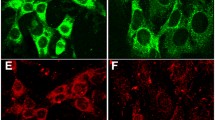
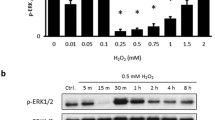
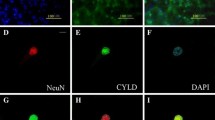
Abstract
Identifying prosurvival mechanisms in stressed neuronal cells would provide protective strategies to hinder neurodegeneration. Recent evidence shows that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a well-established mitogen in endothelial cells, can mediate neuroprotection against damaging insults through the activation of its cognate receptor VEGFR2. In addition, growth factor receptor signaling pathways have been shown to crosstalk with cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase A (PKA) to protect neuronal cells from harmful stimuli. Whether a relationship exists between VEGFR2 and PKA in mediating neuroprotection under stressful conditions is unknown. Using SK-N-SH neuronal cells as a model system, we show that serum deprivation induces an upregulation in VEGF and VEGFR2 that concomitantly serves as a prosurvival signaling pathway. Inhibitor studies revealed that PKA functioned concurrently with VEGFR2 pathway to signal the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK1/2) as protection against caspase-3/7 activation and a subsequent cell death. The loss in cell viability induced by VEGFR2 and PKA inhibition was prevented by caspase inhibition or overexpression of ERK1. Overexpression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-xL also promoted survival when VEGFR2 function was blocked. However, the protection elicited by all three treatments were prevented by the inclusion of a selective inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK), the upstream kinase that activates ERK1/2. Taken together, these findings suggested that PKA and VEGFR2 converge at the MEK/ERK1/2 pathway to protect serum starved neuronal cells from a caspase-dependent cell death.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zachary I (2005) Neuroprotective role of vascular endothelial growth factor: signalling mechanisms, biological function, and therapeutic potential. Neurosignals 14:207–221
Gora-Kupilas K, Josko J (2005) The neuroprotective function of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Folia Neuropathol 43:31–39
Sondell M, Sundler F, Kanje M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci 12:4243–4254
Silverman WF, Krum JM, Mani N et al (1999) Vascular, glial and neuronal effects of vascular endothelial growth factor in mesencephalic explant cultures. Neuroscience 90:1529–1541
Jin KL, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor rescues HN33 neural cells from death induced by serum withdrawal. J Mol Neurosci 14:197–203
Jin KL, Mao XO, Nagayama T et al (2000) Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt signaling by global cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience 100:713–717
Ogunshola OO, Antic A, Donoghue MJ et al (2002) Paracrine and autocrine functions of neuronal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem 277:11410–11415
Matsuzaki H, Tamatani M, Yamaguchi A et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor rescues hippocampal neurons from glutamate-induced toxicity: signal transduction cascades FASEB J 15:1218–1220
Kilic I, Kilic E, Ja¨rve A et al (2006) Human vascular endothelial growth factor protects axotomized retinal ganglion cells in vivo by activating ERK1/2 and Akt Pathways. J Neurosci 26:12439–12446
Wang Y, Mao XO, Xie L et al (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor overexpression delays neurodegeneration and prolongs survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. J Neurosci 27:304–307
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J et al (2006) VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Shraga N et al (2002) The neuropilins: multifunctional semaphorin and VEGF receptors that modulate axon guidance and angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 12:13–19
Tamagnone L, Comoglio PM (2000) Signalling by semaphorin receptors: cell guidance and beyond. Trends Cell Biol 10:377–383
Kilic E, Kilic U, Wang Y et al (2006) The phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway mediates VEGF’s neuroprotective activity and induces blood brain barrier permeability after focal cerebral ischemia. FASEB J 20:1185–1187
Wick A, Wick W, Waltenberger J et al (2002) Neuroprotection by hypoxic preconditioning requires sequential activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and Akt. J Neurosci 15:6401–6407
Jin K, Mao XO, Batteur SP et al (2001) Caspase-3 and the regulation of hypoxic neuronal death by vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuroscience 108:351–358
Stork PJ, Schmitt JM (2002) Crosstalk between cAMP and MAP kinase signaling in the regulation of cell proliferation. Trends Cell Biol 12:258–266
Dumaz N, Marais R (2005) Integrating signals between cAMP and the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signalling pathways. FEBS J 272:3491–3504
