Abstract
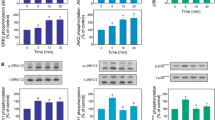
Activation of PKC signaling induces Mg2+ accumulation in liver cells. To test the hypothesis that PKC induces Mg2+ accumulation via MAPKs activation, hepatocytes were incubated in the presence of PD98059 and SB202190 as specific inhibitors of ERK1/2 and p38, respectively, and stimulated for Mg2+ accumulation by addition of PMA or OAG. Accumulation of Mg2+ within the cells was measured by atomic absorbance spectrophotometry in the acid extract of cell pellet. The presence of either inhibitor completely abolished Mg2+ accumulation irrespective of the dose of agonist utilized while having no discernible effect on β -adrenoceptor mediated Mg2+ extrusion. A partial inhibition on α 1-adrenoceptor mediated Mg2+ extrusion was observed only in cells treated with PD98059. To confirm the inhibitory effect of PD98509 and SB202190, total and basolateral liver plasma membrane vesicles were purified in the presence of either MAPK inhibitor during the isolation procedure. Consistent with the data obtained in intact cells, liver plasma membrane vesicles purified in the presence of PD98509 or SB202190 lost the ability to accumulate Mg2+in exchange for intra-vesicular entrapped Na+ while retaining the ability to extrude entrapped Mg2+ in exchange for extra-vesicular Na+. These data indicate that ERK1/2 and p38 are involved in mediating Mg2+ accumulation in liver cells following activation of PKC signaling. The absence of a detectable effect of either inhibitor on β -adrenoceptor induced, Na+-dependent Mg2+ extrusion in intact cells and in purified plasma membrane vesicles further support the hypothesis that Mg2+ extrusion and accumulation occur through distinct and differently regulated transport mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romani A, Scarpa A: Regulation of cellular magnesium. Arch Biochem Biophys 298: 1–12, 1992
Romani A, Scarpa A: Regulation of cellular magnesium. Front Biosci 5: D720–D734, 2000
Scarpa A, Brinley FJ: In situ measurements of free cytosolic magnesium ions. Fed Proc 40: 2646–2652, 1981
Wolf FI, Torsello A, Fasanella S, Cittadini A: Cell physiology of magnesium. Mol Aspects Med 24: 11–26, 2003
Keenan D, Romani A, Scarpa A: Differrential regulationof circulating Mg2+ in the rat by β1 and β2-adrenergic receptor stimulation. Circ Res 77: 973–983, 1995
Gunther T, Vormann J: Mg2+ efflux is accomplished by an amiloride-sensitive Na+/Mg2+ antiport. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 119: 124–131, 1984
Romani A, Marfella C, Scarpa A: Hormonal stimulation of Mg2+ uptake in hepatocytes. Regulation by plasma membrane and intracellular organelles. J Biol Chem 268: 15489–15495, 1993
Cefaratti C, Romani A, Scarpa A: Characterization of two Mg2+ transporters in sealed plasma membrane vesicles from rat liver. Am J Physiol 275: C995–C1008, 1998
Cefaratti C, Romani A, Scarpa A: Differential localization and operation of distinct Mg2+ transporters in apical and basolateral sides of rat liver plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 275: 3772–3780, 2000
Flatman PW: Mechanisms of magnesium trnapsort. Annu Rev Physiol 53: 259–271, 1991
Romani A, Scarpa A: Hormonal control of Mg2+ in the heart. Nature 346: 841–844, 1990
Fagan TE, Cefaratti C, Romani A: Streptozotocin-induced diabetes impairs Mg2+ homeostasis and uptake in rat liver cells. Am J Physiol 286: E184–E193, 2003
Fatholahi M, LaNoue K, Romani A, Scarpa A: Relationship between total and free cellular Mg2+ during metabolic stimulation of rat cardiac myocytes and perfused hearts. Arch Biochem Biophys 374: 395–401, 2000
Romani A, MArfella C, Scarpa A: Regulation of Mg2+ uptake in isolated rat myocytes and hepatocytes by protein kinase C. FEBS Lett 296:135–140, 1992
Quamme GA, Rabkin SW: Cytosolic free magnesium in cardiac myocytes: Identification of a Mg2+ influx pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 167: 1406–1412, 1990
Quamme GA, Dai L-S: Presence of a novel influx pathway for Mg2+ in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol 259: C521–C525, 1990
Yang Z-W, Wang J, Zheng T, Altura BT, Altura BM: Low [Mg2+]o induces contraction of cerebral arteries: role of tyrosine and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Am J Physiol 279: H185–H194, 2000
