Abstract
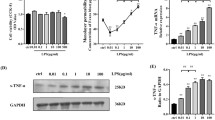
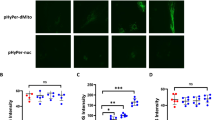
Src-suppressed C kinase substrate (SSeCKS) plays a role in membrane-cytoskeletal remodeling to regulate mitogenesis, cell differentiation, and motility. Previous study showed that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced a selective and strong expression of SSeCKS in the vascular endothelial cells of lung. Here we show that LPS stimulation elevated expression of SSeCKS mRNA and protein in Rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (RPMVEC). LPS potentiated SSeCKS phosphorylation in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and partly induced translocation of SSeCKS from the cytosol to the membrane after LPS challenge. The PKC inhibitor, Calphostin C, significantly decreased LPS-induced phosphorylation of SSeCKS, inhibited SSeCKS translocation and actin cytoskeleton reorganization after LPS challenge, suggesting that PKC may play a role in LPS-induced SSeCKS translocation and actin rearrangement. We conclude that SSeCKS is located downstream of PKC and that SSeCKS and PKC are both necessary for LPS-induced stress fiber formation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McVerry BJ, Garcia JG (2004) Endothelial cell barrier regulation by sphingosine 1-phosphate. J Cell Biochem 92:1075–1085
Waschke J, Baumgartner W, Adamson RH et al (2004) Requirement of Rac activity for maintenance of capillary endothelial barrier properties. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H394–H401
Chakravortty D, Nanda Kumar KS (2000) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces cytoskeletal rearrangement in small intestinal lamina propria fibroblasts: actin assembly is essential for lipopolysaccharide signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1500:125–136
Goldblum SE, Ding X, Brann TW et al (1993) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces actin reorganization, intercellular gap formation, and endothelial barrier dysfunction in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells: concurrent F-actin depolymerization and new actin synthesis. J Cell Physiol 157:13–23
Serikov VB, Choi H, Schmiel K et al (2004) Endotoxin induces leukocyte transmigration and changes in permeability of the airway epithelium via protein-kinase C and extracellular regulated kinase activation. J Endotoxin Res 10:55–65
Hai CM, Hahne P, Harrington EO et al (2002) Conventional protein kinase C mediates phorbol-dibutyrate-induced cytoskeletal remodeling in a7r5 smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res 280:64–74
Massoumi R, Sjolander A (2001) Leukotriene D(4) affects localisation of vinculin in intestinal epithelial cells via distinct tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C controlled events. J Cell Sci 114:1925–1934
Tatin F, Varon C, Genot E et al (2006) A signalling cascade involving PKC, Src and Cdc42 regulates podosome assembly in cultured endothelial cells in response to phorbol ester. J Cell Sci 119:769–781
Harrington EO, Brunelle JL, Shannon CJ et al (2003) Role of protein kinase C isoforms in rat epididymal microvascular endothelial barrier function. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28: 626–636
Brandt D, Gimona M, Hillmann M et al (2002) Protein kinase C induces actin reorganization via a Src- and Rho-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 277:20903–20910
Tang S, Morgan KG, Parker C (1997) Requirement for protein kinase C theta for cell cycle progression and formation of actin stress fibers and filopodia in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 272:28704–28711
Lin X, Tombler E, Nelson PJ (1996) A novel src- and ras-suppressed protein kinase C substrate associated with cytoskeletal architecture. J Biol Chem 271:28430–28438
Gelman IH, Lee K, Tombler E (1998) Control of cytoskeletal architecture by the src-suppressed C kinase substrate, SSeCKS. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 41:1–17
Lin X, Nelson P, Gelman IH (2000) SSeCKS, a major protein kinase C substrate with tumor suppressor activity, regulates G(1) → S progression by controlling the expression and cellular compartmentalization of cyclin D. Mol Cell Biol 20:7259–7272
