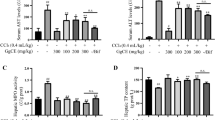
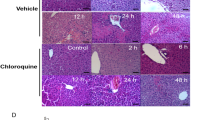
Abstract
The accumulation of hydrophobic bile acids plays a role in the induction of apoptosis and necrosis of hepatocytes during cholestasis. Glycochenodeoxycholate acid (GCDC) triggers a rapid oxidative stress response as an event of glutathione (GSH) depletion and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation. We therefore investigated whether the bioactivity of the antioxidant capillarisin (Cap) prevents GCDC-induced hepatocyte damage. Isolated rat hepatocytes were co-incubated with 100 μM GCDC and 0.5 mg/ml Cap for 4 h. GSH depletion and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS, measure of lipid peroxidation) increased after GCDC exposure, but were markedly suppressed by Cap treatment. Cap protected hepatocytes from a GCDC-induced increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and mitochondrial membrane potential induction, as measured by flow cytometry analysis. In addition, Cap was shown to inhibit GCDC-mediated NF-κB activation by using electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA). In contrast to GCDC, Cap not only significantly decreased cytochrome c release and caspase-3 enzyme activity, but also suppressed heme oxygenase-1 protein and mRNA expression in hepatocytes. These results demonstrate that Cap function as an antioxidant reduced hepatocyte injury caused by hydrophobic bile acids, perhaps by preventing generation of ROS and release of cytochrome c, thereby minimizing hepatocytes apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greim H, Trülzsch D, Roboz J, Dressler K, Czygan P, Hutterer F, Schaffner F, Popper H (1972) Mechanism of cholestasis. 5. Bile acids in normal rat livers and in those after bile duct ligation. Gastroenterology 63:837–845
Spivey JR, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (1993) Glycochenodeoxycholate-induced lethal hepatocellular injury in rat hepatocytes. Role of ATP depletion and cytosolic free calcium. J Clin Invest 92:17–24. doi:10.1172/JCI116546
Patel T, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (1994) Increases of intracellular magnesium promote glycodeoxycholate-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest 94:2183–2192. doi:10.1172/JCI117579
Kwo P, Patel T, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (1995) Nuclear serine protease activity contributes to bile acid-induced apoptosis in hepatocytes. Am J Physiol 268:G613–G621
Sokol RJ, Straka MS, Dahl R, Devereaux MW, Yerushalmi B, Gumpricht E, Elkins N, Everson G (2001) Role of oxidant stress in the permeability transition induced in rat hepatic mitochondria by hydrophobic bile acids. Pediatr Res 49:519–531. doi:10.1203/00006450-200104000-00014
Utanohara S, Tsuji M, Momma S, Morio Y, Oguchi K (2005) The effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on glycochenodeoxycholic acid-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. Toxicology 214:77–86. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2005.05.025
Koseki H, Tsuji M, Utanohara S, Asano Y, Oyamada H, Okazaki M, Oguchi K (2003) Glycochenodeoxycholic acid induced apoptosis in RLN-8 hepatocytes. J Showa Med Assoc 63:405–414
Jaeschke H (1995) Mechanisms of oxidant stress-induced acute tissue injury. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 209:104–111
Fox ES, Kim JC, Tracy TF (1997) NF-kappaB activation and modulation in hepatic macrophages during cholestatic injury. J Surg Res 72:129–134. doi:10.1006/jsre.1997.5172
Wagener FA, Volk HD, Willis D, Abraham NG, Soares MP, Adema GJ, Figdor CG (2003) Different faces of the heme-heme oxygenase system in inflammation. Pharmacol Rev 55:551–571. doi:10.1124/pr.55.3.5
Tüzüner E, Liu L, Shimada M, Yilmaz E, Glanemann M, Settmacher U, Langrehr JM, Jonas S, Neuhaus P, Nussler AK (2004) Heme oxygenase-1 protects human hepatocytes in vitro against warm and cold hypoxia. J Hepatol 41:764–772. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2004.07.013
Komiya T, Tsukui M, Oshio H (1976) Studies on “Inchinko”. I. Capillarisin, a new choleretic substance. Yakugaku Zasshi 96:841–854
Lee TY, Chang HH, Chen JH, Hsueh ML, Kuo JJ (2007) Herb medicine Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in bile duct ligation rats. J Ethnopharmacol 109:318–324. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2006.07.042
Chang WS, Lee YJ, Lu FJ, Chiang HC (1993) Inhibitory effects of flavonoids on xanthine oxidase. Anticancer Res 13:2165–2170
