Abstract
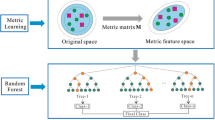
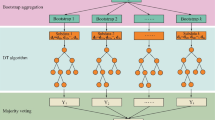
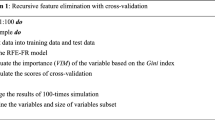
The identification of multivariate geochemical anomalies is critical in mineral exploration. Machine learning algorithms have been successfully employed in the recognition of multivariate geochemical anomalies in support of mineral exploration, owing to their strong ability to learn the complex relationship between geochemical characteristics and mineralization. However, applications of machine learning algorithms suffer from data redundancy and the curse of dimensionality. In this study, a hybrid model combining t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) and random forest (RF) was used to solve the aforementioned problems in geochemical mapping for gold exploration in the northwestern Hubei Province of China. Specifically, t-SNE was used for dimension reduction and feature extraction from the major and trace elements of geochemical survey data, and RF was used for probabilistic classification of geochemical patterns related to gold deposits. A comparative study demonstrated that the hybrid model of t-SNE + RF possesses stronger generalization ability than that of PCA + RF and pure RF. Specifically, after 15 experiments, the mean area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC) values of t-SNE + RF, PCA + RF, and pure RF were 0.83, 0.65, and 0.75, respectively. These results suggest that the hybrid model combining t-SNE and RF can more efficiently recognize geochemical anomalies associated with gold mineralization. Compared with PCA, t-SNE can more effectively identify hidden information in complex and nonlinear geochemical survey data. In addition, it can reduce information redundancy and further improve the efficiency of RF for processing multidimensional geochemical survey data. The high-probability areas obtained by t-SNE + RF showed a strong spatial correlation with known gold deposits, which can provide critical clues for further prospecting in the study area.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agterberg FP (2001) Multifractal simulation of geochemical map patterns. In: Merriam DF, Davis JC (eds) Geologic modeling and simulation, pp 327–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1359-9_17
Aitchison J (1982) The statistical analysis of compositional data. J Roy Stat Soc Ser B (methodol) 44:139–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1982.tb01195.x
Aitchison J (1986) The statistical analysis of compositional data. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-4109-0
Balamurali M (2022) T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding. In: Daya Sagar B, Cheng Q, McKinley J, Agterberg F (eds) Encyclopedia of mathematical geosciences. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series, pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26050-7_446-1
Balamurali M, Melkumyan A (2016) t-SNE based visualisation and clustering of geological domain. In: Hirose A, Ozawa S, Doya K, Ikeda K, Lee M, Liu D (eds) Neural information processing, pp 565–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46681-1_67
Balamurali M, Silversides KL, Melkumyan A (2019) A comparison of t-SNE, SOM and SPADE for identifying material type domains in geological data. Comput Geosci 125:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2019.01.011
Bengio Y, LeCun Y (2007) Scaling learning algorithms towards AI. Large-Scale Kernel Mach 34:1–41. https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/7496.003.0016
Berends HI, Wolkorte R, Ijzerman MJ, Van Putten MJAM (2013) Differential cortical activation during observation and observation-and-imagination. Exp Brain Res 229:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3571-8
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Carranza EJM, Hale M, Faassen C (2008) Selection of coherent deposit-type locations and their application in data driven mineral prospectivity mapping. Ore Geol Rev 33:536–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.07.001
Carranza EJM (2009) Geochemical anomaly and mineral prospectivity mapping in GIS. In: Handbook of exploration and environmental geochemistry, vol 11. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-6275(08)x0001-7
Carranza EJM (2011) Analysis and mapping of geochemical anomalies using logratio-transformed stream sediment data with censored values. J Geochem Explor 110:167–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.05.007
Cevik IS, Olivo GR, Ortiz JM (2021) A combined multivariate approach analyzing geochemical data for knowledge discovery: The Vazante—Paracatu Zinc District, Minas Gerais. Brazil J Geochem Explor 221:106696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106696
Chen Y (1996) Fluidization model for intracontinental collision and its metallogenic significance: theoretical inference and evidences from gold deposits, the eastern Qinling mountains. Earth Sci Front 3:123–130 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Chen Y (1998) Fluidization model for continental collision in special reference to study ore-forming fluid of gold deposits in the eastern Qinling Mountains, China. Prog Nat Sci 8:385–393
Chen Y (2010) Indosinian tectonic setting, magmatism and metallogenesis in Qinling Orogen, central China. Geol China 37:854–865. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.003 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Chen K, Zhu Y (2007) A summary of machine learning and related algorithms. Stat Inf Forum 22:105–112. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2007.05.021 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Chen Y, Santosh M (2014) Triassic tectonics and mineral systems in the Qinling Orogen, central China. Geol J 49:338–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.2618
Chen Y, Wu W (2017) Application of one-class support vector machine to quickly identify multivariate anomalies from geochemical exploration data. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 17:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2016-024