Erlichman J, Gutierrez JR, Zucker S et al (1999) Developmental expression of the protein kinase C substrate/binding protein (clone 72/SSeCKS) in rat testis identification as a scaffolding protein containing an A-kinase-anchoring domain which is expressed during late-stage spermatogenesis. Eur J Biochem 263:797–805
Gelman IH, Tombler E, Vargas JJ et al (2000) A role for SSeCKS, a major protein kinase C substrate with tumour suppressor activity, in cytoskeletal architecture, formation of migratory processes, and cell migration during embryogenesis. Histochem J 32:13–26
Nelson PJ, Moissoglu K, Vargas JJ et al (1999) Involvement of the protein kinase C substrate, SSeCKS, in the actin-based stellate morphology of mesangial cells. J Cell Sci 112:361–370
Gelman IH, Xi Q, Kumar CC (1999) Reexpression of the major PKC substrate, SSeCKS, correlates with the tumor-suppressive effects of SCH51344 on rat-6/src and rat-6/ras fibroblasts but not on rat-6/raf fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci 886:221–224
Kitamura H, Okita K, Fujikura D, Mori K, Iwanaga T, Saito M (2002) Induction of Src-suppressed C kinase substrate (SSeCKS) in vascular endothelial cells by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Histochem Cytochem 50:245–255
Rung-ruangkijkrai T, Fujikura D, Kitamura H et al (2004) The expression of src-suppressed C kinase substrate (SSeCKS) and uptake of exogenous particles in endothelial and reticular cells. Arch Histol Cytol 67:135–147
Chen S, Fei X, Li SH (1995) A new simple method for isolation of microvascular endothelial cells avoiding both chemical and mechanical injuries. Microvasc Res 50:119–128
Hansen-Smith FM, Watson L, Lu DY et al (1988) Griffonia simplicifolia I: fluorescent tracer for microcirculatory vessels in nonperfused thin muscles and sectioned muscle. Microvasc Res 36:199–215
Laitinen L (1987) Griffonia simplicifolia lectins bind specifically to endothelial cells and some epithelial cells in mouse tissues. Histochem J 19:225–234
Disatnik MH, Boutet SC, Lee CH, Mochly-Rosen D, Rando TA (2002) Sequential activation of individual PKC isozymes in integrin-mediated muscle cell spreading: a role for MARCKS in an integrin signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 115:2151–2163
Yang Z, Bochsler PN, Carroll RC et al (1994) Signal transduction pathways of bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bovine vascular endothelial cells. Inflammation 18:221–233
Lidington EA, Moyes DL, McCormack AM et al (1999) A comparison of primary endothelial cells and endothelial cell lines for studies of immune interactions. Transpl Immunol 7:239–246
Karimi G, Fatehi Z, Gholamnejad Z (2006) The role of nitric oxide and protein kinase C in lipopolysaccharidemediated vascular hyporeactivity. J Pharm Pharm Sci 9:119–123
Chen YJ, Hsu KW, Tsai JN et al (2005) Involvement of protein kinase C in the inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by thapsigargin in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2574–2585
Grove BD, Bruchey AK (2001) Intracellular distribution of gravin, a PKA and PKC binding protein, in vascular endothelial cells. J Vasc Res 38:163–175
Nelson PJ, Gelman IH (1997) Cell-cycle regulated expression and serine phosphorylation of the myristylated protein kinase C substrate, SSeCKS: correlation with culture confluency, cell cycle phase and serum response. Mol Cell Biochem 175:233–241
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Scientific Foundation of China Grant 30300099, and Natural Science Foundation of JiangSu province Grant BK2003035, and Natural science Foundation of JiangSu colleges and universities Grant 03KJB180109 and “liu-da-ren-cai-gao-feng” finance assistance of JiangSu province Grant No. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chun Cheng and Haiou Liu are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Liu, H., Ge, H. et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces expression of SSeCKS in rat lung microvascular endothelial cell. Mol Cell Biochem 305, 1–8 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9521-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9521-7