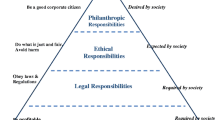
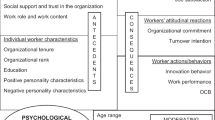
Abstract
Traditionally, corporate governance has focused on the problem of crafting mechanisms to align the interests of owners and managers. The key characteristic has been to minimize the potential for managers to act in their own self-interest at the expense of shareholders. The purpose of this paper is to focus on employees as stakeholders in the governance process. We argue that creating an environment where employees have help in behaving ethically, in the course of their work, is the first step in encouraging them to voice observations of wrongdoing. Seven groups of professionals in the accounting and insurance fields were surveyed during a 10-year period and asked to indicate the extent to which 14 items were helpful in dealing with ethical challenges. Over 2700 responses were analyzed. The findings indicate that professionals think that their organizational culture and policy for voice was more helpful in dealing with ethical dilemmas than was their professional association.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achbar, M. (Producer/Director), J. Abbott (Director) and J. Bakan (Writer): 2004, The Corporation, [Film] Canada: Big Picture Media Corporation.
C. Alford Fred (1999) ArticleTitleWhistle-Blowers American Behavioral Scientist 2 264–77 Occurrence Handle10.1177/00027649921955254
T. Bisoux (2004) ArticleTitleIn Pursuit of Good Governance Biz Ed March/April Vol 3 IssueID3 28–32
R. Beatty E. Zajac (1994) ArticleTitleTop Management Incentives, Monitoring and Risk-Bearing: A Study of Executive Compensation, Ownership and Board Structure in Initial Public Offerings Administrative Science Quarterly 39 313–335
M.M. Blair (1999) Fir-Specific Human Capital and Theories of the Firm M.M. Blair M.J. Roe (Eds) Employees and Corporate Governance Brookings Institution Press Washington D.C
J. Blasi M. Conte D. Kruse (1996) ArticleTitleEmployee Stock Ownership and Corporate Performance among Public Companies Industrial and Labor Relations Review 50 60–78
M. Bommer et al. (1987) ArticleTitleA Behavioral Model of Ethical and Unethical Decision Making Journal of Business Ethics 6 265–280 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00382936
B. Boyd (1994) ArticleTitleBoard Control and CEO Compensation Strategic Management Journal 15 335–344
G.A. Brewer S.C. Selden (1998) ArticleTitleWhistle Blowers in the Federal Civil Service: New Evidence of the Public Service Ethic Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory 8 413–439
J. Child S. Rodrigues (2003) ArticleTitleThe International Crisis of Confidence in Corporations Journal of Management and Governance 7 2133–2140
M. Conyon S. Peck (1998) ArticleTitleBoard Controlremuneration Committees, and Top Management Compensation Academy of Management Journal 41 146–157
W. Crandall J.A. Parnell S. Shadow (1996) ArticleTitleDoes Teaching Business Ethics Really Make a Difference Central Business Review 15 IssueID1 16–19
L.J. Cronbach (1951) ArticleTitleCoefficient Alpha and the Internal Structure of Tests Psychometrika 31 93–96
Darwish, N,. E. Brewer and D.D. Evanoff: 2003, “Corporate Governance: Implications for Financial Services Firms”, Chicago Fed Letter, The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, Dec. no. 197b.
T. Donaldson (1999) ArticleTitleMaking Stakeholder Theory Whole Academy of Management Review 24 IssueID2 237–241
T. Donaldson L.E. Preston (1995) ArticleTitleThe Stakeholder Theory of the Corporation: Concepts, Evidence, and Implications Academy of Management Review Vol. 20 IssueID1 65–91
D.W. Ewing (1983) Do it My Way—or you’re Fired! Employee Rights and the Changing Role of Management Prerogatives John Wiley New York
E.F. Fama (1980) ArticleTitleAgency Problems and the Theory of the Firm Journal of Political Economy 88 288–307 Occurrence Handle10.1086/260866
M.S. Frankel (1989) ArticleTitleProfessional Codes: Why, How, and With What Impact? Journal of Business Ethics 8 109–115 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00382575
R.E. Freeman (1984) Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach Pitman/Ballinger Boston
D.J. Fritzsche (1987) ArticleTitleMarketing/Business Ethics: A Review of Empirical Research Business and Professional Ethics Journal 6 65–79
J.E. Gamble (2000) ArticleTitleManagement Commitment to Innovation and ESOP Stock Concentration Journal of Business Venturing 15 433–447 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0883-9026(99)00037-3
Goodell , R.: 1994, “National Business Ethics Survey Findings”, Ethics Journal Fall/Winter 1, 3 and 5.
