Abstract
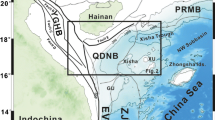
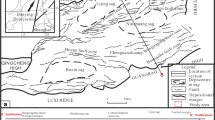
Based upon 2D seismic data, this study confirms the presence of a complex deep-water sedimentary system within the Pliocene-Quaternary strata on the northwestern lower slope of the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea. It consists of submarine canyons, mass-wasting deposits, contourite channels and sheeted drifts. Alongslope aligned erosive features are observed on the eastern upper gentle slopes (<1.2° above 1,500 m), where a V-shaped downslope canyon presents an apparent ENE migration, indicating a related bottom current within the eastward South China Sea Intermediate Water Circulation. Contourite sheeted drifts are also generated on the eastern gentle slopes (~1.5° in average), below 2,100 m water depth though, referring to a wide unfocused bottom current, which might be related to the South China Sea Deep Water Circulation. Mass wasting deposits (predominantly slides and slumps) and submarine canyons developed on steeper slopes (>2°), where weaker alongslope currents are probably dominated by downslope depositional processes on these unstable slopes. The NNW–SSE oriented slope morphology changes from a three-stepped terraced outline (I–II–III) east of the investigated area, into a two-stepped terraced (I–II) outline in the middle, and into a unitary steep slope (II) in the west, which is consistent with the slope steepening towards the west. Such morphological changes may have possibly led to a westward simplification of composite deep-water sedimentary systems, from a depositional complex of contourite depositional systems, mass-wasting deposits and canyons, on the one hand, to only sliding and canyon deposits on the other hand.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouma AH (1964) Turbidites. In: Bouma AH, Brouwer A (eds) Turbidites. Developments in sedimentology, vol 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 247–256. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)70967-1
Chen C-TA (2005) Tracing tropical and intermediate waters from the South China Sea to the Okinawa Trough and beyond. J Geophys Res Oceans 110(C5):C05012. doi:10.1029/2004JC002494
Chen C-TA, Wang S-L (1998) Influence of intermediate water in the western Okinawa Trough by the outflow from the South China Sea. J Geophys Res Oceans 103(C6):12683–12688. doi:10.1029/98JC00366
Chen H, Xie X, Van Rooij D, Vandorpe T, Su M Depositional characteristics and processes of alongslope currents related to a seamount on the northwestern margin of the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea. Mar Geol (under review)
Chen PPH, Chen ZY, Zhang QM (1993) Sequence stratigraphy and continental-margin development of the northwestern shelf of the South China Sea. AAPG bulletin 77(5):842–862
Fang G, Fang W, Fang Y, Wang K (1998) A survey of studies on the South China Sea upper ocean circulation. Acta Oceanogr Taiwan 37(1):1–16
Faugères J-C, Mulder T (2011) Chapter 3—Contour currents and contourite drifts. In: Hüneke H, Mulder T (eds) Deep-sea sediments. Developments in sedimentology, vol 63. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 149–214. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53000-4.00003-2
Faugères J-C, Stow DAV (2008) Chapter 14—Contourite drifts: nature, evolution and controls. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (eds) Contourites. Developments in sedimentology, vol 60. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 257–288. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)10014-0
Faugères J-C, Stow DAV, Imbert P, Vianna A (1999) Seismic features diagnostic of contourite drifts. Mar Geol 162(1):1–38. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00068-7
Frigola J, Moreno A, Cacho I, Canals M, Sierro FJ, Flores JA, Grimalt JO (2008) Evidence of abrupt changes in Western Mediterranean Deep Water circulation during the last 50 kyr: a high-resolution marine record from the Balearic Sea. Quat Int 181(1):88–104. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.06.016
Gong C, Wang Y, Peng X, Li W, Qiu Y, Xu S (2012) Sediment waves on the South China Sea Slope off southwestern Taiwan: implications for the intrusion of the Northern Pacific Deep Water into the South China Sea. Mar Petrol Geol 32(1):95–109. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.12.005
Hampton MA, Lee HJ, Jacques L (1996) Submarine landslides. Rev Geophys 34(1):33–59. doi:10.1029/95RG03287
He Y, Xie X, Kneller BC, Wang Z, Li X (2013) Architecture and controlling factors of canyon fills on the shelf margin in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar Petrol Geol 41:264–276. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.03.002
