Abstract
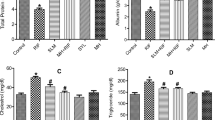
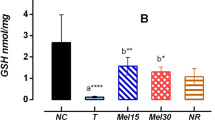
Hepatotoxicity is one of the most serious adverse effects of antituberculosis drugs. The aim of this study was to produce a rat model of isoniazid-rifampicin (INH-RIF) induced hepatotoxicity. Materials and Methods: Wistar rats (100–150 g) were treated with different doses of INH i.e. 25, 50 and 75 mg/kg/day with a fixed dose of RIF i.e. 50 mg/kg/day intragastrically for a period of 28 days. Serum glutamate oxaloacetate aminotransferase (SGOT), glutamate pyruvate aminotransferase (SGPT), bilirubin (Bil) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were estimated at 0,14, 21 and 28 days in rats. Histological analysis was carried out to assess the liver. Results: Treatment of rats with INH–RIF (50 mg/kg/day each) induced hepatotoxicity as judged by elevated serum SGPT, SGOT, Bil and ALP as compared with their base line. Histological evaluation of INH–RIF induced hepatotoxicity also showed liver damage. Conclusion: The present study suggests that 50 mg/kg/day each of INH–RIF was selected as hepatotoxic dose (i.e. minimum dose with maximum hepatotoxicity) in wistar rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahbazian B, Weis SE: Treatment of active tuberculosis: Challenges and prospects. Clin Chest Med 26: 273–282, 2005
Fernandez-Villar A, Sopena B, Fernandez-Villar J, Vazquez-Gallardo R, Ulloa F, Leiro V, Mosteiro M, Pineiro L: The influence of risk factors on the severity of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 8: 1499–1505, 2004
Hussawi Z, Kar P, Husain SA: Antituberculosis drug induced hepatitis: Risk factors, prevention and management. Indian J of Exp Biol 41: 1226–1232, 2003
Quenelle DC, Staas JK, Winchester GAA, Barrow ELW, Barrow WW: Efficacy of microencapsulated rifampicin in mycobacterium tuberculosis infected Mice. Antimicrob Agent Chemo 43: 1144–1115, 1999
Quenelle DC, Winchester GA, Staas JK, Barrlow LW: Treatment of tuberculosis using a combination of sustained released rifampicin loaded microspheres and oral dosing with isoniazid. Ant Agent and Chemo 45: 1637–1644, 2001
Skakun NP, Slivka IuI: Effectiveness of tocopherol and anti-hypoxic agents in liver damage caused by antitubercular agents. Probl Tuberk 3: 57–59, 1991
Reitman J, Franketl SA: Colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic acid and serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase. Am J Clin Path 28: 56–63, 1957
Powell WN: Serum biluribin estimation. Am J Clin Path 14: 55–57, 1944
Bergemer MKC: Method of enzymatic analysis. Academic press, New York 40: 783–785, 1963.
Brown JS, Wilson WE, Grant LD: Dosimetric comparisons of particle deposition and retention in rats and humans. Inhal Toxicol 17: 355–385, 2005
Hardistiy JF, Brix AE: Comparative hepatic toxicity: Pre chronic liver toxicity in rodents. Toxicol Pathol 33: 35–40,2005
Frank I, Lahav D, Aroch I: Myocardial necrosis and severe metabolic acidosis associated with isoniazid poisoning in dog. Vet Reco 151: 638–639, 2002
Attri S, Rana SV, Vaiphei K, Sodi CP, Katyal R, Goel RC, Nain CK, Singh K: Isoniazid—rifampicin induced oxidative hepatic injury protection by N—acetylcysteine. Human & Exp Toxico 19: 517–522, 2000
Kasilo OJ, Nihach CFB, Nahlet M: Isoniazid—International programme on chemical toxicity. Poisons information monograph . Pharmaceutical: 288–291, 1999
Cro HJ, Mood BM, Magarey J: Rifampicin IARC Summary and Evaluation: 24–26, 1980
Rifandin (Hoechst Marian Roussel) In: PDR Phsycian desk reference. 54th ed 2000 oradell. N J Medical Economics Data: 1379–1382, 2000
Ellenhorn MJ, BarCeloux DG: Antiinfective drugs. Medical Toxicology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Human poisioning. Amsterdam Elsevier: 29, 1988
Mandel GL, Sande MA: Antimicrobial agents. Goodman and Gillman. The pharmacologic basis of therapeutics. 7th ed. Macmillian Publish Co: 61–64, 1985
Mitchell JR, Zimmerman HJ, Ishak KG: Thorgierson, U.P. Isoniazid liver injury: Clinical spectrum pathology and probable pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med 84: 181–192, 1976
Karthikryan S: Hepatotoxicity of isoniazid: A study in the activity of marker enzymes of liver toxicity in serum and liver of rabbits. Ind J Pharmaco 36:247–249, 1995
Snodgross W, Potter W, Timbrell JA, Jollow DI: Possible mechanism of isoniazid related hepatic injury. Clin Res 22: 323–326, 1974
Heiserg GB, Hughes WC, Long CM: Rozmaiorkherh. The guinea pigs as model for isoniazid induced reactions. LabAnimal Sci 30: 42–50, 1980
Tasduq SA, Kaiser P, Gupta PK, Kapahi BK: Protective effect of 50% hydroalcoholic fruit extract of Emblica officinalis against antituberculosis drugs induced liver toxicity. Phytother Res 19: 193–197, 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, S.V., Pal, R., Vaiphie, K. et al. Effect of Different Oral Doses of Isoniazid-Rifampicin in Rats. Mol Cell Biochem 289, 39–47 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9145-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9145-3