Abstract
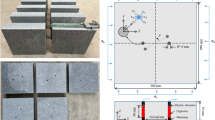
The reef limestone specimens selected in this experiment can be divided into four types according to their morphologies: strongly-cemented compact-type (BM-type), weakly-cemented compact-type (M-type), weakly-cemented loose-type (BS-type), and strongly-cemented loose-type (S-type). Based on the split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) test, the aims of this study were to investigate the dynamic mechanical response and energy dissipation characteristics of reef limestone under impact loads and discuss the relationships of the dynamic fragmentation fractal characteristics with the strain rate and energy dissipation of reef limestone. The results indicated that the length of the compaction section for compact-type reef limestone compared with that of the loose section, which is more significant in the case of decreasing strain rate. The fractal dimension is linearly positively correlated with the strain rate; the fractal dimension of compact-type reef limestone is lower than that of loose-type reef limestone; meanwhile, the dynamic fractal dimension of compact-type reef limestone is more sensitive to the strain rate. The fragmentation fractal dimension of reef limestone under impact loads shows exponential growth with the increase in dynamic strength. The fragmentation fractal dimension of reef limestone is linearly, and positively, correlated with energy dissipation density.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Burton CL, Waltham AC, Mclaren SJ (2001) Strength variation in young reef limestones. Geotechnique 51(10):887–889. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2001.51.10.887
Dai B, Shan QQ, Chen Y, Luo XY (2022) Mechanical and energy dissipation characteristics of granite under cyclic impact loading. J Central South Univ 29(1):116–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-4897-9
Elhakim AF (2015) The use of point load test for Dubai weak calcareous sandstones. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 7(4):452–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmge.2015.06.003
Hong L, Zhou ZL, Yin TB, Liao GY, Ye ZY (2009) Energy consumption in rock fragmentation at intermediate strain rate. J Cent South Univ Technol 16:677–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0112-5
Li JC, Rong LF, Li HB, Hong SN (2018) An SHPB test study on stress wave energy attenuation in jointed rock masses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(2):403–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1586-y
Li CJ, Xu Y, Zhang YT, Li HL (2019) Study on energy evolution and fractal characteristics of cracked coal-rock-like combined body under impact loading. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 38(11):2231–2241. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.James.2019.0446
Li DJ, Shi C, Ruan HN, Li BY, Li WY, Yao XC (2022) Study on shear behavior of coral reef limestone-concrete interface. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 40(4):438–447. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2021.1906365
Liu HF, Zhu CQ, Zheng K, Ma CH, Yi MX (2021) Crack initiation and damage evolution of micritized framework reef limestone in the South China Sea. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(11):5591–5601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02570-4
Luo Y, Wang G, Li XP, Liu TT, Mandal A, Xu MN, Xu K (2020) Analysis of energy dissipation and crack evolution law of sandstone under impact load. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 132:104359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104359
Luo Y, Gong HL, Huang JH, Wang G, Li XP, Wan S (2022) Dynamic cumulative damage characteristics of deep-buried granite from Shuangjiangkou hydropower station under true triaxial constraint. Int J Impact Eng 165:104215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104215
Luo Y, Gong HL, Wei XQ, Zheng SL, Pei CH, Li Xin XP (2023) Dynamic compressive characteristics and damage constitutive model of coral reef limestone with different cementation degrees. Constr Build Mater 362:129783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129783
Ma QY, Cao ZM (2019) Experimental study on fractal characteristics and energy dissipation of stabilized soil based on SHPB test. J Mater Civ Eng 31(11):04019264. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002916
Ma LJ, Wu JW, Wang MY, Dong L, Wei HZ (2020) Dynamic compressive properties of dry and saturated coral rocks at high strain rates. Eng Geol 272:105615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105615
Meng QS, Fan C, Zheng WX, Yu KF (2019) Tests on dynamic properties of coral-reef limestone in South China Sea. Rock and Soil Mechanics 40(01):183–190. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2017.1271
Meng QS, Wu K, Zhou HR, Qin QL, Wang C (2022) Mesoscopic damage evolution of coral reef limestone based on real-time CT scanning. Eng Geol 307:106781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Engel.2022.106781
Wang XZ, Wang R, Meng QS, Chen JW, Chen JW (2008) Research on characteristics of coral reef calcareous rock in Nansha Islands. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27(11):2221–2226. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2017.1271
Wang X, Shan HG, Wang XZ, W, and C. Q. Zhu. (2019) Strength characteristics of reef limestone for different cementation types. Geotech Geol Eng 38(S1):79–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01000-1
