Abstract
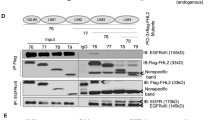
The continual activation of signaling cascades results in dramatic consequences that include loss of cellular growth control and neoplastic transformation. We show here that phosphoinositide 3-kinase and its mediator Akt was constitutively activated in glioma and that this might be due to the aberrant expression of their natural antagonist PTEN. The PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten) tumor suppressor gene modulates cell growth and survival through mechanisms that are incompletely understood. In this study, we investigated the possibility that PTEN mediates its effects through modulation of transcription factor AP-1, which is in part due to decrease in c-fos expression which was dependent on PI3kinase activity. Consistent with a reduction in the c-fos levels, an AP-1 dependent reporter gene was poorly induced in the PTEN expressing cell lines. In contrast to its effect on c-fos, PTEN did not affect the expression of c-Jun and other fos family members. We also show that the effect of PTEN on c-fos expression was due to its ability to antagonize PI3-kinase and could be mimicked by the expression of dominant negative Akt mutant. Taken together, these data indicate that the aberrant expression of PTEN contributes to the activation of the PI3kinase/Akt pathway and its transcription factor mediators in glioma. We conclude that the ectopic expression of PTEN down regulates the proliferation of glioma cells through the suppression of AP-1 and that this target might be essential for its central role in the growth and survival of glioma cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker MD, Alexander E, Hunt WE (1978) Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas: A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg 49:333–343
Walker MD, Green SB, Byar DP (1980) TNF and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. N Engl J Med 303:1323–1329
Davis FG, McCarthy BJ, Freels S (1999) The conditional probability of survival of patients with primary malignant brain tumors: surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) data. Cancer 85:485–491
Cantley LC, Neel BG (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4240–4245
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T, Ruland J, Penninger JM, Siderovski DP, Mak TW (1998) Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell 95:29–39
Myers MP, Pass I, Batty IH, Van der Kaay J, Stolarov JP, Hemmings BA, Wigler MH, Downes CP, Tonks NK (1998) The lipid phosphatase activity of PTEN is critical for its tumor suppressor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13513–13518
Vazquez F, Sellers WR (2000) The PTEN tumor suppressor protein: an antagonist of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1470:M21–M35
Leevers SJ, Vanhaesebroeck B, Waterfield MD (1999) Signaling through phosphoinositide 3-kinases: the lipids take centre stage. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:219–225
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed JC (1997) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282:1318–1321
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Romashkova JA, Makarov SS (1999) NF-kappaB is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signaling. Nature 401:86–89
Reddy SAG, Huang JH, Liao L (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase as a mediator of TNF-induced NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol 164:1355–1363
Koul D, Yao Y, Abbruzzese JL, Yung WK, Reddy SA (2001) Tumor suppressor MMAC/PTEN inhibits cytokine-induced NFkappaB activation without interfering with the IkappaB degradation pathway. J Biol Chem 276:11402–11408
Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:240–246
Curran T, Franza BR Jr (1988) Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell 55:395–397
Eferl R, Wagner EF (2003) AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 3:859–868
Saez E, Rutberg SE, Mueller E, Oppenheim H, Smoluk J, Yuspa SH, Spiegelman BM (1995) c-fos is required for malignant progression of skin tumors. Cell 82:721–732
Malliri AM, Symons RF, Hennigan AF, Hurlstone RF, Lamb T, Wheeler BW (1998) The transcription factor AP-1 is required for EGF-induced activation of rho-like GTPases, cytoskeletal rearrangements, motility, and in vitro invasion of A431 cells. J Cell Biol 143:1087–1099
Belguise KN, Kersual F, Galtier D (2005) FRA-1 expression level regulates proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24:1434–1444
Kustikova O, Kramerov D, Grigorian M, Berezin V, Bock E, Lukanidin E, Tulchinsky E (1998) Fra-1 induces morphological transformation and increases in vitro invasiveness and motility of epithelioid adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 18:7095–7105
Angel P, Karin M (1991) The role of Jun, Fos, the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1072:129–157
Jochum W, Passegué E, Wagner EF (2001) AP-1 in mouse development and tumorigenesis. Oncogene 20:2401–2412
