Abstract
Objective
Women frequently report breastfeeding problems in the early postpartum period. Women who have self-endorsed beliefs that breastfeeding benefits their babies and themselves are more likely to continue breastfeeding despite breastfeeding barriers. Maternal self-endorsed beliefs is a key component of maternal self-regulated motivation. The present study examined the association between maternal self-regulated motivation, breastfeeding duration and exclusivity in Chinese women.
Methods
This was a prospective cohort study, of which we recruited participants in postnatal maternity units of publicly funded hospitals in Hong Kong. Postpartum women were asked to fill in the validated breastfeeding self-regulation questionnaire (BSRQ) before hospital discharge and their breastfeeding status was assessed by telephone follow-ups at 6 and 12 weeks postpartum. Multiple logistic regression was used to study the relationship between breastfeeding self-regulated motivation and the duration of breastfeeding at follow-up.
Results
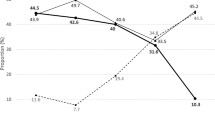
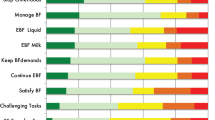
At 6 and 12 weeks postpartum, women who breastfed exclusively scored significantly higher in self-regulated motivation than those who formula-fed. The self-regulated motivation was associated with higher odds of exclusive breastfeeding at 6 weeks and any breastfeeding at 12 weeks postpartum.
Conclusions for Practice
The study found that self-regulated motivation was positively related to breastfeeding duration. Maternal self-regulated motivation toward breastfeeding could be enhanced by the availability of social support and breastfeeding-friendly facilities, resulting in longer breastfeeding duration.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 January 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-021-03347-5
References
Bai, D. L., Fong, D. Y. T., & Tarrant, M. (2015a). Previous breastfeeding experience and duration of any and exclusive breastfeeding among multiparous mothers. Birth, 42(1), 70–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/birt.12152
Bai, D. L., Fong, D. Y. T., & Tarrant, M. (2015b). Factors associated with breastfeeding duration and exclusivity in mothers returning to paid employment postpartum. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 19(5), 990–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-014-1596-7
BouDiab, S., & Werle, C. (2018). What motivates women to breastfeed in Lebanon: An exploratory qualitative analysis. Appetite, 123, 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2017.12.002
Chatterjee, S., & Hadi, A. S. (2015). Regression analysis by example. Wiley.
Dennis, C.-L. (1999). Theoretical underpinnings of breastfeeding confidence: A self-efficacy framework. Journal of Human Lactation, 15(3), 195–201. https://doi.org/10.1177/089033449901500303
Department of Health, HKSAR. (2019). Breastfeeding survey 2019. Retrieved May 2020, from https://www.fhs.gov.hk/english/archive/files/reports/BF_survey_2019.pdf.
Dietrich Leurer, M., & Misskey, E. (2015). “Be positive as well as realistic”: A qualitative description analysis of information gaps experienced by breastfeeding mothers. International Breastfeeding Journal, 10(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-015-0036-7
Elliott-Rudder, M., Pilotto, L., McIntyre, E., & Ramanathan, S. (2014). Motivational interviewing improves exclusive breastfeeding in an Australian randomised controlled trial. Acta Paediatrica, 103(1), e11–e16. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.12434
Fu, I., Fong, D., Heys, M., Lee, I., Sham, A., & Tarrant, M. (2014). Professional breastfeeding support for first-time mothers: A multicentre cluster randomised controlled trial. BJOG, 121(13), 1673–1683. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12884
Hair, J. F. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Prentice Hall.
Hegney, D., Fallon, T., & O’Brien, M. L. (2008). Against all odds: A retrospective case-controlled study of women who experienced extraordinary breastfeeding problems. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 17(9), 1182–1192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02300.x
Hosmer, D. W., Hosmer, T., Le Cessie, S., & Lemeshow, S. (1997). A comparison of goodness-of-fit tests for the logistic regression model. Statistics in Medicine, 16(9), 965–980. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19970515)16:9%3c965::AID-SIM509%3e3.0.CO;2-O
Hospital Authority. (2016). Hosptial authority statistical report 2014–2015. Retrieved September 28, 2018, from www.ha.org.hk/haho/ho/stat/HASR1415_2.pdf
Kestler-Peleg, M., Shamir-Dardikman, M., Hermoni, D., & Ginzburg, K. (2015). Breastfeeding motivation and self-determination Theory. Social Science & Medicine, 144, 19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.09.006
Labbok, M., & Krasovec, K. (1990). Toward consistency in breastfeeding definitions. Studies in Family Planning, 21(4), 226–230.
