Abstract
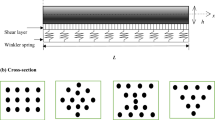
Present study elucidates shear surface wave dispersion and attenuation in a piezoelectric-flexoelectric micro layer bedded over a heterogeneous initially stressed fiber-reinforced host structure with or with out a thin mass loading layer (ZnO layer) at the top surface of the micro-layer. Mechanical imperfection between host structure and electrically active layer is modelled with the help of Shear-lag model. Dual electromechanical coupled (flexoelectric and piezoelectric) field equations are solved by means of analytical technique and dispersion relations are obtained for electroded and non-electroded surface, separately when the infinitesimal mass loading layer is associated or not associated with piezo-flexo layer. With the help of suitable numerical example phase velocity curves and dissipation curves are plotted to illuminate the parametric responses of flexoelectricity, piezoelectricity, dielectricity, imperfection, reinforcement anisotropy and initial tensile stress. Detailed discussions about electromechanical coupling are done for different cases. Influence of piezoelectricity, dielectricity and flexoelectricity on mass loading sensitivity are also expatiated. The study may provide theoretical guidelines in investigations about mass loading sensitivity of SAW sensors with piezo-flexo coupling.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins, J.E.: Finite plane deformation of thine elastic sheets reinforced with inextensible cords. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 249(961), 125–150 (1956)
Alam, P., Kundu, S., Badruddin, I., Khan, T.: Dispersion and attenuation characteristics of love-type waves in a fiber-reinforced composite over a viscoelastic substrate. Phys. Wave Phenom. 27(4), 281–289 (2019)
Ballantine, D., Jr., White, R.M., Martin, S.J., Ricco, A.J., Zellers, E., Frye, G., Wohltjen, H.: Acoustic Wave Sensors: Theory, Design and Physico-Chemical Applications. Elsevier, New York (1996)
Belfield, A., Rogers, T., Spencer, A.: Stress in elastic plates reinforced by fibres lying in concentric circles. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 31(1), 25–54 (1983)
Beni, Y.T.: Size-dependent torsional wave propagation in fg flexoelectric micro/nanotubes. In: Waves in Random and Complex Media, pp. 1–23 (2022)
Biswas, M., Sahu, S.A.: Surface wave dispersion in imperfectly bonded flexoelectric-piezoelectric/fgpm bi-composite in contact of newtonian liquid. In: Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, pp. 1–18 (2022)
Chattopadhyay, A., Singh, A.: G-type seismic waves in fibre reinforced media. Meccanica 47(7), 1775–1785 (2012)
Chen, Z., Hu, Y., Yang, J.: Shear horizontal piezoelectric waves in a piezoceramic plate imperfectly bonded to two piezoceramic half-spaces. J. Mech. 24(3), 229–239 (2008)
Dai, H., Yan, Z., Wang, L.: Nonlinear analysis of flexoelectric energy harvesters under force excitations. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 16(1), 19–33 (2020)
Du, J., Jin, X., Wang, J., Xian, K.: Love wave propagation in functionally graded piezoelectric material layer. Ultrasonics 46(1), 13–22 (2007)
Enderlein, J., Chilla, E., Fröhlich, H.-J.: Comparison of the mass sensitivity of love and Rayleigh waves in a three-layer system. Sens. Actuators A 42(1–3), 472–475 (1994)
Fan, H., Yang, J., Xu, L.: Antiplane piezoelectric surface waves over a ceramic half-space with an imperfectly bonded layer. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 53(9), 1695–1698 (2006)
Ghobadi, A., Golestanian, H., Beni, Y.T., Żur, K.K.: On the size-dependent nonlinear thermo-electro-mechanical free vibration analysis of functionally graded flexoelectric nano-plate. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 95, 105585 (2021)
Gupta, M., Meguid, S., Kundalwal, S.: Synergistic effect of surface-flexoelectricity on electromechanical response of bn-based nanobeam. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 18(1), 3–19 (2022)
Herrmann, F., Jakoby, B., Rabe, J., Büttgenbach, S.: Microacoustic sensors for liquid monitoring. Sens. Update 9(1), 105–160 (2001)