A.W. Gouldner (1957) ArticleTitleCosmopolitans and Locals: Toward an Analysis of Latent Social Roles Administrative Science Quarterly 2 281–306
A.W. Gouldner (1958) ArticleTitleCosmopolitans and Locals: Toward an Analysis of Latent Social Roles Administrative Science Quarterly 2 444–480
Gourevitch , Peter: 2003, “Corporate Governance: Global Markets, National Politics”, in M. Kahler and D.A. Lake (eds.), 2003 Governance in a Global Economy (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press).
H. Hansmann (1996) Ownership of Enterprise Harvard University Press Cambridge MA
W.H. Hegarty H.P. Sims SuffixJr. (1979) ArticleTitleOrganizational Philosophy, Policies, and Objectives Related to Unethical Decision Behavior: A Laboratory Experiment Journal of Applied Psychology 64 IssueID3 331–338 Occurrence Handle10.1037//0021-9010.64.3.331
A.J. Hillman G.D. Keim R.A. Luce (2001) ArticleTitleBoard Composition and Stakeholder Performance: Do Stakeholder Directors Make a Difference Business and Society 40 IssueID3 295–315
M.A. Hitt R.D. Ireland R.E. Hoskisson (2003) Strategic Management: Competitiveness ad Globalization, Mason South-Western College Publishing Ohio
M. Huse (2003) ArticleTitleRenewing Management and Governance: New Paradigms of Governance? Journal of Management and Governance 7 211–221 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025004111314
M.C. Jensen (2000) A Theory of the Firm: Governance, Residual Claims, and Organizational Forms Harvard University Press Cambridge Mass
P. Jos M.E. Tompkins S.W. Hays (1989) ArticleTitleIn Praise of Difficult People: A Portrait of the Committed Whistle-blowe Public Administration Review Nov/Dec. 552–561
A.A. Kennedy (2000) The End of Shareholder Value: Corporations at the Crossroads Perseus Publishing Cambridge Mass
R.O. Keohane J.S. Nye SuffixJr. (2000) Introduction J.S. Nye SuffixJr. J.D. Donahue (Eds) Governance in a Globalizing World Brookings Institution Washington D.C 1–41
King, M.: 2004, “Rules are Made to be Broken”, BizEd March/April Vol 3, 3, 35.
T.A. Koachan (2003) ArticleTitleRestoring Trust in American Corporations: Addressing the Root Cause Journal of Management and Governance 7 223–231 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025049223409
E.E. Lawler (1992) The Ultimate Advantage: Creating the High-Involvement Organization Jossey-Bass San Francisco
D.I. Levine (1995) Reinventing the Workplace: How Business and Employees can both Win Brookings Institution Press Washington D.C
L. Lowenstein (1988) What’s Wrong with Wall Street Addison-Wesley Reading Mass
M.P. Miceli J.P. Near (1992) Blowing the Whistle: The Organizational and Legal Implications for Companies and Employees Lexington New York
M.P. Miceli M. Rehg J.P. Near K.C. Ryan (1999) ArticleTitleCan Laws Protect Whistle-blowers Work and Occupations 26 IssueID1 129–52
Millstein, I.M.: 2003, Corporate Goverance: Creating our own Laws as Managers,’ Address delivered to the National Association of Corporate Directors, Annual Corporate Governance Conference, Washington, D.C. , from Vital Speeches of the Day, City News Publishing Co.
