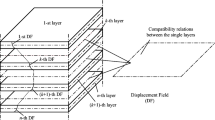
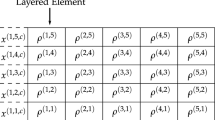
Abstract
This article examines the effective flexural modulus of a multilayered micro-system evolving into alternative layered structures consisting of three dissimilar materials. A multiscale model of the bending stiffness is presented to capture the impact of changing the constituent materials, the layer architecture and the cross-section geometry. The results are plotted onto maps to show the existence of specific domains, within which fall the effective properties of all possible tri-material multilayered configurations. The potential to stiffen a bi-material system is demonstrated by integrating additional layers of a more flexible material for given constraints on the volume fraction. The proposed scheme is conducive to contrast structural alternatives in constrained and unconstrained design. A case study shows how the maps enable optimum selection among various design concepts, which may range from monolithic materials with alternative shape geometries to systems consisting of two and three materials arranged in dissimilar multiple layer architectures.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Cross sectional area
- B :
-
Width (m)
- b :
-
Internal width (m)
- c :
-
Dimensionless multiplicator of cross-section internal width (c = b/B)
- c 1 :
-
Beam curvature
- d :
-
Dimensionless multiplicator of cross-section internal height (d = h/H)
- D :
-
Rectangular cross-section envelope
- E :
-
Young’s modulus (GPa)
- E D, ρ D :
-
Effective of properties of prismatic beam
- E T, ρ T :
-
Effective of properties of shaped beam
- h :
-
Internal height (m)
- H :
-
Height (m)
- I :
-
Second moment of area (m4)
- J T :
-
Cross-section torsional constant (m4)
- l :
-
Beam length (m)
- M b :
-
Bending moment per unit width
- m :
-
Mass (mg)
- n :
-
Exponent of Lame’ curves
- p :
-
Performance index
- q :
-
Scaling parameter of performance index
- r g :
-
Radius of gyration (m)
- u, v :
-
Envelope multiplicators
- S :
-
Shape
- V :
-
Volume (m3)
- ρ :
-
Material density (mg/m3)
- λ :
-
Envelope efficiency parameter
- ψ :
-
Shape transformer
References
Ashby, M.F.: Materials and shape. Acta Metall. Mater. 39(6), 1025–1039 (1991). doi:10.1016/0956-7151(91)90189-8
Ashby, M.F.: Criteria for selecting the components of composites. Acta Metall. Mater. 41(5), 131–135 (1993a). doi:10.1016/0956-7151(93)90242-K
Ashby, M.F.: Criteria for selecting the components of composites. Acta Metall. Mater. 41(5), 131–135 (1993b). doi:10.1016/0956-7151(93)90242-K
Ashby, M.F.: Material Selection in Mechanical Design. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1999)
Caldwell, J.B., Woodhead, R.G.: Ship structures: some possibilities for improvement. Transactions of North East Cost Institution of Engineers and shipbuilders 89, 101–120 (1973)
Cheggour, N., Ekin, J.W., Thieme, C.L.H., Xie, Y.-Y., Selvamanickam, V., Feenstra, R.: Reversible axial-strain effect in Y–Ba–Cu–O coated conductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 18(12), S319–S324 (2005). doi:10.1088/0953-2048/18/12/016
Cox, H.L.: The design of structures of least weight. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1965)
Degani, O., Seter, D.J., Socher, E., Kaldor, S., Nemirovsky, Y.: Optimal design and noise consideration of micro machined vibrating rate gyroscope with modulated integrative differential optical sensing. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 7, 329–338 (1998). doi:10.1109/84.709652
de Silva, C.W.: Sensors and Actuators: Control System. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (2007)
Ferguson, A.T., Li, L., Nagaraj, V.T., Balachandran, B., Piekarski, B., DeVoe, D.L.: Modeling and design of composite free–free beam piezoelectric resonators. Sens. Actuators 118(1), 63–69 (2005). doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(04)00540-0
Gad-el-Hak, M.: The MEMS Handbook, II edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (2002)
Galayko, D., Kaiser, A., Legrand, B., Buchaillot, L., Collard, D., Combi, C.: Tunable bandpass T-filter with electrostatically- driven polysilicon micromechanical resonators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 117, 115–120 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.sna.2004.06.002
Hong, Y.S., Lee, J.H., Kim, S.H.: A laterally driven symmetric micro-resonator for gyroscopic applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 10, 452–458 (2000). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/10/3/322