Lau, C. Y. K., Fong, D. Y. T., Choi, A. Y. Y., Ng, J. W. Y., Sing, C., & Tarrant, M. (2017). Development and measurement properties of the Chinese breastfeeding self-regulation questionnaire. Midwifery, 44, 24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2016.10.012
Lau, C. Y. K., Lok, K. Y. W., & Tarrant, M. (2018). Breastfeeding duration and the theory of planned behavior and breastfeeding self-efficacy framework: A systematic review of observational studies. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 22(3), 327–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-018-2453-x
Lok, K., Bai, D. L., & Tarrant, M. (2015). Predictors of breastfeeding initiation in Hong Kong and Mainland China born mothers. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0719-5
Lok, K. Y. W., Bai, D. L., & Tarrant, M. (2017). Family members’ infant feeding preferences, maternal breastfeeding exposures and exclusive breastfeeding intentions. Midwifery, 53, 49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2017.07.003
Miller, W. R., & Rollnick, S. (2013). Motivational interviewing: Helping people change. Retrieved http://public.eblib.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=1034770
Mizrak Sahin, B., Ozerdogan, N., Ozdamar, K., & Gursoy, E. (2019). Factors affecting breastfeeding motivation in primiparious mothers: An application of breastfeeding motivation scale based on self-determination theory. Health Care for Women International, 40(6), 637–652. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2018.1526289
Muelbert, M., & Giugliani, E. R. J. (2018). Factors associated with the maintenance of breastfeeding for 6, 12, and 24 months in adolescent mothers. BMC Public Health, 18(1), 675. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5585-4
Racine, E. F., Frick, K. D., Strobino, D., Carpenter, L. M., Milligan, R., & Pugh, L. C. (2009). How motivation influences breastfeeding duration among low-income women. Journal of Human Lactation, 25(2), 173–181. https://doi.org/10.1177/0890334408328129
Ryan, R. M. (2012). Motivation, personality, and development within embedded social contexts: An overview of self-determination theory. The Oxford handbook of human motivation (pp. 85–107). Oxford University Press.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2017). Self-determination theory: Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness. Guilford Press.
Spencer, R. L., Greatrex-White, S., & Fraser, D. M. (2015). ‘I thought it would keep them all quiet’. Women’s experiences of breastfeeding as illusions of compliance: An interpretive phenomenological study. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 71(5), 1076–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.12592
Symon, A. G., Whitford, H., & Dalzell, J. (2013). Infant feeding in Eastern Scotland: A longitudinal mixed methods evaluation of antenatal intentions and postnatal satisfaction—The feeding your baby study. Midwifery, 29(7), e49–e56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2012.06.017
Tarrant, M., Dodgson, J. E., & Wu, K. M. (2014). Factors contributing to early breast-feeding cessation among Chinese mothers: An exploratory study. Midwifery, 30(10), 1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2014.03.002
Tarrant, M., Fong, D. Y., Wu, K. M., Lee, I. L., Wong, E. M., Sham, A., Lam, C., & Dodgson, J. E. (2010). Breastfeeding and weaning practices among Hong Kong mothers: A prospective study. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-10-27
Tarrant, M., Lok, K. Y. W., Fong, D. Y. T., Wu, K. M., Lee, I. L. Y., Sham, A., Lam, C., Bai, D. L., Wong, K. L., Wong, E. M. Y., Chan, N. P. T., & Dodgson, J. E. (2016). Effect on baby-friendly hospital steps when hospitals implement a policy to pay for infant formula. Journal of Human Lactation, 32(2), 238–249. https://doi.org/10.1177/0890334415599399
UCLA Statistical Consulting Group. Stata data analysis examples: Logistic regression power analysis. From https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stata/dae/logistic-regression-power-analysis/. Assessed 28 September 2018. (n.d.).
Wallenborn, J. T., Perera, R. A., Wheeler, D. C., Lu, J., & Masho, S. W. (2019). Workplace support and breastfeeding duration: The mediating effect of breastfeeding intention and self-efficacy. Birth, 46(1), 121–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/birt.12377
Wells, K. J., Thompson, N. J., & Kloeblen-Tarver, A. S. (2002). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and intention to breast-feed. American Journal of Health Behavior, 26(2), 111–120.
World Health Organization. (2003). Global strategy for infant and young child feeding. WHO.
World Health Organization. (2008). Indicators for assessing infant and young child feeding practices: Part I definition. WHO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, C.Y.K., Fong, D.Y.T., Chan, V.H.S. et al. The Effect of Maternal Self-Regulated Motivation on Breastfeeding Continuation. Matern Child Health J 26, 441–448 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-021-03274-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-021-03274-5