Huang, Y., Li, X.: Shear waves guided by the imperfect interface of two magnetoelectric materials. Ultrasonics 50(8), 750–757 (2010)
Jiang, X., Huang, W., Zhang, S.: Flexoelectric nano-generator: materials, structures and devices. Nano Energy 2(6), 1079–1092 (2013)
Kaur, T., Sharma, S.K., Singh, A.K.: Influence of imperfectly bonded micropolar elastic half-space with non-homogeneous viscoelastic layer on propagation behavior of shear wave. Waves Random Complex Med. 26(4), 650–670 (2016)
Kumari, R., Singh, A.K., Ray, A.: Love-type wave in low-velocity piezoelectric-viscoelastic stratum with mass loading. Acta Mech. 232(4), 1253–1271 (2021)
Kundalwal, S., Ray, M., Meguid, S.: Shear lag model for regularly staggered short fuzzy fiber reinforced composite. J. Appl. Mech. 81(9) (2014)
Kundalwal, S., Kumar, S.: Multiscale modeling of stress transfer in continuous microscale fiber reinforced composites with nano-engineered interphase. Mech. Mater. 102, 117–131 (2016)
Kundalwal, S., Shingare, K., Rathi, A.: Effect of flexoelectricity on the electromechanical response of graphene nanocomposite beam. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 15(3), 447–470 (2019)
Kundalwal, S., Shingare, K., Gupta, M.: Flexoelectric effect on electric potential in piezoelectric graphene-based composite nanowire: analytical and numerical modelling. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 84, 104050 (2020)
Kundu, S., Gupta, S., Manna, S.: Propagation of love wave in fiber-reinforced medium lying over an initially stressed orthotropic half-space. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 38(11), 1172–1182 (2014)
Li, P., Jin, F.: Bleustein-gulyaev waves in a transversely isotropic piezoelectric layered structure with an imperfectly bonded interface. Smart Mater. Struct. 21(4), 045009 (2012)
Liang, X., Hu, S., Shen, S.: Effects of surface and flexoelectricity on a piezoelectric nanobeam. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(3), 035020 (2014)
Liang, X., Hu, S., Shen, S.: Size-dependent buckling and vibration behaviors of piezoelectric nanostructures due to flexoelectricity. Smart Mater. Struct. 24(10), 105012 (2015)
Liu, J., Wang, Y., Wang, B.: Propagation of shear horizontal surface waves in a layered piezoelectric half-space with an imperfect interface. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 57(8), 1875–1879 (2010)
Ma, W., Cross, L.E.: Flexoelectricity of barium titanate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(23), 232902 (2006)
Maranganti, R., Sharma, N., Sharma, P.: Electromechanical coupling in nonpiezoelectric materials due to nanoscale nonlocal size effects: Green’s function solutions and embedded inclusions. Phys. Rev. B 74(1), 014110 (2006)
Mondal, S., Sahu, S.A., Goyal, S.: Mathematical analysis of surface wave transference through imperfect interface in fgpm bedded structure. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 1–18 (2020)
Nguyen, T.D., Mao, S., Yeh, Y.-W., Purohit, P.K., McAlpine, M.C.: Nanoscale flexoelectricity. Adv. Mater. 25(7), 946–974 (2013)
Nirwal, S., Sahu, S.A., Singhal, A., Baroi, J.: Analysis of different boundary types on wave velocity in bedded piezo-structure with flexoelectric effect. Compos. B Eng. 167, 434–447 (2019)
Ogilvy, J.: The mass-loading sensitivity of acoustic love wave biosensors in air. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 30(17), 2497 (1997)
Qi, L.: Rayleigh wave propagation in semi-infinite flexoelectric dielectrics. Phys. Scr. 94(6), 065803 (2019)
Ray, A., Singh, A.K.: Electromechanical coupling and mass loading sensitivity of sh waves in a dielectrically imperfect piezoelectric structure. Int. J. Solids Struct. 210, 49–65 (2021)
Sahu, S.A., Saroj, P.K., Paswan, B.: Shear waves in a heterogeneous fiber-reinforced layer over a half-space under gravity. Int. J. Geomech. 15(2), 04014048 (2015)
Sharma, V., Sharma, V.: Love waves in fiber-reinforced layer imperfectly bonded to microstructural couple stress substrate. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 58 (2020)
Shu, L., Wei, X., Pang, T., Yao, X., Wang, C.: Symmetry of flexoelectric coefficients in crystalline medium. J. Appl. Phys. 110(10), 104106 (2011)
