 2.7 A resolution: implications of conformational changes for polymerization and inhibition mechanisms. Structure 4:853–860
Jacobo-Molina A, Ding J, Nanni RG, Clark AD Jr, Lu X, Tantillo C, Williams RL, Kamer G, Ferris AL, Clark P et al (1993) Crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 A resolution shows bent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6320–6324
Ding J, Das K, Hsiou Y, Sarafianos SG, Clark AD Jr, Jacobo-Molina A, Tantillo C, Hughes SH, Arnold E (1998) Structure and functional implications of the polymerase active site region in a complex of HIV-1 RT with a double-stranded DNA template-primer and an antibody Fab fragment at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol 284:1095–1111
Sarafianos SG, Das K, Tantillo C, Clark AD Jr, Ding J, Whitcomb JM, Boyer PL, Hughes SH, Arnold E (2001) Crystal structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in complex with a polypurine tract RNA:DNA. EMBO J 20:1449–1461
Huang H, Chopra R, Verdine GL, Harrison SC (1998) Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science 282:1669–1675
Kiefer JR, Mao C, Braman JC, Beese LS (1998) Visualizing DNA replication in a catalytically active Bacillus DNA polymerase crystal. Nature 391:304–307
Li Y, Korolev S, Waksman G (1998) Crystal structures of open and closed forms of binary and ternary complexes of the large fragment of Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase I: structural basis for nucleotide incorporation. EMBO J 17:7514–7525
Sawaya MR, Prasad R, Wilson SH, Kraut J, Pelletier H (1997) Crystal structures of human DNA polymerase beta complexed with gapped and nicked DNA: evidence for an induced fit mechanism. Biochemistry 36:11205–11215
Fisher TS, Prasad VR (2002) Substitutions of Phe61 located in the vicinity of template 5′-overhang influence polymerase fidelity and nucleoside analog sensitivity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem 277:22345–22352
Fisher TS, Darden T, Prasad VR (2003) Substitutions at Phe61 in the beta3-beta4 hairpin of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase reveal a role for the Fingers subdomain in strand displacement DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol 325:443–459
Agopian A, Depollier J, Lionne C, Divita G (2007) p66 Trp24 and Phe61 are essential for accurate association of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with primer/template. J Mol Biol 373:127–140
Hsieh JC, Zinnen S, Modrich P (1993) Kinetic mechanism of the DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem 268:24607–24613
Pandey PK, Kaushik N, Singh K, Sharma B, Upadhyay AK, Kumar S, Harris D, Pandey VN (2002) Insertion of a small peptide of six amino acids into the beta7-beta8 loop of the p51 subunit of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase perturbs the heterodimer and affects its activities. BMC Biochem 3:18
Arts EJ, Li X, Gu Z, Kleiman L, Parniak MA, Wainberg MA (1994) Comparison of deoxyoligonucleotide and tRNA(Lys-3) as primers in an endogenous human immunodeficiency virus-1 in vitro reverse transcription/template-switching reaction. J Biol Chem 269:14672–14680
Sharma B, Kaushik N, Singh K, Kumar S, Pandey VN (2002) Substitution of conserved hydrophobic residues in motifs B and C of HIV-1 RT alters the geometry of its catalytic pocket. Biochemistry 41:15685–15697
Lee R, Kaushik N, Modak MJ, Vinayak R, Pandey VN (1998) Polyamide nucleic acid targeted to the primer binding site of the HIV-1 RNA genome blocks in vitro HIV-1 reverse transcription. Biochemistry 37:900–910
Ausubel F, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JS, Smith JA, Struhl K (1987) Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Intersciences, New York
Harris D, Lee R, Misra HS, Pandey PK, Pandey VN (1998) The p51 subunit of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase is essential in loading the p66 subunit on the template primer. Biochemistry 37:5903–5908
Pandey VN, Kaushik N, Rege N, Sarafianos SG, Yadav PN, Modak MJ (1996) Role of methionine 184 of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 reverse transcriptase in the polymerase function and fidelity of DNA synthesis. Biochemistry 35:2168–2179
Astatke M, Grindley ND, Joyce CM (1995) Deoxynucleoside triphosphate and pyrophosphate binding sites in the catalytically competent ternary complex for the polymerase reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment). J Biol Chem 270:1945–1954
Tong W, Lu CD, Sharma SK, Matsuura S, So AG, Scott WA (1997) Nucleotide-induced stable complex formation by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry 36:5749–5757
Sharma B, Kaushik N, Upadhyay A, Tripathi S, Singh K, Pandey VN (2003) A positively charged side chain at position 154 on the beta8-alphaE loop of HIV-1 RT is required for stable ternary complex formation. Nucleic Acids Res 31:5167–5174
Pandey PK, Kaushik N, Talele TT, Yadav PN, Pandey VN (2001) The beta7-beta8 loop of the p51 subunit in the heterodimeric (p66/p51) human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase is essential for the catalytic function of the p66 subunit. Biochemistry 40:9505–9512
Peletskaya EN, Boyer PL, Kogon AA, Clark P, Kroth H, Sayer JM, Jerina DM, Hughes SH (2001) Cross-linking of the fingers subdomain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase to template-primer. J Virol 75:9435–9445
Jorgensen W, Maxwell D, Tirado-Rives J (1996) Development and testing of the OPLS all atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 118:11225–11236
Polesky AH, Steitz TA, Grindley ND, Joyce CM (1990) Identification of residues critical for the polymerase activity of the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 265:14579–14591
Depollier J, Hourdou ML, Aldrian-Herrada G, Rothwell P, Restle T, Divita G (2005) Insight into the mechanism of a peptide inhibitor of HIV reverse transcriptase dimerization. Biochemistry 44:1909–1918
Tachedjian G, Radzio J, Sluis-Cremer N (2005) Relationship between enzyme activity and dimeric structure of recombinant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Proteins 60:5–13
Doublie S, Tabor S, Long AM, Richardson CC, Ellenberger T (1998) Crystal structure of a bacteriophage T7 DNA replication complex at 2.2 Å resolution. Nature 391:251–258
Ling H, Boudsocq F, Woodgate R, Yang W (2001) Crystal structure of a Y-family DNA polymerase in action: a mechanism for error-prone and lesion-bypass replication. Cell 107:91–102
Matamoros T, Kim B, Menendez-Arias L (2008) Mechanistic insights into the role of Val75 of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in misinsertion and mispair extension fidelity of DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol 375:1234–1248
Kim B, Ayran JC, Sagar SG, Adman ET, Fuller SM, Tran NH, Horrigan J (1999) New human immunodeficiency virus, type 1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1 RT) mutants with increased fidelity of DNA synthesis. Accuracy, template binding, and processivity. J Biol Chem 274:27666–27673
Kim B, Hathaway TR, Loeb LA (1998) Fidelity of mutant HIV-1 reverse transcriptases: interaction with the single-stranded template influences the accuracy of DNA synthesis. Biochemistry 37:5831–5839
Acknowledgment
This research was partly supported by grants from the NIAID/NIH (AI074477 and AI42520 to VNP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, A.K., Talele, T.T. & Pandey, V.N. Impact of template overhang-binding region of HIV-1 RT on the binding and orientation of the duplex region of the template-primer. Mol Cell Biochem 338, 19–33 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0316-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0316-x