Wang F, Wang HB, Xu Y, Cheng B, Wang QQ (2021a) Analysis of energy dissipation characteristics of damaged sandstone under impact load. Shock Vib 2021:4200452. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4200452
Wang JG, Zuo T, Li XL, Tao ZH, Ma J (2021b) Study on the fractal characteristics of the pomegranate biotite schist under impact loading. Geofluids 2021:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1570160
Wang XZ, Wang X, Shen JH, Ding HZ, Wen DS, Zhu CQ, Lv SZ (2022) Foundation filling performance of calcareous soil on coral reefs in the South China Sea. Appl Ocean Res 129:103386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2022.103386
Wang G, Luo Y, Gong HL, Liu TT, Li XP, Song LB (2023) Investigations on the macro-meso mechanical properties and energy dissipation mechanism of granite shear fracture under dynamic disturbance. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 2023:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.3584
Wei HZ, Ma LJ, Wu JW, Yu J, Li Z, Xu R (2022) Dynamic mechanical behavior of coral rock subjected to high strain rate loading. Marine Geophys Res 43(3):30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-022-094993-x
Wu J, Fu H, Zhang L, Zhang XY, Guy DY (2022a) Stability analysis of surrounding rock in underground chamber excavation of coral reef limestone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55(8):4717–4742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-0222-02869-w
Wu K, Meng QS, Wang C, Qin QL, Li CS (2022b) Experimental investigation of damage evolution characteristics of coral reef limestone based on acoustic emission and digital volume correlation techniques. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56(3):2357–2374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03186-y
Wu K, Meng QS, Wang C, Qin QL, Li CS (2023) Experimental investigation of damage evolution characteristics of coral reef limestone based on acoustic emission and digital volume correlation techniques. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56(3):2357–2374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03186-y
Wu K, Meng QS, Qin QL, Jiang X, Wang C (2022) Microscopic mechanisms of coral reef limestone crack propagation. Marine Geores Geotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2022.2143305
Xie HP, Li LY, Peng RD, Ju Y (2009) Energy analysis and criteria for structural failure of rocks. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 1(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1235.2009.00011
Xie HP, Li LY, Ju Y, Peng RD, Yang YM (2011) Energy analysis for damage and catastrophic failure of rocks. Science China Technol Sci 54(1):199–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11431-011-4639-Y
Yang RS, Li WY, Yue ZW (2020) Comparative study on dynamic mechanical properties and energy dissipation of rocks under impact loads. Shock Vib 2020:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8865099
Zhang B, Lei XW, Wei HZ, Meng QS, Li XX, Wang XZ (2021) Study on pore structure characteristics of coral skeleton limestone based on CT scans. J Eng Geol 29(06):1692–1699. https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-584
Zhang XY, Zhang LW, Wu J, Fu H, Dian LY (2022) Tunnel stability analysis of coral reef limestone stratum in ocean engineering. Ocean Eng 265:112636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112636
Zhongshan DW, Xiong W, Meng QS, Si JF, Wu Y (2021) Experimental study on fracture characteristics of underwater drilling and blasting of coral reef limestone. Blasting 38(02):24–31. https://doi.org/10.3963/j.Issa.1001-487X.2021.02.004
Zhu CQ, Qin Y, Meng QS, Wang XZ, Wang R (2014) Formation and sedimentary evolution characteristics of Yongshu Atoll in the South China Sea Islands. Ocean Eng 84:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.03.035
Zhu CQ, Liu HF, Zhou B (2016) Micro-structures and the basic engineering properties of beach calcarenites in South China Sea. Ocean Eng 114:224–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.01.009
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewer for their careful review of this paper.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51979208), Sanya Science and Education Innovation Park of Wuhan University of Technology (Grant No. 2022KF0025), the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (No. 521CXTD444), the Hainan Provincial Joint Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City (Grant No. 2021JJLH0068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, formal analysis, funding acquisition. YL: data curation, methodology, writing—original draft. HL: conceptualization, methodology, visualization. YG (Corresponding author): writing—original draft, supervision, data curation, investigation. HG: Formal analysis, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there are no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participant
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors have confirmed the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Li, Y., Lin, H. et al. Impact-induced fragmentation of coral reef limestone based on fractal theory. Mar Geophys Res 45, 7 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-023-09539-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-023-09539-8