Yang Z-W, Wang J, Altura BT, Altura BM: Extracellular magnesium deficiency induces contractin of arterial muscle: role of PI3-kinase and MAPK signaling pathways. Eur J Physiol 439: 240–247, 2000
Touyz RM, Yao G: Modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by magnesium – Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Cell Physiol 197: 326–335, 2003
Touyz RM, Yao G: Up-regulation of vascular and renal mitogen-activated protein kinases in hypertensive rats is normalized by inhibitors of Na+/Mg2+ exchanger. Clin Sci 105: 235–242, 2003
Seglen PO: Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol 13: 29–83, 1976
Romani A, Marfella C, Scarpa A: Regulation of magnesium uptake and release in the heart and in isolated ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 72: 1139–1148, 1993
Fagan TE, Romani A: Activation of Na+- and Ca2+-dependent Mg2+ extrusion by alpha1- and beta-adrenergic agonists in rat liver cells. Am J Physiol 279: G943–G950, 2000
Fagan TE, Romani A: Alpha1-adrenoceptor-induced Mg2+ extrusion from rat hepatocytes occurs via Na+-dependent transport mechanism. Am J Physiol 280: G1145–G1156, 2001
Romani A, Mathews V: Scarpa A, Parallel stimulation of glucose and Mg2+ accumulation by insulin in rat hearts and cardiac ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 86: 326–333, 2000
Ishijima S, Sonoda T: Tatibana M, Mitogen-induced early increase in cytosolic free Mg2+ concentration in single swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Am J Physiol 261: C1074-C1080, 1991
Voels T, Nillieus B, Hoefs S, van der Kemp AW, Droogmans G, Bindels RJ: Hoenderop JG. TRPM6 forms the Mg2+ influx channel involved in intestinal and renal Mg2+ absorption. J Biol Chem 279: 19–25, 2004
Nadler MJ, Hermosura MC, Inabe K, Perraud AL, Zhu Q, Stokes AJ, Kurosaki T, Pinet JO, Penner R, Scharenberg AM, Fleig A: LTRPC7 is a Mg. ATP regulated divalent cation channel required for cell viability. Nature 411: 509–595, 2001
Owsianik G, Talavera K, Voets T, Nilius Bernd: Permeation and selectivity of TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol 68: 4.1–4.33, 2006
Wabbaken T, Rian E, Kveinie M, Aaseim H-C: The human solute carrier SLC41A1 belongs to a novel eukaryotic subfamily with homology to prokaryotic MgtE Mg2+ transporters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306: 718–724, 2003
Goytain A, Quamme GA: Functional characterization of the human solute carrier, SLC41A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330: 701–705, 2005
Goytain A, Quamme GA: Identification and characterization of a novel mammalian Mg2+ transporter with channel-like properties. BMC Genomics 6: 48, 2005
Goytain A, Quamme GA: Functional characterization of ACDP2 (ancient conserved domain protein), a divalent metal transporter. Physiol Genomics 22: 382–389, 2005
Wen-Sheng W, Jun-Ming H: Activation of protein kinase C alpha is required for TPA-triggered ERK (MAPK) signaling and growth inhibition of human hepatoma cell HepG2. J Biomed Sci. 12: 289–296.33, 2005
Ohashi K, Kanazawa A, Tsakada S, Maeda S, PKCepsilon induces interleukin−6 expression through the MAPK pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327: 707–712, 2005
Ryer EJ, Sakakibara K, Wang C, Sarkar D, Fisher PB, Faries PL, Kent KC, Liu B: Protein kinase C delta induces apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells through induction of the tumor suppressor p53 by both p38-dependent and p38-independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 280: 35310–35317, 2005
Waas WF, Dalby KN: Physiological concentrations of divalent magnesium ion activate the Serine/Threonine specific protein kinase ERK2. Biochemistry 42: 2960–2970, 2003
Kim SJ, Kang HS, Kang MS, Yu X, Park SY, Kim IS, Kim NS, Kim SZ, Kwak YG, Kim JS: alpha1-Agonists-induced Mg2+ efflux is related to MAP kinase activation in the heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333: 1132–1138, 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, L.M., Cefaratti, C., Perry, B. et al. Involvement of ERK1/2 and p38 in Mg2+ accumulation in liver cells. Mol Cell Biochem 288, 191–199 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9139-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9139-1