Abstract
Objectives
To describe the prevalence of overweight and obesity among children under 5 years old, assess the indicators of breastfeeding practices, and explore the associations between breastfeeding practices and early childhood overweight/obesity.
Methods
The survey was conducted in 20 counties in central and western China in 2016. All children under 5 years old were physically measured for anthropometric data and their breastfeeding practices were obtained through a face-to-face questionnaire interview. We performed logistic regressions to assess the associations of different breastfeeding practices with overweight/obesity.
Results
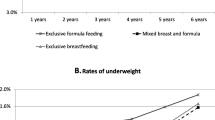
The prevalence of overweight and obesity among children under 5 years old were 8.7% and 2.6%, respectively. Overall, 93.6% of children were breastfed, while only 20.7% had exclusive breastfeeding under 6 months of age and about half of the children under 5 years old were weaned at 12 months. Compared with children with a duration of breastfeeding ≥ 12 months, children who have been breastfed for < 6 months were significantly associated with a 97% increased risk of overweight/obesity (OR 1.97, 95% CI 1.34–2.88, P = 0.001).
Conclusions for Practice
The present study showed that overweight and obesity among children under 5 years old in central and western China remained an important childhood health concern. The rates of most indicators of breastfeeding practices were low, which needed more public attention. Moreover, we found that a shorter duration of breastfeeding was associated with an increased risk of overweight/obesity among children in central and western China.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajala, O., Mold, F., Boughton, C., Cooke, D., & Whyte, M. (2017). Childhood predictors of cardiovascular disease in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews,18(9), 1061–1070.
Bartok, C. J., & Ventura, A. K. (2009). Mechanisms underlying the association between breastfeeding and obesity. The International Journal of Paediatric Obesity,4(4), 196–204.
Escribano, J., Luque, V., Ferre, N., Mendez-Riera, G., Koletzko, B., Grote, V., et al. (2012). Effect of protein intake and weight gain velocity on body fat mass at 6 months of age: The EU Childhood Obesity Programme. International Journal of Obesity,36(4), 548–553.
Guo, S., Fu, X., Scherpbier, R. W., Wang, Y., Zhou, H., Wang, X., et al. (2013). Breastfeeding rates in central and western China in 2010: Implications for child and population health. Bulletin of the World Health Organization,91(5), 322–331.
Harder, T., Bergmann, R., Kallischnigg, G., & Plagemann, A. (2005). Duration of breastfeeding and risk of overweight: A meta-analysis. American Journal of Epidemiology,162(5), 397–403.
Hosseini, M., Navidi, I., Hesamifard, B., Yousefifard, M., Jafari, N., Poorchaloo, S. R., et al. (2013). Weight, height and body mass index nomograms; Early adiposity rebound in a sample of children in tehran, iran. International Journal of Preventive Medicine,4(12), 1414–1420.
Jing, H., Xu, H., Wan, J., Yang, Y., Ding, H., Chen, M., et al. (2014). Effect of breastfeeding on childhood BMI and obesity: The China Family Panel Studies. Medicine,93(10), e55.
Jingxiong, J., Rosenqvist, U., Huishan, W., Koletzko, B., Guangli, L., Jing, H., et al. (2009). Relationship of parental characteristics and feeding practices to overweight in infants and young children in Beijing China. Public Health Nutrition,12(7), 973–978.
Li, H. (2006). (2008) A national epidemiological survey on obesity of children under 7 years of age in nine cities of China. Chinese Journal of Paediatrics,46(3), 174–178.
Liang, Y., Hou, D., Zhao, X., Wang, L., Hu, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2015). Childhood obesity affects adult metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Endocrine,50(1), 87–92.
Liu, P., Qiao, L., Xu, F., Zhang, M., Wang, Y., & Binns, C. W. (2013). Factors associated with breastfeeding duration: A 30-month cohort study in northwest China. Journal of Human Lactation,29(2), 253–259.
Lo, J. C., Maring, B., Chandra, M., Daniels, S. R., Sinaiko, A., Daley, M. F., et al. (2014). Prevalence of obesity and extreme obesity in children aged 3–5 years. Pediatric Obesity,9(3), 167–175.
Moons, K. G., Donders, R. A., Stijnen, T., & Harrell, F. J. (2006). Using the outcome for imputation of missing predictor values was preferred. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology,59(10), 1092–1101.
Moreno, L. A., & Rodriguez, G. (2007). Dietary risk factors for development of childhood obesity. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care,10(3), 336–341.
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). (2017). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet,390(10113), 2627–2642.
Savino, F., & Liguori, S. A. (2008). Update on breast milk hormones: Leptin, ghrelin and adiponectin. Clinical Nutrition,27(1), 42–47.