Huang, X.M.H., Ekinci, K.L., Yang, Y.T., Zorman, C.A., Mehregany, M., Roukes, M.L.: Nanoelectromechanical silicon carbide resonators for ultra-high frequency applications. In: Proceedings of the 2002 Sensor, Actuator and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head, SC, 2–6 June 2002, pp. 368–369
Huber, J.E., Fleck, N.A., Ashby, M.F.: The selection of mechanical actuators based on performance indices. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 453, 2185–2205 (1997)
Jennifer, W.L.Z., Chan, H.-Y., To, T.K.H., Lai, K.W.C., Li, W.J.: Polymer MEMS actuators for underwater micromanipulation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 9(2), 334–342 (2004). doi:10.1109/TMECH.2004.828652
Khaled, A.-R.A., Vafai, K., Yang, M., Zhang, X., Ozkan, C.S.: Analysis, control and augmentation of microcantilever deflections in bio-sensing systems. Sens. Actuators 94, 103–115 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00231-4
Lange, D., Hagleitner, C., Herzog, C., Brand, O., Baltes, H.: Magnetic actuation and MOS-transistor sensing for CMOS-integrated resonators. In: 15th IEEE International Conference on Micro-Electro Mechanical Systems, MEMS 2002, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, 20–24 January 2002, pp. 304–307
Lin, S.: Effect of electric load impedances on the performance of sandwich piezoelectric transducers. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 51(10), 864–869 (2004a)
Lin, S.: Piezoelectric ceramic rectangular transducers in flexural vibration. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 51(7), 1280–1286 (2004b)
Marie, R., Jensenius, H., Thaysen, J., Christensen, C.B., Boisen, A.: Adsorption kinetics and mechanical properties of thiol-modified DNA-oligos on gold investigated by microcantilever sensors. Ultramicroscopy 91, 29–36 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0304-3991(02)00079-7
Melamud, R., Kim, B., Hopcroft, M.A., Chandorkar, S., Agarwal, M., Jha, C., Bhat, S., Park, K.K., Kenny, T.W.: Composite flexural mode resonator with reduced temperature coefficient of frequency. In: Solid-State Sensors, Actuators, and Microsystems Workshop, South Carolina, 4–8 June 2006
Mertens, J., Finot, E., Thundat, T., Fabre, A., Nadal, M.-H., Eyraud, V., Bourillot, E.: Effects of temperature and pressure on microcantilever resonance response. Ultramicroscopy 97(1), 119–126 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0304-3991(03)00036-6
Nguyen, C.T.-C.: Micromechanical resonators for oscillators and filters. In: Proceeding 1995 IEEE International Ultrasonic Symposium Seattle, WA, USA (1995)
Nguyen, C.T.-C., Katehi, L.P.B., Rebeiz, G.M.: Micromachined devices for wireless communications. Proc. IEEE. 86, 1756–1768 (1998). doi:10.1109/5.704281
Nguyen, C.T.-C.: Frequency-selective MEMS for miniaturized low-power communication devices. IEEE. Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 47(8), 1486–1503 (1999)
Nguyen, C.T.-C.: Vibrating RF MEMS for next generation wireless applications. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, Orlando, Florida, 3–6 October 2004, pp. 257–264
Parkhouse, J.G.: Structuring a process of material dilution. In: Nooshin, H. (ed.) Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Space Structures, pp. 367–374. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, New York (1984)
Pasini, D.: Material and shape selection for optimizing flexural vibrations in multilayered resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 15(6), 1745–1758 (2006a). doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2006.885997
Pasini, D.: Shape transformers for material and shape selection of lightweight beams. J. Mater. Des. 28(7), 2071–2079 (2006b)
Pasini, D., Smith, D.J., Burgess, S.C.: Structural efficiency maps for beams subjected to bending. Proc. Instn Mech. Engrs, Part L. J. Mater. Des. Appl. 217(3), 207–220 (2003)
Prasanna, S., Spearing, S.M.: Materials selection and design of microelectrothermal bimaterial actuators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16(2), 248–259 (2007). doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2006.889528
Rakshit, S., Ananthasuresh, G.K.: Simultaneous material selection and geometry design of statically determinate trusses using continuous optimization. J. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 35(1), 55–68 (2008). doi 10.1007/s00158-007-0116-4
