Abstract
Combining mobile cranes with the cable parallel manipulators (CPMs), a cooperative CPMs for multiple mobile cranes (CPMMCs) was designed in this paper. The kinematics were derived on the basis of the configuration of the CPMMCs, aiming at numerical estimation of workspace subject to the constraints on the cable tensions and mobile cranes’ structure. Kinematic error, caused by machining, assembly and operation, is one of the major error sources for CPMMCs during high-precision hoisting, which can be estimated by means of error modeling. Kinematics error model was established based on closed-loop vector method. The influences of different error sources on the accuracy are investigated with sensitivity analysis in statistics. Finally, the system is simulated with expected trajectory of the payload based on the established kinematics and error model of the CPMMCs. The simulation results not only provide rationale for design of the CPMMCs, but also of certain guiding significance in practical engineering application.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- m :
-
Mass of the load
- D :
-
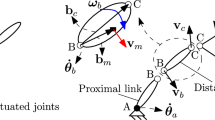
Distance between each mobile crane
- d :
-
The horizontal distance between the pulley center and hoisting point of load
- L :
-
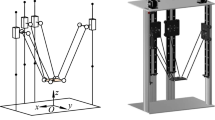
Length of boom
- h :
-
Vertical distance between the lower hinge joints of boom and cylinder
- a :
-
Horizontal distance between the lower hinge joint of boom and the slewing axis
- e :
-
Horizontal distance between the lower hinge joint of hydraulic cylinder and the slewing
- ls :
-
Distance between the lower hinge joint of boom and the upper hinge joint of cylinder
- l :
-
Cable length between the hoisting point to the endpoint of boom
- lc :
-
Length of luffing hydraulic cylinder
- φ :
-
The slewing angle
- γ:
-
The inclination angle of cable
- R :
-
The working radius
- T :
-
The tension of cable
- de A :
-
Position error of the pulley center
- dq A :
-
Kinematics error sources of mobile crane
- J A :
-
Jacobian matrix of the three groups of the mobile crane
- de 0 :
-
Position error of the end-effector of the CPM
- dq 0 :
-
Kinematics error sources of the CPM
- J 0 :
-
Jacobian matrix of the CPM
- de :
-
Position error of the end-effector
- dq :
-
24 error sources for kinematic parameters
- J :
-
Jacobian matrix of the CPMMCs
- S :
-
Local sensitivity
- \( \overline{S} \) :
-
Global sensitivity
- V :
-
Volume of the workspace
- S k :
-
Sensitivity coefficient
- σ:
-
The standard deviation of the kinematics error sources
References
Albus, J.S., Bostelman, R.V., Dagalakis, N.: The NIST Robocrane. J. Robot. Syst. 10(5), 709–724 (1993)
Alikhani, A., Behzadipour, S., Alasty, A., Vanini, S.A.S.: Design of a large-scale cable-driven robot with translational motion. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 27(2), 357–366 (2011)
Bouchard, S., Gosselin, C.M.: Workspace optimization of a very large cable-driven parallel mechanism for a radio telescope application. In: Proceedings of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Las Vegas, USA (2007)
Caro, S., Binaud, N., Wenger, P.: Sensitivity analysis of 3-RPR planar parallel manipulators. J. Mech. Des. 131(12), 1–13 (2009)
Castelli, G., Ottaviano, E., Rea, P.: A Cartesian Cable-Suspended Robot for improving end-users’ mobility in an urban environment. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 30(3), 335–343 (2014)
Duan, B.Y., Qiu, Y.Y., Zhang, F.S., Zi, B.: On design and experiment of the feed cable-suspended structure for super antenna. Mechatronics 19(4), 503–509 (2009)
Fahham, H.R., Farid, M., Khooran, M.: Time optimal trajectory tracking of redundant planar cable-suspended robots considering both tension and velocity constraints. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 133(1), 011004 (2011)
Gouttefarde, M., Daney, D., Merlet, J.-P.: Interval-analysis-based determination of the wrench-feasible workspace of parallel cable-driven robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27(1), 1–13 (2011)
He, R.B., Zhao, Y.J., Yang, S.N., Yang, S.Z.: Kinematic-parameter identification for serial-robot calibration based on POE formula. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26(3), 411–423 (2010)
Heikkilä, M., Linjama, M.: Displacement control of a mobile crane using a digital hydraulic power management system. Mechatronics 23(4), 452–461 (2013)