Okada Y, Miyauchi N, Suzuki K, Kobayashi T, Tsutsui C, Mayuzumi K, Nishibe S, Okuyama T (1995) Search for naturally occurring substances to prevent the complications of diabetes. II. Inhibitory effect of coumarin and flavonoid derivatives on bovine lens aldose reductase and rabbit platelet aggregation. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 43:1385–1387
Kühnau J (1976) The flavonoids. A class of semi-essential food components: their role in human nutrition. World Rev Nutr Diet 24:117–191
Chu CY, Tseng TH, Hwang JM, Chou FP, Wang CJ (1999) Protective effects of capillarisin on tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage in rat primary hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 73:263–268. doi:10.1007/s002040050615
Li CC, Shen HL, Lii CK, Liu KL, Yang JJ, Chen HW (2005) Prostaglandin E2 down-regulation of cytochrome P-450 2B1 expression induced by phenobarbital is through EP2 receptor in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:424–430. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.023
Fraga CG, Leibovitz BE, Tappel AL (1998) Lipid peroxidation measured as thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in tissue slices: Characterization and comparison between homogenates and microsomes. Free Radic Biol Med 4:155–161. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(88)90023-8
Reed DJ, Babson JR, Beatty PW, Brodie AE, Ellis WW, Potter DW (1980) High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of nanomole levels of glutathione, glutathione disulfide, and related thiols and disulfides. Anal Biochem 106:55–62. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(80)90118-9
Moldéus P, Högberg J, Orrenius S (1978) Isolation and use of liver cells. Methods Enzymol 52:60–71. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(78)52006-5
Ufer C, Borchert A, Kuhn H (2003) Functional characterization of cis- and trans-regulatory elements involved in expression of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase. Nucleic Acids Res 31:4293–4303. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg650
Graf D, Kurz AK, Reinehr R, Fischer R, Kircheis G, Häussinger D (2002) Prevention of bile acid-induced apoptosis by betaine in rat liver. Hepatology 36:829–839
Yerushalmi B, Dahl R, Devereaux MW, Gumpricht E, Sokol RJ (2001) Bile acid-induced rat hepatocyte apoptosis is inhibited by antioxidants and blockers of the mitochondrial permeability transition. Hepatology 33:616–626. doi:10.1053/jhep.2001.22702
Gao D, Wei C, Chen L, Huang J, Yang S, Diehl AM (2004) Oxidative DNA damage and DNA repair enzyme expression are inversely related in murine models of fatty liver disease. Am J Physiol 287:G1070–G1077. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00422.2003
Chen J, Petersen DR, Schenker S, Henderson GI (2000) Formation of malondialdehyde adducts in livers of rats exposed to ethanol: role in ethanol-mediated inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:544–552. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2000.tb02023.x
Kristal BS, Park BK, Yu BP (1996) 4-Hydroxyhexenal is a potent inducer of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 271:6033–6038. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.11.6033
Liu TZ, Lee KT, Chern CL, Cheng JT, Stern A, Tsai LY (2001) Free radical-triggered hepatic injury of experimental obstructive jaundice of rats involves overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines and enhanced activation of nuclear factor kappa B. Ann Clin Lab Sci 31:383–390
Schoemaker MH, Gommans WM, Conde de la Rosa L, Homan M, Klok P, Trautwein C, van Goor H, Poelstra K, Haisma HJ, Jansen PL, Moshage H (2003) Resistance of rat hepatocytes against bile acid-induced apoptosis in cholestatic liver injury is due to nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J Hepatol 39:153–161. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(03)00214-9
Sass G, Soares MC, Yamashita K, Seyfried S, Zimmermann WH, Eschenhagen T, Kaczmarek E, Ritter T, Volk HD, Tiegs G (2003) Heme oxygenase-1 and its reaction product, carbon monoxide, prevent inflammation-related apoptotic liver damage in mice. Hepatology 38:909–918
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following: Grant nos. CCMP95-RD-207 from the Committee on Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, Department of Health, NSC96-2320-B-182-021-MY2 from the National Science Council, Taiwan, and CMRPD160201 from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, TY., Chen, FY., Chang, HH. et al. The effect of capillarisin on glycochenodeoxycholic acid-induced apoptosis and heme oxygenase-1 in rat primary hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 325, 53–59 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-0019-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-0019-8