Hernández-Molina FJ, Llave E, Somoza L, Fernandez-Puga MC, Maestro A, Leon R, Medialdea T, Barnolas A, Garcia M, del Rio VD, Fernandez-Salas LM, Vazquez JT, Lobo F, Dias JMA, Rodero J, Gardner J (2003) Looking for clues to paleoceanographic imprints: a diagnosis of the Gulf of Cadiz contourite depositional systems. Geology 31(1):19–22. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0019:LFCTPI>2.0.CO;2
Hernández-Molina FJ, Llave E, Stow DAV, García M, Somoza L, Vázquez JT, Lobo FJ, Maestro A, Díaz del Río V, León R, Medialdea T, Gardner J (2006) The contourite depositional system of the Gulf of Cádiz: a sedimentary model related to the bottom current activity of the Mediterranean outflow water and its interaction with the continental margin. Deep Sea Res Part II 53(11–13):1420–1463. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2006.04.016
Hernández-Molina FJ, Llave E, Stow DAV (2008a) Chapter 19 continental slope contourites. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (eds) Contourites. Developments in sedimentology, vol 60. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 379–408. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)10019-X
Hernández-Molina FJ, Maldonado A, Stow DAV (2008b) Chapter 18 abyssal plain contourites. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (eds) Contourites. Developments in sedimentology, vol 60. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 345–378. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)10018-8
Hernández-Molina FJ, Paterlini M, Violante R, Marshall P, de Isasi M, Somoza L, Rebesco M (2009) Contourite depositional system on the Argentine Slope: an exceptional record of the influence of Antarctic water masses. Geology 37(6):507–510. doi:10.1130/G25578a.1
Hernández-Molina FJ, Paterlini M, Somoza L, Violante R, Arecco MA, de Isasi M, Rebesco M, Uenzelmann-Neben G, Neben S, Marshall P (2010) Giant mounded drifts in the Argentine Continental Margin: origins, and global implications for the history of thermohaline circulation. Mar Petrol Geol 27(7):1508–1530. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.04.003
Hernández-Molina FJ, Serra N, Stow D, Llave E, Ercilla G, Van Rooij D (2011a) Along-slope oceanographic processes and sedimentary products around the Iberian margin. Geo Mar Lett 31(5–6):315–341. doi:10.1007/s00367-011-0242-2
Hernández-Molina FJ, Stow DAV, Llave E, Rebesco M, Ercilla G, Rooij D, Mena A, Vázquez J-T, Voelker AL (2011b) Deep-water circulation: processes & Products (16–18 June 2010, Baiona): introduction and future challenges. Geo Mar Lett 31(5–6):285–300. doi:10.1007/s00367-011-0261-z
Imbo Y, De Batist M, Canals M, Prieto MJ, Baraza J (2003) The Gebra slide: a submarine slide on the Trinity Peninsula Margin, Antarctica. Mar Geol 193(3–4):235–252. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00664-3
Jiang T, Zhang Y, Xie X, Ren J, Zhang C (2010) Characteristics and origin of sediment waves in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Geo Temas 11:193–194
Laberg JS, Vorren TO (2000) The Trænadjupet slide, offshore Norway-morphology, evacuation and triggering mechanisms. Mar Geol 171(1–4):95–114. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00112-2
Lastras G, Canals M, Amblas D, Ivanov M, Dennielou B, Droz L, Akhmetzhanov A (2006) Eivissa slides, western Mediterranean Sea: morphology and processes. Geo Mar Lett 26(4):225–233. doi:10.1007/s00367-006-0032-4
Li Q, Zhao Q, Zhong G, Jian Z, Tian J, Cheng X, Chen M (2008) Deep water ventilation and stratification in the Neogene South China Sea. Earth Sci 18(2):95–108
Li Q, Zhong G, Tian J (2009) Stratigraphy and sea level changes. In: Wang P, Li Q (eds) The South China Sea. Developments in paleoenvironmental research, vol 13. Springer, Netherlands, pp 75–170. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9745-4_3
Li H, Wang Y, Zhu W, Xu Q, He Y, Tang W, Zhuo H, Wang D, Wu J, Li D (2013) Seismic characteristics and processes of the Plio-Quaternary unidirectionally migrating channels and contourites in the northern slope of the South China Sea. Mar Petrol Geol. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.12.010
Liu Z, Huang W, Li J, Wang P, Wang R, Yu K, Zhao J (2009) Sedimentology. In: Wang P, Li Q (eds) The South China Sea. Developments in paleoenvironmental research, vol 13. Springer, Netherlands, pp 171–295. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9745-4_4
Lüdmann T, Kin Wong H, Wang P (2001) Plio-Quaternary sedimentation processes and neotectonics of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Mar Geol 172(3–4):331–358. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00129-8
