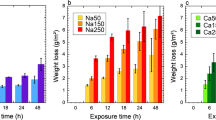
On the example of model solutions (simulators), we study the corrosiveness of hypochlorite-containing waste waters prior to and after their interaction with organic waste waters. It is established that, for low concentrations of hypochlorite, it has a higher corrosiveness than tap water. As a result of the addition of simulators of organic waste waters to hypochlorite-containing waters, their corrosiveness decreases to the level of tap water, most likely due to the neutralization of hypochlorite and the formation of the products of oxidation of organic substances with adsorption properties. For strengthening the interaction of hypochlorite with organic compounds and rapid reduction of the corrosiveness of hypochlorite wastes, it is reasonable to intensify the reactions of oxidation by using catalysts and ultrasonic treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. O. Znak and N. M. Hnatyshyn, “Energy-saving technology of the purification of waste waters at the ‘Karpatnaftokhim’ OJSC,” in: Proc. of the 3rd Scientific and Practical Conference [in Ukrainian], ONAKhT, Odessa (2012).
A. I. Malakhov, K. M. Tyutina, and T. E. Tsupak, Corrosion and the Fundamental of Electroplating [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1987).
N. M. Hnatyshyn, Z. O. Znak, V. M. Sribnyi, and O. I. Zin’, “Investigation of the process of oxidation of organic compounds in waste waters of the olefin plant at the ‘Karpatnaftokhim’ OJSZC,” in: 13th Internat. Scientific and Practical Conf. “Natural-Water Resources of the Carpathian Region” [in Ukrainian], Lviv (2014), pp. 58–60.
G. W. Walter, “A review of impedance plot methods used for corrosion performance analysis of painted metals,” Cor. Sci., 26, No. 9, 681–703 (1986).
S. S. Vinogradova, I. O. Iskhakova, R. A. Kaidrikov, and B. L. Zhuravlev, Method of Impedance Spectroscopy in Corrosion Investigations: A Manual [in Russian], Kazan Nats. Issled. Tekh. Univ., Kazan (2012).
N. P. Zhuk, A Course of Corrosion Theory and Corrosion Protection [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1976).
B. Gaur, “Corrosion of mild steel in hypochlorite solution—An electrochemical and weight-loss study,” Indian J. Chem. Technol., 1, 225–229 (1994).
N. S. Akhmetov, General and Inorganic Chemistry [in Russian], Vysshaya Shkola, Moscow (2001).
B. V. Tilak and C. P. Chen, “Electrolytic sodium chlorate technology: Current status. Chlor-Alkali and Chlorate Technology,” in: MacMullin Memorial Symposium: Proc., of the Symposium (January 1999), H. S. Burney. Electrochemical Society (1999), pp. 8–39.
S. A. Kaluzhena and S. А. Muratova, “Passivation of iron in subalkali solutions at different temperatures and under various hydrodynamic conditions,” Vestn. VGU, Ser. Khim., No. 1, 50–54 (2004).
EIS Spectrum Analyser, http://www.abc.chemistry.bsu.by/vi/analyser/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 53, No. 1, pp. 108–112, January–February, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Znak, Z.O., Zin’, О.І. Reduction of the Corrosiveness of Liquid Wastes of the Production of Chlorine and Caustic Soda. Mater Sci 53, 123–128 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-017-0052-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-017-0052-4