D’Angelo G, Lee H, Weiner RI (1997) cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits the mitogenic action of vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor in capillary endothelial cells by blocking Raf activation. J Cell Biochem 67:353–366
Yao H, York RD, Misra-Press A et al (1998) The cyclic adenosine monophosphate–dependent protein kinase (PKA) is required for the sustained activation of mitogen activated kinases and gene expression by nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem 273:8240–8247
Park K, Luo JM, Hisheh S et al (2004) Cellular mechanisms associated with spontaneous and ciliary neurotrophic factor-cAMP-induced survival and axonal regeneration of adult retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 24:10806–10815
Troadec JD, Marien M, Mourlevat S et al (2002) Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK(1/2)) signaling pathway by cyclic AMP potentiates the neuroprotective effect of the neurotransmitter noradrenaline on dopaminergic neurons. Mol Pharmacol 62:1043–1052
Filippa N, Sable C L, Filloux C et al (1999) Mechanism of Protein Kinase B Activation by Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein. Kinase Mol Cell Biol 19:4989–5000
Wang G, Qi C, Fan GH et al (2005) PACAP protects neuronal differentiated PC12 cells against the neurotoxicity induced by a mitochondrial complex I inhibitor, rotenone. FEBS Lett 579:4005–4011
Rockwell P, Martinez J, Papa L et al (2004) Redox regulates COX-2 upregulation and cell death in the neuronal response to cadmium. Cell Signal 16:343–353
Horbinski C, Chu CT (2005) Kinase signaling cascades in the mitochondrion: a matter of life or death. Free Radic Biol Med 38:2–11
Hetman M, Gozdz A (2004) Role of extracellular signal regulated kinases 1 and 2 in neuronal survival. Eur J Biochem 271:2050–2055
Vossler MR, Yao H, York RD et al (1997) cAMP activates MAP Kinase and Elk-1 through a B-Raf- and Rap1-dependent pathway. Cell 89:73–82
Chong H, Vikis HG, Guan KL (2003) Mechanisms of regulating the Raf kinase family. Cell Signal 15:463–469
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J et al (2006) VEGF receptor signalling — in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371
Bouschet T, Perez V, Fernandez C et al (2003) Stimulation of the ERK pathway by GTP-loaded Rap1 requires the concomitant activation of Ras, Protein Kinase C, and Protein Kinase A in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 278:4778–4785
Iida N, Namikawa K, Kiyama H et al (2001) Requirement of Ras for the activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase by calcium influx, cAMP, and neurotrophin in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 21:6459–6466
Han BH, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF protects the neonatal brain from hypoxic-ischemic injury in vivo via the ERK pathway. J Neurosci 20:5775–5781
Putz T, Culig Z, Eder IE et al (1999) Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor blockade inhibits the action of EGF, insulin-like growth factor I, and a protein kinase A activator on the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 59:227–233
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656
Eliseev RA, VanWinkle B, Rosier RN et al (2004) Diazoxide-mediated preconditioning against apoptosis involves activation of cAMP-response element-binding Protein (CREB) and NFκB. J Biol Chem 279:46748–46754
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH et al (2000) MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 79:355–369
Mori M, Uchida M, Watanabe T et al (2003) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2 induces Bcl-xL up-regulation via inhibition of caspase activities in erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol 195:290–297
Impey S, Obrietan K, Wong ST et al (1998) Cross talk between ERK and PKA is required for Ca2+ stimulation of CREB-dependent transcription and ERK nuclear translocation. Neuron 21:869–883
Lee HJ, Bach JH, Chae HS et al (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase attenuates 3-hydroxykynurenine-induced neuronal cell death. J Neurochem 88:647–656
Jin K, Mao XO, Zhu Y et al (2002) MEK and ERK protect hypoxic cortical neurons via phosphorylation of Bad. J Neurochem 80:119–125
Baek JH, Jang JE, Kang CM et al (2000) Hypoxia-induced VEGF enhances tumor survivability via suppression of serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 19:4621–4631
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grant (NIGMS SCORE to P.R.) and Grant Number RR03037 from the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NCRR or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomes, E., Papa, L., Hao, T. et al. The VEGFR2 and PKA pathways converge at MEK/ERK1/2 to promote survival in serum deprived neuronal cells. Mol Cell Biochem 305, 179–190 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9542-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9542-2