Lüdmann T, Wong HK, Berglar K (2005) Upward flow of North Pacific Deep Water in the northern South China Sea as deduced from the occurrence of drift sediments. Geophys Res Lett 32(5):L05614. doi:10.1029/2004GL021967
Mulder T (2011) Chapter 2—Gravity processes and deposits on continental slope, rise and abyssal plains. In: Hüneke H, Mulder T (eds) Deep-sea sediments. Developments in sedimentology, vol 63. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 25–148. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53000-4.00002-0
Mulder T, Cochonat P (1996) Classification of offshore mass movements. J Sediment Res 66(1):43–57. doi:10.1306/D42682AC-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Mulder T, Faugères JC, Gonthier E (2008) Chapter 21 mixed turbidite-contourite systems. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (eds) Contourites. Developments in sedimentology, vol 60. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 435–456. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)10021-8
Mulder T, Hüneke H, Van Loon AJ (2011) Chapter 1—Progress in deep-sea sedimentology. In: Hüneke H, Mulder T (eds) Deep-sea sediments. Developments in sedimentology, vol 63. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–24. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53000-4.00001-9
Preu B, Hernández-Molina FJ, Violante R, Piola AR, Paterlini CM, Schwenk T, Voigt I, Krastel S, Spiess V (2013) Morphosedimentary and hydrographic features of the northern Argentine margin: the interplay between erosive, depositional and gravitational processes and its conceptual implications. Deep Sea Res Part I 75:157–174. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2012.12.013
Qu T, Lindstrom EJ (2004) Northward intrusion of Antarctic intermediate water in the Western Pacific. J Phys Oceanogr 34(9):2104–2118. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(2004)034<2104:NIOAIW>2.0.CO;2
Qu T, Girton JB, Whitehead JA (2006) Deepwater overflow through Luzon Strait. J Geophys Res Oceans 111(C1):C01002. doi:10.1029/2005JC003139
Rasmussen S, Lykke-Andersen H, Kuijpers A, Troelstra SR (2003) Post-Miocene sedimentation at the continental rise of Southeast Greenland: the interplay between turbidity and contour currents. Mar Geol 196(1–2):1–16. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00043-4
Shao L, Li X, Wang P, Jian Z, Wei G, Pang X, Liu Y (2004) Sedimentary record of the tectonic evolution of the South China Sea since the oligocene-evidence from deep sea sediments of ODP Site 1148. Adv Earth Sci 19(4):539–544
Shao L, Li X, Geng J, Pang X, Lei Y, Qiao P, Wang L, Wang H (2007) Deep water bottom current deposition in the northern South China Sea. Sci China Ser D 50(7):1060–1066. doi:10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y
Stow DAV, Hunter S, Wilkinson D, Hernández-Molina FJ (2008) Chapter 9 the nature of contourite deposition. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (eds) Contourites. Developments in sedimentology, vol 60. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 143–156. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)10009-7
Sun Z, Zhou D, Zhong Z, Xia B, Qiu X, Zeng Z, Jiang J (2006) Research on the dynamics of the South China Sea opening: evidence from analogue modeling. Sci China Ser D 49(10):1053–1069. doi:10.1007/s11430-006-1053-6
Sun Z, Zhong Z, Keep M, Zhou D, Cai D, Li X, Wu S, Jiang J (2009) 3D analogue modeling of the South China Sea: a discussion on breakup pattern. J Asian Earth Sci 34(4):544–556. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.09.002
Tian J, Qu T (2012) Advances in research on the Deep South China Sea circulation. Chin Sci Bull 57(24):3115–3120. doi:10.1007/s11434-012-5269-x
Varnes DJ (1978) Slope movement types and processes. In: Schuster RL, Krizek RJ (eds) Landslides-analysis and control. Transp Res Board, Spec Rep 176. National Research Council, Washington, DC, pp 12–33
Viana AR, Almeida JW, Machado LC (1999) Different styles of canyon infill related to gravity and bottom current processes: Example from the upper slope of the SE Brazilian Margin. In: 6th international congress of the Brazil. Geophys Soc, Rio De Janeiro, p. SBGF0199
Wang H (2007) Sedimentation processes and its response in deep-water environment of the northern continental margin, the South China Sea. Ph.D. thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing
Wang P, Li Q (2009a) Introduction. In: Wang P, Li Q (eds) The South China Sea. Developments in paleoenvironmental research, vol 13. Springer, Netherlands, pp 1–23. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9745-4_1