Singh, A.K., Lakshman, A., Mistri, K.C., Pal, M.K.: Torsional surface wave propagation in an imperfectly bonded corrugated initially-stressed poroelastic sandwiched layer. J. Porous Media 21(6) (2018)
Singh, A.K., Parween, Z., Chaki, M.S., Mahto, S.: Influence of loose bonding, initial stress and reinforcement on love-type wave propagating in a functionally graded piezoelectric composite structure. Smart Struct. Syst. 22(3), 341–358 (2018)
Singh, A., Singh, S., Kumari, R., Ray, A.: Impact of point source and mass loading sensitivity on the propagation of an sh wave in an imperfectly bonded fgppm layered structure. Acta Mech. 231(6), 2603–2627 (2020)
Singh, S., Singh, A., Guha, S.: Shear waves in a piezo-fiber-reinforced-poroelastic composite structure with sandwiched functionally graded buffer layer: power series approach. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 92, 104470 (2022)
Spencer, A.J.M., et al.: Continuum Theory of the Mechanics of Fibre-Reinforced Composites, vol. 282. Springer, Berlin (1984)
Tagantsev, A.: Piezoelectricity and flexoelectricity in crystalline dielectrics. Phys. Rev. B 34(8), 5883 (1986)
Talbi, A., Sarry, F., Le Brizoual, L., Elmazria, O., Alnot, P.: Sezawa mode saw pressure sensors based on zno/si structure. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 51(11), 1421–1426 (2004)
Vishwakarma, S.K., Panigrahi, T.R., Kaur, R.: Sh-wave propagation in linearly varying fiber-reinforced viscoelastic composite structure uninitial stress. Arab. J. Geosci. 12(2), 59 (2019)
Wu, H., Xiong, X., Zu, H., Wang, J.H.-C., Wang, Q.-M.: Theoretical analysis of a love wave biosensor in liquid with a viscoelastic wave guiding layer. J. Appl. Phys. 121(5), 054501 (2017)
Yang, W., Liang, X., Shen, S.: Electromechanical responses of piezoelectric nanoplates with flexoelectricity. Acta Mech. 226(9), 3097–3110 (2015)
Yang, W., Liang, X., Shen, S.: Love waves in layered flexoelectric structures. Phil. Mag. 97(33), 3186–3209 (2017)
Yang, W., Deng, Q., Liang, X., Shen, S.: Lamb wave propagation with flexoelectricity and strain gradient elasticity considered. Smart Mater. Struct. 27(8), 085003 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/aacd34
Yurkov, A., Dejneka, A., Yudin, P.: Flexoelectric polarization induced by inhomogeneous heating and implications for energy harvesting. Int. J. Solids Struct. 162, 96–104 (2019)
Zimmermann, C., Mazein, P., Rebiere, D., Dejous, C., Josse, F., Pistre, J.: A theoretical study of love wave sensors mass loading and viscoelastic sensitivity in gas and liquid environments. In: IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, 2004, Vol. 2, , pp. 813–816. IEEE (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Appendix A (without mass loading)
1.1.1 For electrically open case:
\(B_{11} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{12} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{13} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1}\) \(B_{14} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1},\)
\(B_{21}=(-a^f_{11}+se^f_{15}+ik_1 s(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{22}=-(-a^f_{11}+se^f_{15}+ik_1 s(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{23}=(-a^f_{11}+te^f_{15}+ik_1 t(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _2 e^{-m^f _2 h_1},\) \(B_{24}=-(-a^f_{11}+te^f_{15}+ik_1 t(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1},\)
\(B_{31} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(B_{32} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(B_{33} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2,\) \(B_{34} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2,\) \(B_{35}=-(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})),\)
\(B_{41}=-\chi s,\) \(B_{42}=-\chi s,\) \(B_{43}=-\chi t,\) \(B_{44}=-\chi t,\) \(B_{45}=(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})-\chi , \)
\(B_{51}=1, \) \(B_{52}=1,\) \(B_{53}=1,\) \(B_{54}=1\)
1.1.2 For electrically short case:
\(H_{11} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{12} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{13} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1},\) \(H_{14} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1},\)