Huang, T., Li, Y., Tang, G.B., Li, S.W., Zhao, X.Y., Whitehouse, D.J., Chetewyn, D.G.: Error modeling, sensitivity analysis and assembly process of a class of 3 DOF parallel kinematic machines with parallelogram struts. Sci. China (Series E) 45(5), 467–476 (2002)
Klosinski, J.: Swing-free stop control of the slewing motion of a mobile crane. Control Eng. Pract. 13(4), 451–460 (2005)
Lau, D., Oetomo, D., Halgamuge, S.K.: Wrench-closure workspace generation for cable driven parallel manipulators using a hybrid analytical–numerical approach. ASME J. Mech. Des. 133(7), 071004 (2011)
Lin, M.-T., Wu, S.-K.: Modeling and analysis of servo dynamics errors on measuring paths of five-axis machine tools. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 66(3), 1–14 (2011)
Marc, A.: Workspace and stiffness analysis of a three-degree-of-freedom spatial cable-suspended parallel mechanism while considering cable mass. Mech. Mach. Theory 66(3), 1–13 (2011)
McCarthy, J.M.: 21st century kinematics: synthesis, compliance, and tensegrity. ASME J. Mech. Robot. 3(2), 020201 (2011)
Michael, N., Fink, J., Kumar, V.: Cooperative manipulation and transportation with aerial robots. Auton. Robot. 30(1), 73–86 (2011)
Oh, S.R., Agrawal, S.K.: Cable suspended planar robots with redundant cables: controllers with positive tensions. IEEE Trans. Robot. 21(3), 457–465 (2005)
Otis, M.J.-D., Perreault, S., Nguyen-Dang, T.-L., Lambert, P., Gouttefarde, M., Laurendeau, D., Gosselin, C.: Determination and management of cable interferences between two 6-DOF foot platforms in a cable-driven locomotion interface. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. A Syst. Hum. 39(3), 528–544 (2009)
Perreault, S., Cardou, P., Gosselin, C.M., Otis, M.J.-D.: Geometric determination of the interference-free constant-orientation workspace of parallel cable-driven mechanisms. ASME J. Mech. Robot. 2(3), 031016 (2010)
Uddin, M.S., Ibaraki, S., Matsubara, A., Matsushita, T.: Prediction and compensation of machining geometric errors of five-axis machining centers with kinematic errors. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 33(2), 194–201 (2009)
Wang, Y.B., Wu, H.P., Handroos, H.: Accuracy improvement of a hybrid robot for ITER application using POE modeling method. Fusion Eng. Des. 88(9–10), 1877–1880 (2013)
Xu, Q.S., Li, Y.M.: Error analysis and optimal design of a class of translational parallel kinematic machine using particle swarm optimization. Robotica 27(1), 67–78 (2009)
Yamamoto, M., Yanai, N., Mohri, A.: Trajectory control of incompletely restrained parallel-wire-suspended mechanism based on inverse dynamics. IEEE Trans. Robot. 20(5), 840–850 (2004)
Yang, Y., Zhang, Y.R., Lemaire-Semail, B.: A new planar 4-DOF spring and cable driven force feedback device. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 6192, pp. 237–242 (2010)
Zhang, D., Su, X.M., Gao, Z., Qian, J.J.: Design, analysis and fabrication of a novel three degrees of freedom parallel robotic manipulator with decoupled motions. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 9(3), 199–212 (2013)
Zi, B., Zhu, Z.C., Du, J.L.: Analysis and control of the cable-supporting system including actuator dynamics. Control Eng. Pract. 19(5), 491–501 (2011)
Zi, B., Qian, S., Ding, H.F., Kecskeméthy, A.: Design and analysis of cooperative cable parallel manipulators for multiple mobile cranes. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 9(207), 1–10 (2012a)
Zi, B., Wu, X., Lin, J., Zhu, Z.C.: Inverse kinematics and singularity analysis for a 3-DOF hybrid-driven cable-suspended parallel robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 9(133), 1–9 (2012b)
Zi, B., Ding, H.F., Wu, X., Kecskeméthy, A.: Error modeling and sensitivity analysis of a hybrid-driven based cable parallel manipulator. Precis. Eng. 1(38), 197–211 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51275515) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013RC09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, S., Zi, B., Zhang, D. et al. Kinematics and error analysis of cooperative cable parallel manipulators for multiple mobile cranes. Int J Mech Mater Des 10, 395–409 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-014-9250-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-014-9250-5