Chen Y, Lu L, Li X (2014) Application of continuous restricted Boltzmann machine to identify multivariate geochemical anomaly. J Geochem Explor 140:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.02.013
Cheng Q (1999) Spatial and scaling modelling for geochemical anomaly separation. J Geochem Explor 65:175–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(99)00028-X
Cheng Q (2007) Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, China. Ore Geol Rev 32:314–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.10.002
Cheng Q (2012) Singularity theory and methods for mapping geochemical anomalies caused by buried sources and for predicting undiscovered mineral deposits in covered areas. J Geochem Explor 122:55–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.07.007
Cheng Q, Agterberg FP, Ballantyne SB (1994) The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods. J Geochem Explor 51:109–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2
Cheng Q, Xu Y, Grunsky E (2000) Integrated spatial and spectrum method for geochemical anomaly separation. Nat Resour Res 9:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010109829861
Cohen DR, Kelley DL, Anand R, Coker WB (2010) Major advances in exploration geochemistry, 1998–2007. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 10:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1144/1467-7873/09-215
Dong S, Huang Z (2013) A brief theoretical overview of random forests. J Integr Technol 2:1–7 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Dong Y, Santosh M (2016) Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Res 29:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009
Erfani SM, Rajasegarar S, Karunasekera S, Leckie C (2016) High-dimensional and large-scale anomaly detection using a linear one-class SVM with deep learning. Pattern Recogn 58:121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.03.028
Fabrigar LR, Wegener DT (2011) Exploratory factor analysis. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199734177.001.0001
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn Lett 27:861–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Filzmoser P, Garrett RG, Reimann C (2005) Multivariate outlier detection in exploration geochemistry. Comput Geosci 31:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2004.11.013
Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C (2009a) Principal component analysis for compositional data with outliers. Environmetrics 20:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1002/env.966
Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C (2009b) Univariate statistical analysis of environmental (compositional) data: problems and possibilities. Sci Total Environ 407:6100–6108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.008
Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C (2010) The bivariate statistical analysis of environmental (compositional) data. Sci Total Environ 408:4230–4238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.05.011
Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C (2012) Interpretation of multivariate outliers for compositional data. Comput Geosci 39:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.06.014
Fu J, Zhang Y, Cai J (2004) Characteristics of main ore-host strata and their metallogenic elements in Wudang-yunxi and Yunxian region. Geol Sci Technol Inf 23:51–56 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Ghosh D, Cabrera J (2021) Enriched random forest for high dimensional genomic data. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2021.3089417
Gonbadi AM, Tabatabaei SH, Carranza EJM (2015) Supervised geochemical anomaly detection by pattern recognition. J Geochem Explor 157:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.06.001
Goovaerts P (1997) Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756898631502
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Gebre-Mariam M, Hagemann SG, Robert F (1998) Orogenic gold deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geol Rev 13:7–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
Grunsky EC (2010) The interpretation of geochemical survey data. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 10:27–74. https://doi.org/10.1144/1467-7873/09-210
Grunsky EC, Arne D (2021) Mineral-resource prediction using advanced data analytics and machine learning of the QUEST-South stream-sediment geochemical data, southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 21:2020–2054. https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2020-054
Harris RJ (2001) A primer of multivariate statistics. Psychology Press. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410600455
Hawkes HE, Webb JS (1962) Geochemistry in mineral exploration. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-196304000-00016
Jindal P, Kumar D (2017) A review on dimensionality reduction techniques. Int J Comput Appl 173:42–46. https://doi.org/10.5120/ijca2017915260
Khalid S, Khalil T, Nasreen S (2014) A survey of feature selection and feature extraction techniques in machine learning. In: 2014 Science and information conference, pp 372–378. https://doi.org/10.1109/SAI.2014.6918213
Kürzl H (1988) Exploratory data analysis: recent advances for the interpretation of geochemical data. J Geochem Explor 30:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(88)90066-0
