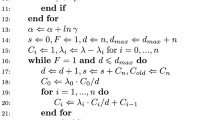Abstract
Many objects studied in biology, medicine or material sciences create spatial formations of random shape in which we can observe mutual interactions among those objects. In order to analyse the data composed of such patterns, we use the methods of spatial statistics. Recently, extended random-disc Quermass-interaction process was studied, simulated and consequently statistically analysed using MCMC maximum likelihood method (MCMC MLE). However, this analysis brought some problems. First, it was quite time-consuming, secondly, in some special cases, the parameter estimates may undervalue the real parameter values. In this paper, we describe how we can solve these problems by dimension reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daley DJ, Vere-Jones D (2003, 2008) An introduction to the theory of point processes, 2nd edn, vol I, II. Springer, New York
Dereudre D (2009) Existence of Quermass processes for non locally stable interaction and non bounded convex grains. Adv Appl Prob 41:664–681
Dereudre D, Lavancier F, Staňková Helisová K (2013) Estimation of all the parameters of Quermass model via a Takacs-Fiksel approach. Scand J Statist (submitted). ArXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1207.5998
Diggle P (1981) Binary mosaics and the spatial pattern of heather. Biometrics 37:531–539
Kendall WS, van Lieshout MNM, Baddeley AJ (1999) Quermass–interaction processes: conditions for stability. Adv Appl Prob 31:315–342
Li K-C (1991) Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction. J Am Stat Assoc 86:316–327
Møller J, Waagepetersen R (2004) Statistical inference and simulations for spatial point processes. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Møller J, Helisová K (2008) Power diagrams and interaction process for unions of discs. Adv Appl Prob 40:321–347
Møller J, Helisová K (2010) Likelihood inference for unions of interacting discs. Scand J Statist 37:365–381
Mrkvička T, Mattfeldt T (2011) Testing histological images of mammary tissues on compatibility with the Boolean model of random sets. Image Anal Stereol 30:11–18
Mrkvička T, Rataj J (2008) On estimation of intrinsic volume densities of stationary random closed sets. Stoch Process Appl 118:213–231
Rencher AC (2002) Methods of multivariate analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley & Sons, New York
Stoyan D, Kendall WS, Mecke J (1995) Stochastic geometry and its applications. Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Šedivý O, Staněk J, Kratochvílová B, Beneš V (2013) Sliced inverse regression and independence in random marked sets with covariates. Adv Appl Prob 45 (to appear)
Zikmundová M, Staňková Helisová K, Beneš V (2012) Spatio-temporal model for a random set given by a union of interacting discs. Methods Comp Appl Prob 14:883–894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staňková Helisová, K., Staněk, J. Dimension Reduction in Extended Quermass-Interaction Process. Methodol Comput Appl Probab 16, 355–368 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-013-9343-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-013-9343-x