Abstract
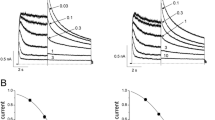
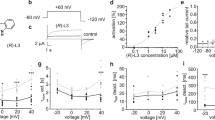
Common clinically used drugs block the delayed rectifier K+ channels and prolong the cardiac action potential duration associated with long QT syndrome. Here, we investigated the mechanism of hERG K+ channel current (I hERG) blockade expressed in HEK-293 cells by sibutramine HCl, a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Sibutramine HCl inhibited I hERG in a concentration-dependent manner with the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 2.5 μM at −40 mV. I hERG inhibition by sibutramine HCl showed weak voltage dependency, but the time-dependence of I hERG inhibition was developed relatively rapidly on membrane depolarization. On hERG channel gating for the S6 and pore regions, the S6 residue hERG mutant Y652A and F656A largely reduced the blocking potency of I hERG, unlike the pore-region mutants T623A and S624A. These results indicate that sibutramine HCl preferentially inhibits the hERG potassium channel through the residue Y652 and F656, in a supratherapeutic concentration should be avoided by patients with high susceptibility for cardiac arrhythmia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witchel HJ, Hanconx JC (2000) Familial and acquired long QT syndrome and the cardiac rapid delayed rectifier potassium current. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27:753–766. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03337.x
Reilly JG, Ayis SA, Ferrier IN, Jones SJ, Thomas SH (2000) QTc interval abnormalities and psychotropic drug therapy in psychiatric patients. Lancet 355:1048–1052. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02035-3
Need AC, Motulsky AG, Goldstein DB (2005) Priorities and standards in pharmacogenetic research. Nat Genet 37:671–681. doi:10.1038/ng1593
Ryan DH, Kaiser P, Bray GA (1995) Sibutramine: a novel new agent for obesity treatment. Obes Res 3:553S–559S
Harrison-Woolrych M, Clark DW, Hill GR, Rees MI, Skinner JR (2006) QT interval prolongation associated with sibutramine treatment. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:464–469. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02574.x
Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT (1995) A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the Ikr potassium channel. Cell 81:299–307. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90340-2
Mitcheson JS, Sanguinetti MC (1999) Biophysical properties and molecular basis of cardiac rapid and slow delayed rectifier potassium channels. Cell Physiol Biochem 9:201–216. doi:10.1159/000016317
Lees-Miller JP, Duan Y, Teng GQ, Duff HJ (2000) Molecular determinant of high-affinity dofetilide binding to HERG1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes: involvement of S6 sites. Mol Pharmacol 57:367–374
Mitcheson JS, Chen J, Lin M, Culberson C, Sanguinetti MC (2000) A structural basis for drug-induced long QT syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12329–12333. doi:10.1073/pnas.210244497
Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, Green ED, Keating MT (1995) A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell 80:795–803. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90358-5
Thomas D, Gut B, Wendt-Nordahl G, Kiehn J (2002) The antidepressant drug fluoxetine is an inhibitor of human ether-a-go-go-related gene (HERG) potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:543–548. doi:10.1124/jpet.300.2.543
Spector PS, Curran ME, Keating MT (1996) Class III antiarrhymic drugs block HERG, a human cardiac delayed rectifier K+ channel. Open-channel block by methanesulfonanilides. Circ Res 78:499–503
Fernandez D, Ghanta A, Kauffman GW, Sanguinetti MC (2004) Physicochemical features of the HERG channel drug binding site. J Biol Chem 279:10120–10127. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310683200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ki-Suk Kim and Eun-Joo Kim are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KS., Kim, EJ., Lee, HA. et al. Effect of sibutramine HCl on cardiac hERG K+ channel. Mol Cell Biochem 320, 125–131 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9914-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9914-2