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Lei S, Tang G, Zhang Z (1998) Characteristics of structurally controlling mineralization in the Yingdonggou silvergold deposit, Zhushan, northwest Hubei. Geoscience 12:81–86 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Li J, Zhang Y, Luo Y (2003) Geological-geochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of Xujiapo gold-silver deposit in northwest Hubei province. Geolo Sci Technol Inf 22:75–79. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.04.014 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Li N, Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhao T, Deng X, Wang Y, Ni Z (2007) Molybdenum deposits in East Qinling. Earth Sci Front 14:186–198. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.019 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Li W, Zhou W, Chen S, Li Y, Deng X, Zhong R (2010) Geological characteristics of the Yindonggou silver deposit in Hubei Province and its implication for ore genesis. Earth Sci Front 17:177–185 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Li J, Zhang X, Li Y (2011) Geological characteristics and prospecting prognosis of Santianmen gold deposit in Yunxi County, Hubei Province. Resour Environ Eng 25:22–28. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2011.01.005 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Ling W, Ren B, Duan R, Liu X, Mao X, Peng L, Liu Z, Cheng J, Yang H (2007) Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geological significance of the Wudang group, Yaolinghe group and mafic intrusive rocks in the Southern Qinling. Chin Sci Bull 52:1445–1456. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.12.015 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Luo Z, Xiong Y, Zuo R (2020) Recognition of geochemical anomalies using a deep variational autoencoder network. Appl Geochem 122:104710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104710
Luo Z, Zuo R, Xiong Y, Wang X (2021) Detection of geochemical anomalies related to mineralization using the GANomaly network. Appl Geochem 131:105043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105043
Luo Z, Zuo R, Xiong Y (2022) Visual interpretable deep learning algorithm for geochemical anomaly recognition. Nat Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-022-10080-5
Mao JW, Pirajno F, Xiang JF, Gao JJ, Ye HS, Li YF, Guo BJ (2011) Mesozoic molybdenum deposits in the east Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt: characteristics and tectonic settings. Ore Geol Rev 43:264–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.07.009
Moeini H, Torab FM (2017) Comparing compositional multivariate outliers with autoencoder networks in anomaly detection at Hamich exploration area, east of Iran. J Geochem Explor 180:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.05.008
Nykänen V, Lahti I, Niiranen T, Korhonen K (2015) Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) as validation tool for prospectivity models - A magmatic Ni–Cu case study from the Central Lapland Greenstone Belt, Northern Finland. Ore Geol Rev 71:853–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.007
Reichstein M, Camps-Valls G, Stevens B, Jung M, Denzler J, Carvalhais N (2019) Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 566:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett RG, Dutter R (2008) Statistical data analysis explained. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470987605
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Fabian K, Hron K, Birke M, Demetriades A, Dinelli E, Ladenberger A (2012) The concept of compositional data analysis in practice—total major element concentrations in agricultural and grazing land soils of Europe. Sci Total Environ 426:196–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.032
Rencher AC (2002) Methods of multivariate analysis, 2nd edn. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471271357
Sinclair AJ (1974) Selection of threshold values in geochemical data using probability graphs. J Geochem Explor 3:129–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(74)90030-2
Soni J, Prabakar N, Upadhyay H (2020) Visualizing high-dimensional data using t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding algorithm. In: Arabnia HR, Daimi K, Stahlbock R, Soviany C, Heilig L, Brüssau K (eds) Principles of data science, pp 189–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-43981-1_9
Tukey JW (1977) Exploratory data. Analysis. https://doi.org/10.2307/2286300
van der Maaten L, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9:2579–2605
van der Maaten L, Postma E, van den Herik H (2009) Dimensionality reduction: a comparative review. J Mach Learn Res 10:66–71
Wang J, Zuo R (2020) Assessing geochemical anomalies using geographically weighted lasso. Appl Geochem 119:104668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104668
Wang X, Xie X, Zhang B, Hou Q (2011) Geochemical Probe into China’s continental crust. Acta Geosci Sin 32:65–83. https://doi.org/10.3975/cagsb.2011.s1.05
Wang Z, Dong Y, Zuo R (2019a) Mapping geochemical anomalies related to Fe–polymetallic mineralization using the maximum margin metric learning method. Ore Geol Rev 107:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.027
Wang Z, Zuo R, Dong Y (2019b) Mapping geochemical anomalies through integrating random forest and metric learning methods. Nat Resour Res 28:1285–1298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09471-y
Wu W, Chen Y (2018) Application of isolation forest to extract multivariate anomalies from geochemical exploration data. Glob Geol 21:36–47. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-9736.2018.01.04
Xie X, Mu X, Ren T (1997) Geochemical mapping in China. J Geochem Explor 60:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(97)00029-0
Xie X, Wang X, Zhang Q, Zhou G, Cheng H, Liu D, Cheng Z, Xu S (2008) Multi-scale geochemical mapping in China. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 8:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1144/1467-7873/08-184
Xiong Y, Zuo R (2016) Recognition of geochemical anomalies using a deep autoencoder network. Comput Geosci 86:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.10.006
Xiong Y, Zuo R (2020) Recognizing multivariate geochemical anomalies for mineral exploration by combining deep learning and one-class support vector machine. Comput Geosci 140:104484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104484
