Abstract
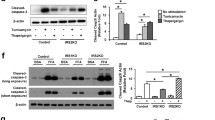
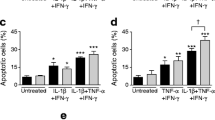
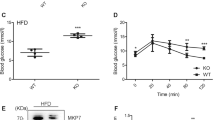
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis is crucial for β-cell function and survival. Direct as well as indirect evidence has pointed toward Ca2+ as an important determinant of interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis. In the present study, we show that IL-1β-induced apoptosis and necrosis in primary rat β-cells and MIN6 cells largely depends on ER stress, ER Ca2+ release, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation. β-cells also showed marked sensitivity to apoptosis induced by sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) blockers, thapsigargin and cyclopiazonic acid (CPA). IL-1β induced ER Ca2+ release, which was paralleled by an IL-1β-dependent induction of JNK activation and the ER stress response, including activation of PRK (RNA-dependent protein kinase)-like ER kinase (PERK). Furthermore, reduced activation of JNK, utilizing JNK inhibitor SP600125, resulted in significant protection from IL-1β- or thapsigargin-induced apoptosis via ER stress. In conclusion, our results suggest that the IL-1β-induced depletion of ER Ca2+ and activation of the ER stress via JNK pathway are potential contributory mechanisms to β-cell death.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPA:
-
Cyclopiazonic acid
- eIF2α:
-
α Subunit of translation initiation factor 2
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- PBA:
-
4-Phenyl butyric acid
- PERK:
-
Double-stranded RNA-activated kinase-like kinase
- SERCA:
-
Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase
References
Harding HP, Zeng H, Zhang Y et al (2001) Diabetes mellitus and exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in perk−/−mice reveals a role for translational control in secretory cell survival. Mol Cell 7:1153–1163. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00264-7
Scheuner D, Mierde DV, Song B et al (2005) Control of mRNA translation preserves endoplasmic reticulum function in beta cells and maintains glucose homeostasis. Nat Med 11:757–764. doi:10.1038/nm1259
Ladiges WC, Knoblaugh SE, Morton JF et al (2005) Pancreatic β-cell failure and diabetes in mice with a deletion mutation of the endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone gene P58IPK. Diabetes 54:1074–1081. doi:10.2337/diabetes.54.4.1074
Ma Y, Hendershot LM (2004) ER chaperone functions during normal and stress conditions. J Chem Neuroanat 28:51–65. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2003.08.007
Rutkowski DT, Kaufman RJ (2004) A trip to the ER: coping with stress. Trends Cell Biol 14:20–28. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2003.11.001
Berridge MJ (2002) The endoplasmic reticulum: a multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium 32:235–249. doi:10.1016/S0143416002001823
Oyadomari S, Takeda K, Takiguchi M et al (2001) Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10845–10850. doi:10.1073/pnas.191207498
Pipeleers DG, in’t Veld PA, Van de Winkel M et al (1985) A new in vitro model for the study of pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology 117:806–816
Ling Z, Hannaert JC, Pipeleers D (1994) Effect of nutrients, hormones and serum on survival of rat islet beta cells in culture. Diabetologia 37:15–21. doi:10.1007/BF00428772
Hohmeier HE, Newgard CB (2004) Cell lines derived from pancreatic islets. Mol Cell Endocrinol 228:121–128. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2004.04.017
Miyazaki J, Araki K, Yamato E et al (1990) Establishment of a pancreatic beta cell line that retains glucose-inducible insulin secretion: special reference to expression of glucose transporter isoforms. Endocrinology 127:126–132
Delaney CA, Pavlovic D, Hoorens A et al (1997) Cytokines induce deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks and apoptosis in human pancreatic islet cells. Endocrinology 138:2610–2614. doi:10.1210/en.138.6.2610
Kutlu B, Cardozo AK, Darville MI (2003) Discovery of gene networks regulating cytokine-induced dysfunction and apoptosis in insulin-producing INS-1 cells. Diabetes 52:2701–2719. doi:10.2337/diabetes.52.11.2701
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Welch WJ, Brown RC (1996) Influence of molecular and chemical chaperones on protein folding. Cell Stress Chaperones 1:109–115. doi:10.1379/1466-1268(1996)001<0109:IOMACC>2.3.CO;2
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L et al (2006) Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science 313:1137–1140. doi:10.1126/science.1128294
Shi Y, Vattem KM, Sood R et al (1998) Identification and characterization of pancreatic eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha-subunit kinase, PEK, involved in translational control. Mol Cell Biol 18:7499–7509
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Ron D (1999) Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 397:271–274. doi:10.1038/16729
Diaz-Horta O, Kamagate A, Herchuelz A et al (2002) Na/Ca exchanger overexpression induces endoplasmic reticulum—related apoptosis and caspase-12 activation in insulin-releasing BRIN-BD11 cells. Diabetes 51:1815–1824. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.6.1815
Cardozo AK, Heimberg H, Heremans Y et al (2001) A comprehensive analysis of cytokine-induced and nuclear factor-B-dependent genes in primary rat pancreatic β-cells. J Biol Chem 276:48879–48886. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108658200
Cardozo AK, Kruhoffer M, Leeman R et al (2001) Identification of novel cytokine-induced genes in pancreatic β-cells by high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Diabetes 50:909–920. doi:10.2337/diabetes.50.5.909
Heimberg H, Heremans Y, Jobin C et al (2001) Inhibition of cytokine-induced NF-B activation by adenovirus-mediated expression of a NF-B super-repressor prevents β-cell apoptosis. Diabetes 50:2219–2224. doi:10.2337/diabetes.50.10.2219
Giannoukakis N, Rudert WA, Trucco M et al (2000) Protection of human islets from the effects of interleukin-1β by adenoviral gene transfer of an IB repressor. J Biol Chem 275:36509–36513. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005943200
van Eylen F, Antoine MH, Lebrun P et al (1994) Inhibition of Na/Ca exchange stimulates insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 8:425–429
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China to Qin Wang (30770837) and supported by Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project, Project Number: B205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zhang, H., Zhao, B. et al. IL-1β caused pancreatic β-cells apoptosis is mediated in part by endoplasmic reticulum stress via the induction of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 324, 183–190 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9997-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9997-9