Abstract
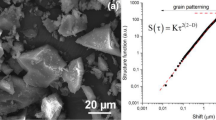
Mylonite is the result of the dynamic metamorphism and minerals in mylonite are deformed gradually with an increase in the degree of metamorphism. Quantifying the degree of deformation including the irregularities of shapes and the frequency distribution of the minerals becomes one of the most challenging efforts in mylonite analysis. Fractal modelling has been demonstrated in this paper to be an effective mean to achieve the above goal. Perimeter-Area fractal model was used to quantify the irregularities in the geometries and Cumulative Number-Area model is used to characterize the irregularities of distribution of quartzs in mylonites, respectively. Examples of quartz from five types of mylonites with different degree of deformation within the foreland of the Moine Thrust Zone in NW Scotland are chosen to study the evolution processes of deformation. As the main mineral component of quartzite mylonite, patterns are extracted from digital photomicrographics of the multiscale-grey image grid data to show quartz grains with different degree of deformation, The areas and perimeters of the quartz grains were calculated by GIS-based image processing technologies. From type one to type five, with an increase in degree of deformation, the corresponding Perimeter-Area exponent \({D_{\rm AP}}\) increases from 1.20, 1.28, 1.38, 1.46, to 1.60, respectively, the fractal dimension \({D_{\rm P}}\) of the perimeter from 1.07, 1.08, 1.17, 1.23, to 1.44, as well as the exponent of Cumulative Number- Area from 0.50, 0.51, 0.58, 0.82, to 0.85, respectively. The result has shown that as increase of the intensity of deformation, the shape of quartz grains tends to be more irregular, grain size tends to be smaller, and the number of grains increases. The results obtained using GSI model has indicated that as an increase in the intensity of deformation, the patterns of quartz grains tends to be more stratified and randomness increases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, Q., 1994, Multifractal modeling and spatial analysis with GIS: Gold potential estimation in the Mitchell-Sulphurets area, northwestern British Columbia: Unpublisted doctoral dissertation, The University of Ottawa, 268 p.
Cheng, Q., 1995, The perimeter-area fractal model and its application to geology: Math. Geol., v. 27, no. 1, p. 69–82.
Cheng, Q., Russell, H., Sharpe, D., Kenny, F., and Qin, Q., 2001, GIS-based statistical and fractal/multifractal analysis of surface stream patterns in the Oak Ridges Moraine: Comput. & Geosci., v. 27, no. 5, p. 513–526.
Elliott, D., 1976, The motion of thrust sheets: Jour. Geophys. Res., v. 81, p. 949–963.
Elliott, D., and Johnson, M. R. W., 1980, The structural evolution of the northern part of the Moine thrust zone: Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh Earth Sci., v. 71, p. 69–96.
ESRI, 2004, Using ArcGIS Spatial Analysis. ESRI, New York, p 63.
Goodchild, M. F., 1988, Lake on fractal surfaces: A null hypothesis for lake-rich landscapes: Math. Geol., v. 20, no. 6, p. 615–630.
Gulbin, Y. L., and Evangulova, E. B., 2003, Morphometry of quartz aggregates in granites: Fractal images reference to nucleation and growth processes: Math. Geol., v. 35, no. 7. p. 819–833.
Law, R. D., Casey, M., and Knipe, R. J., 1986, Kinemetic and tectonic significance of microstructures and crystallographic fabrics within quartz mylonites from the Assynt and Eriboll regions of the Moine Thrust zone, NW Scotland. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sci., v. 77, p. 99–125.
Law, R. D., and Potts, G. J., 1987, The Tarskavaig Nappe of Skye, northwest Scotland: A re-examination of the fabrics and their kinematic significance: Geol. Mag., v. 124, p. 231–248.
Lovejoy, S., 1982, Area-perimeter relation for rain and cloud areas: Science, v. 216, no. 4542, p. 185–187.
Lovejoy, S., and Schertzer, D., 1991, Multifractal analysis techniques and the rain and cloud fields from 10–3 to 106 m, in Schertzer, D., and Lovejoy, S., eds., Nonlinear Variability in Geophysics: Kluwer., Dordrecht, 318 pp.
Mandelbrot, B. B., 1977, Fractals: form, chance, and dimension: Freeman, San Francisco, 365 p.
Mandelbrot, B. B., 1983, The fractal geometry of nature (updated and augmented edition): Freeman, New York, 468 p.
Mandelbrot, B. B., Passoja, D. E., and Paullay, A. J., 1984, Fractal character of fracture surfaces of metals: Nature, v. 308, no. 5961, p. 721–722.
Weathers, M. S., Bird, J. M., Cooper, R. F., and Kohlstedt, D. C., 1979, Differential stress determined from deformation induced microstructures of the Moine thrust zone: Jour. Geophys. Res., v. 84, p. 7459–7509.
Zhang, Z., Mao, H., and Cheng, Q., 2001, Fractal geometry of element distribution on mineral surface: Math. Geol., v. 33, no. 2, p. 217–228.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Cheng, Q., Cao, L. et al. Fractal Modelling of the Microstructure Property of Quartz Mylonite During Deformation Process. Math Geol 39, 53–68 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-006-9065-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-006-9065-5