\(H_{21}= e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{22}=e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{23}=e^{-m^f _2 h_1},\) \(H_{24}=e^{m^f _2 h_1},\)
\(H_{31} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(H_{32} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(H_{33} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2\) \(H_{34} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2,\) \(H_{35}=-(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})),\)
\(H_{41}=-\chi s,\) \(H_{42}=-\chi s,\) \(H_{43}=-\chi t,\) \(H_{44}=-\chi t,\) \(H_{45}=(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})-\chi , \)
\(H_{51}=1, \) \(H_{52}=1,\) \(H_{53}=1,\) \(H_{54}=1\)
1.2 Appendix B (with mass loading)
1.2.1 For electrically open case:
\(B_{11} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1} -\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{12} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1} -\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{13} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1}-\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _2 e^{-m^f _2 h_1}\) \(B_{14} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1}-\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _1 e^{m^f _2 h_1}\) \(B_{21}=(-a^f_{11}+se^f_{15}+ik_1 s(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{22}=-(-a^f_{11}+se^f_{15}+ik_1 s(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(B_{23}=(-a^f_{11}+te^f_{15}+ik_1 t(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _2 e^{-m^f _2 h_1},\) \(B_{24}=-(-a^f_{11}+te^f_{15}+ik_1 t(h_{41}+\frac{h_{52}}{2}))m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1},\)
\(B_{31} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(B_{32} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(B_{33} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2\) \(B_{34} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2,\) \(B_{35}=-(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})),\)
\(B_{41}=-\chi s,\) \(B_{42}=-\chi s,\) \(B_{43}=-\chi t,\) \(B_{44}=-\chi t,\) \(B_{45}=(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})-\chi , \)
\(B_{51}=1, \) \(B_{52}=1,\) \(B_{53}=1,\) \(B_{54}=1\)
1.2.2 For electrically short case:
\(H_{11} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1} -\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _1 e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{12} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1} -\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _1 e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{13} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1}-\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _2 e^{-m^f _2 h_1}\) \(H_{14} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2 e^{m^f _2 h_1}-\rho ^m H {k_1}^2 c^2 m^f _1 e^{m^f _2 h_1}\)
\(H_{21}= e^{-m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{22}=e^{m^f _1 h_1},\) \(H_{23}=e^{-m^f _2 h_1},\) \(H_{24}=e^{m^f _2 h_1},\)
\(H_{31} = (sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(H_{32} = -(sc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _1,\) \(H_{33} = (tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2\) \(H_{34} = -(tc^f_{44}+e^f_{15}-ik_1 \frac{h_{41}}{2})m^f _2,\) \(H_{35}=-(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})),\)
\(H_{41}=-\chi s,\) \(H_{42}=-\chi s,\) \(H_{43}=-\chi t,\) \(H_{44}=-\chi t,\) \(H_{45}=(\mu '_{T}\xi _1+a^2_1(\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})\xi _1+a_1 a_2 ik_1 (\mu '_{T}-\mu '_{L})-\chi , \)
\(H_{51}=1, \) \(H_{52}=1,\) \(H_{53}=1,\) \(H_{54}=1\)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, S.A., Biswas, M. Mass loading effect on surface wave in piezoelectric–flexoelectric dielectric plate clamped on fiber-reinforced rigid base. Int J Mech Mater Des 18, 919–938 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-022-09613-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-022-09613-w
Keywords
- Flexoelectricity
- Piezoelectricity
- Imperfect interface
- Fiber-reinforcement
- Initial stress
- Heterogeneity
- Mass loading sensitivity