Wang P, Li Q (2009b) Oceanographical and geological background. In: Wang P, Li Q (eds) The South China Sea. Developments in paleoenvironmental research, vol 13. Springer, Netherlands, pp 25–73. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9745-4_2
Wang P, Prell W, Blum P, et al (2000) Proc. ODP, Init. Repts., 184: College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program). doi:10.2973/odp.proc.ir.184.2000
Wang H, Yuan S, Gao H (2010) The contourite system and the framework of contour current circulation in the South China Sea. Geo Temas 11:179–180
Wang D, Wang Q, Zhou W, Cai S, Li L, Hong B (2013) An analysis of the current deflection around Dongsha Islands in the northern South China Sea. J Geophys Res Oceans 118(1):490–501. doi:10.1029/2012JC008429
Wynn RB, Masson DG (2008) Chapter 15—Sediment waves and bedforms. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (eds) Developments in sedimentology, vol 60. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 289–300. doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(08)10015-2
Wynn RB, Stow DAV (2002) Classification and characterisation of deep-water sediment waves. Mar Geol 192(1–3):7–22. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00547-9
Wynn RB, Weaver PPE, Ercilla G, Stow DAV, Masson DG (2000) Sedimentary processes in the Selvage sediment-wave field, NE Atlantic: new insights into the formation of sediment waves by turbidity currents. Sedimentology 47(6):1181–1197. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3091.2000.00348.x
Xie L (2009) Study on the circulation in Western North Pacific and the water exchange between the Pacific and the South China Sea. Ph.D thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao
Xie X, Zhang C, Ren J, Yao B, Wan L, Chen H, Kang B (2011) Effects of distinct tectonic evolutions on hydrocarbon accumulation in northern and southern continental marginal basins of South China Sea. Chin J Geophys Ch 54(12):3280–3291. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.026
Xie Q, Xiao JG, Wang DX, Yu YQ (2013) Analysis of deep-layer and bottom circulations in the South China Sea based on eight quasi-global ocean model outputs. Chin Sci Bull 58(1):1–7. doi:10.1007/s11434-013-5791-5
Xue H, Chai F, Pettigrew N, Xu D, Shi M, Xu J (2004) Kuroshio intrusion and the circulation in the South China Sea. J Geophys Res Oceans 109(C2):C02017. doi:10.1029/2002JC001724
Yuan D (2002) A numerical study of the South China Sea deep circulation and its relation to the Luzon Strait transport. Acta Oceanol Sin 21(2):187–202
Yuan S (2009) Sedimentary system of deepwater channel, the slope area of northern South China Sea. Ph.D thesis, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao
Zhao Q (2005) Late Cainozoic ostracod faunas and paleoenvironmental changes at ODP Site 1148, South China Sea. Mar Micropaleontol 54(1–2):27–47. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2004.09.002
Zhao Q, Li Q, Jian Z (2009) Deep waters and oceanic connection. In: Wang P, Li Q (eds) The South China Sea. Springer, Netherlands, pp 395–437. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9745-4_6
Zheng H-B, Yan P (2012) Deep-water bottom current research in the northern South China Sea. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 30(2):122–129. doi:10.1080/1064119X.2011.586015
Zhu M, Graham S, Pang X, McHargue T (2010) Characteristics of migrating submarine canyons from the middle Miocene to present: implications for paleoceanographic circulation, northern South China Sea. Mar Petrol Geol 27(1):307–319. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.05.005
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91028009), the Key project of Hubei Natural Science Foundation (No. 2008CDA095), the Ph.D. Program Foundation of Ministry of Education (No. 20100145110002) and the National Key Projects of Oil and Gas (No. 2011ZX05025-002-02). This article is also a contribution to IGCP project 619 and INQUA project 1204. We would like to acknowledge the Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, Nanhai West Oil Corporation for providing geophysical data. The exchange-student programme for H. Chen was framed under the Cooperation Agreement between the China University of Geosciences (P. R. China) and Ghent University (Belgium). We appreciate Mr. Jing-Liang Guo’s help for English improvement. We thank the reviewers for their comments that significantly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Xie, X., Van Rooij, D. et al. Depositional characteristics and spatial distribution of deep-water sedimentary systems on the northwestern middle-lower slope of the Northwest Sub-Basin, South China Sea. Mar Geophys Res 34, 239–257 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9191-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9191-7