E.W. Morrison F.J. Milliken (2000) ArticleTitleOrganizational Silence: A Barrier to Change and Development in a Pluralistic World Academy of Management Review 25 IssueID4 706–725
B.S. Moskal (1991) ArticleTitleIs Industry Ready for Adult Relationships? Industry Week, January 21 18–25
P.E. Murphy (1988) ArticleTitleImplementing Business Ethics Journal of Business Ethics 7 907–915
J.P. Near M.P. Miceli (1985) ArticleTitleOrganizational Dissidence: The Case of Whistle-Blowing Journal of Business Ethics 4 1–16 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00382668
C.J. Nemeth (1997) ArticleTitleManaging Innovation: When Less is More California Management Review 1 59–74
Nephin, D.: 2003, ‘Ethics Hotlines Heating up at Corporations’, The Network.
J. Pencavel (2001) Worker Participation: Lessons from the Worker Co-ops of the Pacific Northwest Russell Sage Foundation New York
J.L. Perry (1993) Whistle-Blowing, Organizational Performance, and Organizational Control H.G. Frederickson (Eds) Ethics and Public Administration M.E. Sharpe Armonk NY 79–99
J. Pfeffer (1994) Competitive Advantage through People Harvard Business School Press Boston
J.A. Raelin (1985) The Clash of Cultures Harvard Business School Press Boston
J.A. Raelin (1989) ArticleTitleProfessional and Business Ethics: Bridging the Gap Management Review 78 39–42
Rich, A.J., S.S. Smith and P.H. Mihalek:1990, ‘Are Corporate Codes of Conduct Effective?’ Management Accounting September, 34–35.
J. Rothschild T.D. Miethe (1999) ArticleTitleWhistle-Blower Disclosures and Management Retaliation Work and Occupations 26 IssueID1 107–29
K.D. Ryan D.K. Oestreich (1991) Driving Fear Out of the Workplace: How to overcome the Invisible Barriers to Quality, Productivity, and Innovation Jossey-Bass San Francisco
E.H. Schein (1985) Organizational Culture and Leadership Jossey-Bass San Francisco
M.E. Schnake M.P. Dumler D.S. Cochran T.R. Barnett (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of Differences in Superior and Subordinate Perception of Superiors’ Communication Practices Journal of Business Communication 27 37–50
J.A. Schweikart (1992) ArticleTitleCognitive-Contingency Theory and the Study of Ethics in Accounting Journal of Business Ethics 11 471–478 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00870558
Shinn, J.: 2001, “Private Profit or Public Convergence?” Unpublished manuscript, Princeton University, in M. Kahler and D.A. Lake (eds.), 2003, ‘Governance in a Global Economy (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press).
R.R. Sims (1992) ArticleTitleThe Challenge of Ethical Behavior in Organizations Journal of Business Ethics 11 505–513 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00881442
G.M. Spreitzer (1995) ArticleTitlePsychological Empowerment in the Workplace: Dimensions, Measurement, and Validation Academy of Management Journal 38 1442–1465
L. Sprague G.L. Ruud (1988) ArticleTitleBoat-rocking in the High-Technology Culture American Behavioral Scientist 32 169–193
J. Stevens (1986) Applied Multivariate Statistics for the Social Sciences Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Hillsdale NJ
L.K. Trevino (1986) ArticleTitleEthical Decision Making in Organizations: A Person-Situation Interactionist Model Academy of Management Review 11 601–618
B. Victor J.B. Cullen (1988) ArticleTitleThe Organizational Bases of Ethical Work Climates Administrative Science Quarterly 33 101–125
J.A. Waters F. Bird (1987) ArticleTitleThe Moral Dimension of Organizational Culture Journal of Business Ethics 6 15–22 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00382944
O.E. Williamson (1985) The Economic Institutions of Capitalism The Free Press New York
M. Wood T. Patrick (2003) ArticleTitleJumping on the Bandwagon: Outside Representation in Corporate Governance Journal of Business and Economic Studies. 9 IssueID2 48–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clapham, S.E., Cooper, R.W. Factors of Employees’ Effective Voice in Corporate Goverance*. J Manage Governance 9, 287–313 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-005-7421-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-005-7421-3