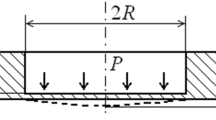
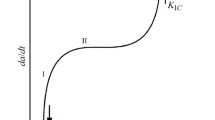
We propose a theoretical-experimental approach to the determination of the concentration of hydrogen in the process zone. The plots of the dependences of the concentration of hydrogen on the mechanical characteristics of the material and external load are constructed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Sofronis and R. M. McMeeking, “Numerical analysis of hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip” J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 37, 317–350 (1989).
A. H. M. Krom, R. W. J. Koers, and A. Bakkerr, “Hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip,” J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 47, No. 4, 971–992 (1999).
H. Kanayama, T. Shingoh, S. Ndong-Mefane, et al., “Numerical analysis of hydrogen diffusion problems using the finite element method,” J. Theor. Appl. Mech. Jap., 56, 389–400 (2008).
R. Miresmaeili, M. Ogino, R. Shioya, et al., “Finite element analysis of the stress and deformation fields around the blunting crack tip,” Mem. Fac. Eng., Kyushu Univ., 68, No. 4, 151–161 (2008).
L. Liu, R. Miresmaeili, M. Ogino, et al., “Finite element implementation of an elastoplastic constitutive equation in the presence of hydrogen,” J. Comput. Sci. Technol., 5, No. 1, 62–76 (2011).
A. Taha and P. Sofronis, “A micromechanics approach to the study of hydrogen transport and embrittlement,” Eng. Fract. Mech., 68, 803–837 (2001).
H. Kotake, R. Matsumoto, S. Taketomi, et al., “Transient hydrogen diffusion analyses coupled with crack-tip plasticity under cyclic loading,” Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip., 85, 540–549 (2008).
J. Toribio, A. Valiente, R. Cortes, et al., “Modeling hydrogen embrittlement in 316L austenitic stainless steel for the first wall of the Next European Torus,” Fusion Eng. Des., 29, 442–147 (1995).
J. Toribio, D. Vergara, M. Lorenzo, and V. Kharin, “Two-dimensional numerical modeling of hydrogen diffusion assisted by stress and strain,” WIT Trans. Eng. Sci., 65, 131–140 (2009).
J. Toribio, V. Kharin, D. Vergara, and M. Lorenzo, “Optimization of the simulation of stress-assisted hydrogen diffusion for the studies of hydrogen embrittlement of notched bars,” Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., 46, No. 6, 91–106 (2010); English translation: Mater. Sci., 46, No. 6, 819–833 (2010).
V. V. Panasyuk, Mechanics of Quasibrittle Fracture of Materials [in Russian], Nauka, Kiev (1991).
O. E. Andreikiv and O. V. Hembara, Fracture Mechanics and Durability of Metallic Materials in Hydrogen-Containing Environments [in Ukrainian], Nauka, Kyiv (2008).
T. Yokobori, T. Nemoto, K. Saton, and T. Yamada, “Numerical analysis of hydrogen diffusion and concentration in solid with emission around the crack tip,” Eng. Fract. Mech., 55, No. 1, 47–60 (1996).
T. Yokobori, Ya. Chinda, T. Nemoto, et al., “The characteristics of hydrogen diffusion and concentration around a crack tip concerned with hydrogen embrittlement,” Corr. Sci., 44, 407–424 (2002).
M. Wang, E. Akiyama, and K. Tsuzaki, “Determination of the critical hydrogen concentration for delayed fracture of high strength steel by constant load test and numerical calculation,” Corr. Sci., 48, 2189–2202 (2006).
M. Stashchuk and M. Dorosh, “Evaluation of hydrogen stress in metal and redistribution of hydrogen around crack-like defects,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 37, 14687–14699 (2012).
R. D. Cook, D. S. Malkus, M. E. Plesha, and R. J. Witt, Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis, John Wiley, New York (2002).
A. H. M. Krom, R. W. J. Koers, and A. Bakkerr, “Hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip,” J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 47, 971–992 (1999).
V. V. Panasyuk, Ya. L. Ivanyts’kyi, and O. P. Maksymenko, “Analysis of the elastoplastic deformation of the material in the process zone,” Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., 40, No. 5, 67–73 (2004); English translation: Mater. Sci., 40, No. 5, 648–655 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 50, No. 3, pp. 7–14, May–June, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panasyuk, V.V., Ivanyts’kyi, Y.L., Hembara, О.V. et al. Influence of the Stress-Strain State on the Distribution of Hydrogen Concentration in the Process Zone. Mater Sci 50, 315–323 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-014-9723-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-014-9723-6