Rasmussen, P.A., Thaysen, J., Hansen, O., Eriksen, S.C., Boisen, A.: Optimised cantilever biosensor with piezoresistive read-out. Ultramicroscopy 97(1), 371–376 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0304-3991(03)00063-9
Sader, J.E.: Frequency response of cantilever beams immersed in viscous fluids with applications to the atomic force microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 64–76 (1998). doi:10.1063/1.368002
Sandberg, R., Boisen, A., Svendsen, W.: Characterization system for resonant micro- and nanocantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 125101 (2005a)
Sandberg, R., Mølhave, K., Boisen, A., Svendsen, W.: Effect of gold coating on the Q-factor of a resonant cantilever. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 2249–2253 (2005b). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/12/006
Sandberg, R., Svendsen, W., Mølhave, K., Boisen, A.: Temperature and pressure dependence of resonance in multi-layer microcantilevers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 1454–1458 (2005c). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/8/011
Senturia, S.D.: Microsystem Design. Kluwer, Norwell, MA (2001)
Serre, C., Perez-Rodrıguez, A., Morante, J.R., Gorostiza, P., Esteve, J.: Determination of micromechanical properties of thin films by beam bending measurements with an atomic force microscope. Sens. Actuators 74, 134–138 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(98)00347-1
Shanley, F.R.: Weight–strength Analysis of Aircraft Structures, 2nd edn. New York, Dover (1960)
Sharpe, W.N.: Mechanical properties of MEMS materials, chapter 3. In: Gad-el-Hak, M. (ed.) The MEMS Handbook, pp. 3–33. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (2001)
Shieh, J., Huber, J.E., Fleck, N.A., Ashby, M.F.: The selection of sensors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 461–504 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0079-6425(00)00011-6
Smith, D.J., Partbridge, P.G.: Flexural stiffness envelopes for planar system containing two dissimilar materials. Proc. Instn Mech. Engrs, Part L. J. Mater. Des. Appl. 213, 1–20 (1999)
Sova, M., Bogdan, I.: Coplanar waveguide resonator design for array antenna applications. In: 6th International Conference on Telecommunications in Modern Satellite, Cable and Broadcasting Service, vol. 1, pp. 57–59. Las Alamitos, USA (2003)
Spaepen, F.: Interfaces and stresses in thin films. Acta Mater. 48(1), 31–42 (2000). doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00286-4
Spearing, S.M.: Materials issues in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Acta Mater. 48, 179–196 (2000). doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00294-3
Taka, A.M., Omodaka, A., Takeshima, N., Fujita, H.: Fabrication and operation of polyimide bimorph actuators for a ciliary motion system. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2, 146–150 (1993)
Thaysen, J., Yalcinkaya, A.D., Vettiger, P., Menon, A.: Polymer-based stress sensor with integrated readout. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 35, 2698–2703 (2002). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/35/21/302
Vengallatore, S., Spearing, S.M.: Materials selection for microfabricated electrostatic actuators. Sens. Actuators 102A, 279–285 (2003)
Wang, W., Soper, S.A.: Bio-MEMS; Technologies and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (2006)
Wang, K., Wong, A.-C., Nguyen, C.T.-C.: VHF free–free beam high-Q micromechanical resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 9(3), 347–360 (2000). doi:10.1109/84.870061
Wong, A.C., Nguyen, C.T.-C.: Micromechanical mixer-filters. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13, 100–112 (2004). doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2003.823218
Yang, G.H., Chen, J.B., Pan, F.: The effects of layer thickness on the microstructure and magnetic properties of evaporated Co/Ag films. Phys. Status Solidi A 194(1), 71–80 (2002)
Yue, M., Lin, H., Dedrick, D.E., Satyanarayana, S., Majumdar, A., Bedekar, A.S., Jenkins, J.W., Sundaram, S.: A 2-D microcantilever array for multiplexed biomolecular analysis. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13, 290–299 (2004). doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2003.823216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasini, D. Bend stiffness of laminate microstructures containing three dissimilar materials. Int J Mech Mater Des 5, 175–193 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-008-9093-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-008-9093-z