Shaulian E, Karin M (2001) AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20:2390–2400
Huang C, Schmid PC, Ma WY, Schmid HH, Dong Z (1997) Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase is necessary for 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced cell transformation and activated protein 1 activation. J Biol Chem 272:4187–4194
Koul D, Jasser SA, Lu Y, Davies MA, Shen R, Shi Y, Mills GB, Yung WK (2002) Motif analysis of the tumor suppressor gene MMAC/PTEN identifies tyrosines critical for tumor suppression and lipid phosphatase activity. Oncogene 15:2357–2364
Reddy SAG, Huang JH, Liao WSL (1997) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in interleukin 1 signaling. Physical interaction with the interleukin 1 receptor and requirement in NFkappaB and AP-1 activation. J Biol Chem 272:29167–29172
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, Baldocchi R, Godfrey T, Collins C, Pinkel D, Powell B, Mills GB, Gray JW (1999) PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 21:99–102
Gopalan SM, Wilczynska KM, Konik BS, Bryan L, Kordula T (2006) Astrocyte-specific expression of the alpha1-antichymotrypsin and glial fibrillary acidic protein genes requires activator protein-1. J Biol Chem 281:1956–1963
Sizemore N, Leung S, Stark GR (1999) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to interleukin-1 leads to phosphorylation and activation of the NF-kappaB p65/RelA subunit. Mol Cell Biol 19:4798–4805
Huang C, Ma WY, Dong Z (1996) Requirement for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in epidermal growth factor-induced AP-1 transactivation and transformation in JB6 P+ cells. Mol Cell Biol 16:6427–6435
Van Leeuwen JE, Paik PK, Samelson LE (1999) Activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells-(NFAT) and activating protein 1 (AP-1) by oncogenic 70Z Cbl requires an intact phosphotyrosine binding domain but not Crk(L) or p85 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase association. J Biol Chem 274:5153–5162
Fahy BN, Schlieman M, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ (2003) AKT inhibition is associated with chemosensitisation in the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA-PaCa-2. Br J Cancer 89:391–397
Shah SA, Potter MW, Hedeshian MH, Kim RD, Chari RS, Callery MP (2001) PI-3′ kinase and NF kappaB cross-signaling in human pancreatic cancer cells. J Gastrointest Surg 5:603–612
Hu Q, Klippel A, Muslin AJ, Fantl WJ, Williams LT (1995) Ras-dependent induction of cellular responses by constitutively active phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Science 268:100–102
Barber JR, Verma IM (1987) Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol 7:2201–2211
Holt JT, Gopal TV, Moulton AD, Nienhuis AW (1986) Inducible production of c-fos antisense RNA inhibits 3T3 cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4794–4798
Piechaczyk M, Blanchard JM (1994) c-fos proto-oncogene regulation and function. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 17:93–131
Bland KI, Konstadoulakis MM, Vezeridis MP, Wanebo HJ (1995) Oncogene protein co-expression. Value of Ha-ras, c-myc, c-fos, and p53 as prognostic discriminants for breast carcinoma. Ann Surg 221:706–718
Arteaga CL, Holt JT (1996) Tissue-targeted antisense c-fos retroviral vector inhibits established breast cancer xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res 56:1098–1103
Gee JM, Ellis IO, Robertson JF, Willsher P, McClelland RA, Hewitt KN, Blamey RW, Nicholson RI (1995) Immunocytochemical localization of Fos protein in human breast cancers and its relationship to a series of prognostic markers and response to endocrine therapy. Int J Cancer 22:269–273
Preston GA, Lyon TT, Yin Y, Lang JE, Solomon G, Annab L, Srinivasan DG, Alcorta DA, Barrett JC (1996) Induction of apoptosis by c-Fos protein. Mol Cell Biol 16:211–218
Gajate C, Alonso MT, Schimmang T, Mollinedo F (1996) C-Fos is not essential for apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 21:267–272
Roffler-Tarlov S, Brown JJ, Tarlov E, Stolarov J, Chapman DL, Alexiou M, Papaioannou VE (1996) Programmed cell death in the absence of c-Fos and c-Jun. Development 122:1–9
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the University Cancer Foundation at The University of Texas M .D. Anderson Cancer Center to D.K and grant R01 CA-056041 from the National Institute of Health to W. K. A. Yung. We thank Betty P. Notzon (Department of Scientific publications, M. D. Anderson) for editorial assistance, Dr. John F. de Groot (Department of Neuro-Oncology, M. D. Anderson) for critical reading of the manuscript and Randall Evans (Department of Bone Marrow transplantation, M. D. Anderson) for his contribution to the confocal studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koul, D., Shen, R., Shishodia, S. et al. PTEN down regulates AP-1 and targets c-fos in human glioma cells Via PI3-kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 300, 77–87 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9371-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9371-8