Tchoubi, S., Sobngwi-Tambekou, J., Noubiap, J. J., Asangbeh, S. L., Nkoum, B. A., & Sobngwi, E. (2015). Prevalence and risk factors of overweight and obesity among children aged 6–59 months in cameroon: A multistage, stratified cluster sampling nationwide survey. PLoS ONE,10(12), e0143215.
United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (2009) UNICEF MICS Tools. Sampling: Designing and Selecting the Sample. Retrieved 22 May 2018 from: Http://mics.unicef.org/tools?round=mics4.
Uwaezuoke, S., Eneh, C., & Ndu, I. (2017). Relationship between exclusive breastfeeding and lower risk of childhood obesity: A narrative review of published evidence (p. 11). Clinical Medicine Insights: Pediatrics.
Wang, A., Scherpbier, R. W., Huang, X., Guo, S., Yang, Y., Josephs-Spaulding, J., et al. (2017). The dietary diversity and stunting prevalence in minority children under 3 years old: A cross-sectional study in forty-two counties of Western China. British Journal of Nutrition,118(10), 840–848.
Ward, Z. J., Long, M. W., Resch, S. C., Giles, C. M., Cradock, A. L., & Gortmaker, S. L. (2017). Simulation of growth trajectories of childhood obesity into adulthood. New England Journal of Medicine,377(22), 2145–2153.
World Health Organization (2008) Indicators for assessing infant and young child feeding practices (Part I). Retrieved 8 Oct 2018 from: Http://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/infantfeeding/9789241596664/en/.
World Health Organization (2009) Infant and young child feeding: Model chapter for textbooks for medical students and allied health professionals. WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee: World Health Organization. Geneva.
World Health Organization (2012) Born too soon: The global action report on preterm births. Retrieved 29 Sep 2018 from: Https://www.who.int/pmnch/media/news/2012/201204_borntoosoon-report.pdf.
World Health Organization (2017) Obesity and overweight. Retrieved 8 Oct 2018 from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/..
Xie, S., Wang, J., Li, N., Jiang, W., Yang, S., Li, X., et al. (2014). Survey on overweight and obesity of preschool children in rural areas from ten provinces of China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi,35(4), 425–428.
Xu, F., Binns, C., Wu, J., Yihan, R., Zhao, Y., & Lee, A. (2007a). Infant feeding practices in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, People's Republic of China. Public Health Nutrition,10(2), 198–202.
Xu, F., Binns, C., Yu, P., & Bai, Y. (2007b). Determinants of breastfeeding initiation in Xinjiang, PR China, 2003–2004. Acta Paediatrica,96(2), 257–260.
Yan, J., Liu, L., Zhu, Y., Huang, G., & Wang, P. P. (2014). The association between breastfeeding and childhood obesity: A meta-analysis. BMC Public Health,14, 1267.
Zhang, J., Himes, J. H., Guo, Y., Jiang, J., Yang, L., Lu, Q., et al. (2013). Birth weight, growth and feeding pattern in early infancy predict overweight/obesity status at two years of age: A birth cohort study of Chinese infants. PLoS ONE,8(6), e64542.
Zheng, J. S., Liu, H., Li, J., Chen, Y., Wei, C., Shen, G., et al. (2014). Exclusive breastfeeding is inversely associated with risk of childhood overweight in a large Chinese cohort. Journal of Nutrition,144(9), 1454–1459.
Zhou, H., Wang, X. L., Ye, F., Zeng, X. L., & Wang, Y. (2012). Relationship between child feeding practices and malnutrition in 7 remote and poor counties, P R China. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition,21(2), 234–240.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the effort and support of all the participants from 20 surveyed counties of 10 provinces (Sajia and Angren County of Tibet, Chabuchaer and Zhaosu County of Xinjiang, Sinan and Dejiang County of Guizhou, Datong and Huangzhong County of Qinghai, Yulong and Huaping County of Yunnan, Yuexi and Ganluo County of Sichuan, Wen and Qinyang County of Henan, Yudu and Gan County of Jiangxi, She and Quzhou County of Hebei, Hongsibao and Tongxin County of Ningxia).
Funding
This study was funded by UNICEF China (“Health, Nutrition and WASH” [NO. 501]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Committee of Peking University Health Science Centre.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was provided by all caregivers of the children prior to their inclusion in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Q., Yang, Y., Liu, X. et al. Breastfeeding Practices and Overweight/Obesity Among Children Under 5 Years of Age: A Multistage Random Sampling Survey in Central and Western China. Matern Child Health J 24, 998–1007 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-020-02945-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-020-02945-z