Xiong Y, Zuo R (2021) Robust feature extraction for geochemical anomaly recognition using a stacked convolutional denoising autoencoder. Math Geosci 54:623–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-021-09935-z
Xiong Y, Zuo R, Luo Z, Wang X (2021) A physically constrained variational autoencoder for geochemical pattern recognition. Math Geosci 54:783–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-021-09979-1
Xu B, Huang JZ, Williams G, Wang Q, Ye Y (2012a) Classifying very high-dimensional data with random forests built from small subspaces. Int J Data Warehouse Min 8:44–63. https://doi.org/10.4018/jdwm.2012040103
Xu T, Ma C, Lv X, Liu X (2012b) Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of Shejiayuan Silver gold deposits in Yunxi County Hubei Province. Resour Environ Eng 26:104–110. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2012.02.003 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Yin B, Zuo R, Xiong Y, Li Y, Yang W (2021) Knowledge discovery of geochemical patterns from a data-driven perspective. J Geochem Explor 231:106872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2021.106872
Yu X, Xiao F, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang K (2019) Application of hierarchical clustering, singularity mapping, and Kohonen neural network to identify Ag–Au–Pb–Zn polymetallic mineralization associated geochemical anomaly in Pangxidong district. J Geochem Explor 203:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.04.007
Yue S, Deng X (2019) Geological and ore-forming characteristics of Ag–Au and polymetallic deposits in northwestern Hubei, China. Earth Sci Front 26:106–128 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Yue S, Zhai Y, Deng X, Yu J, Yang L (2013) Fluid inclusion and H-O isotope geochemistry and ore genesis of the Yindonggou deposit, Zhushan County, Hubei, China. Acta Petrol Sin 29:27–45 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang S, Xiao K, Carranza EJM, Yang F, Zhao Z (2019) Integration of auto-encoder network with density-based spatial clustering for geochemical anomaly detection for mineral exploration. Comput Geosci 130:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2019.05.011
Zhu F, Li W, Hu C (2017) Mineragraphy and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of Yindonggou Ag-Au deposit, south Qinling mountains, China. Acta Mineral Sin 37:386–394 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Ziaii M, Pouyan AA, Ziaei M (2009) Neuro-fuzzy modelling in mining geochemistry: Identification of geochemical anomalies. J Geochem Explor 100:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.03.004
Ziaii M, Doulati Ardejani F, Ziaei M, Soleymani AA (2012) Neuro-fuzzy modeling based genetic algorithms for identification of geochemical anomalies in mining geochemistry. Appl Geochem 27:663–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.12.020
Zuo R (2011) Identifying geochemical anomalies associated with Cu and Pb–Zn skarn mineralization using principal component analysis and spectrum–area fractal modeling in the Gangdese Belt, Tibet (China). J Geochem Explor 111:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.06.012
Zuo R (2018) Selection of an elemental association related to mineralization using spatial analysis. J Geochem Explor 184:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.10.020
Zuo R, Carranza EJM (2011) Support vector machine: a tool for mapping mineral prospectivity. Comput Geosci 37:1967–1975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2010.09.014
Zuo R, Wang J (2016) Fractal/multifractal modeling of geochemical data: a review. J Geochem Explor 164:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.04.010
Zuo R, Xiong Y (2018) Big data analytics of identifying geochemical anomalies supported by machine learning methods. Nat Resour Res 27:5–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-017-9357-0
Zuo R, Wang Z (2020) Effects of random negative training samples on mineral prospectivity mapping. Nat Resour Res 29:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09668-6
Zuo R, Xiong Y (2020) Geodata science and geochemical mapping. J Geochem Explor 209:106431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106431
Zuo R, Xia Q, Zhang D (2013a) A comparison study of the C–A and S–A models with singularity analysis to identify geochemical anomalies in covered areas. Appl Geochem 33:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.02.009
Zuo R, Xia Q, Wang H (2013b) Compositional data analysis in the study of integrated geochemical anomalies associated with mineralization. Appl Geochem 28:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.10.031
Zuo R, Carranza EJM, Wang J (2016) Spatial analysis and visualization of exploration geochemical data. Earth Sci Rev 158:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.04.006
Zuo R, Wang J, Xiong Y, Wang Z (2021a) The processing methods of geochemical exploration data: past, present, and future. Appl Geochem 132:105072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105072
Zuo R, Wang J, Yin B (2021b) Visualization and interpretation of geochemical exploration data using GIS and machine learning methods. Appl Geochem 134:105111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105111
Zuo R, Xiong Y, Wang J, Carranza EJM (2019) Deep learning and its application in geochemical mapping. Earth Sci Rev 192:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.02.023
Acknowledgements
We are grateful Dr. Guoxiong Chen (guest editor) and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions which improved this study. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42172326 and 41972303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Zuo, R., Xiong, Y. et al. Revealing Geochemical Patterns Associated with Mineralization Using t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding and Random Forest. Math Geosci 55, 321–344 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-022-10024-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-022-10024-y