Abstract
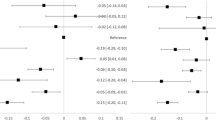
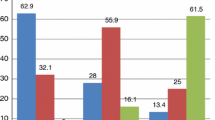
Introduction There is limited research on the relation between weight misperceptions and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among U.S. adolescents. Methods Baseline data (n = 1509) collected in 2012 from the Team Up for Healthy Living project were used. Measures included BMI percentiles calculated from measured height and weight; self-perception of weight status; and the 23-item PedsQL™ Inventory. Multiple linear regression was performed after adjustment for covariates to examine associations between weight misperception and HRQoL. Results Compared to accurate weight perception, weight underestimation was associated with higher total HRQoL (β = 2.41), physical health (β = 2.77), and emotional (β = 2.83), social (β = 2.47) and psychosocial functioning (β = 2.38) (all p < 0.05). Weight overestimation was associated with lower social functioning (β = −13.13, p < 0.05). Stratified by gender, associations were observed only in males. Discussion Weight underestimation had greater association with HRQoL than weight overestimation; and varied by gender. Better understanding of these associations will assist in improving the health of adolescents in Southern Appalachia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M. M., Fang, H., & Rizzo, J. A. (2010). Body weight, self-perception and mental health outcomes among adolescents. Journal of Mental Health Policy and Economics, 13(2), 53–63.
Beck, J., Schaefer, C. A., Nace, H., Steffen, A. D., Nigg, C., Brink, L., et al. (2012). Accuracy of self-reported height and weight in children aged 6 to 11 years. Preventing Chronic Disease. doi:10.5888/pcd9.120021.
Blashill, A. J., & Wilhelm, S. (2014). Body image distortions, weight, and depression in adolescent boys: Longitudinal trajectories into adulthood. Psychology of Men and Masculinity, 15(4), 445–451.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2009). Estimated county-level prevalence of diabetes and obesity-United States, 2007. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 58(45), 1259–1263.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2014, October 27-last update). Health-related quality of life (HQROL). http://www.cdc.gov/hrqol/index.htm. Accessed 12 Dec 2014.
Chung, A. E., Perrin, E. M., & Skinner, A. C. (2013). Accuracy of child and adolescent weight perceptions and their relationships to dieting and exercise behaviors: A NHANES study. Academy of Pediatrics,. doi:10.1016/j.acap.2013.04.011.
Dalton, W. T., I. I. I., Wang, L., Southerland, J. L., Schetzina, K. E., & Slawson, D. L. (2014). Utilizing self-reported versus actual weight and height data contributes to different weight misperception classifications. Southern Medical Journal,. doi:10.14423/01.SMJ.0000450708.52011.7c.
Davis, R. E., Armstrong, D. K., Dignan, M., Norling, G. R., & Redmond, J. (2006). Evaluation of educational materials on colorectal cancer screening in Appalachian Kentucky. Preventing Chronic Disease [serial online]. http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2006/apr/05_0030.htm. Accessed 13 April 2016.
de la Haye, K., Robins, G., Mohr, P., & Wilson, C. (2010). Obesity-related behaviors in adolescent friendship networks. Social Networks,. doi:10.1016/j.socnet.2009.09.001.
Edwards, N. M., Pettingell, S., & Borowsky, I. W. (2010). Where perception meets reality: Self-perception of weight in overweight adolescents. Pediatrics,. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-0185.
Farhat, T., Iannotti, R. J., & Summersett-Ringgold, F. (2015). Weight, weight perceptions, and health-related quality of life among a national sample of US girls. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics,. doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000000172.
Ferrans, C. E., Zerwic, J. J., Wilbur, J. E., & Larson, J. L. (2005). Conceptual model of health-related quality of life. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 37, 336–342.
Fletcher, A., Bonell, C., & Sorhaindo, A. (2011). You are what your friends eat: a systematic review of social network analyses of young people’s eating behaviors and bodyweight. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health,. doi:10.1136/jech.2010.113936.
Haraldstad, K., Christophersen, K. A., Eide, H., Nativg, G. K., & Helseth, S. (2011). Predictors of health-related quality of life in a sample of children and adolescents: a school survey. Journal of Clinical Nursing,. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03693.x.
Hayward, J., Millar, L., Petersen, S., Swinburn, B., & Lewis, A. J. (2014). When ignorance is bliss: Weight perception, body mass index and quality of life in adolescents. International Journal of Obesity,. doi:10.1038/ijo.2014.78.
Heshmat, R., Kelishadi, R., Motamed-Gorji, N., Motlagh, M. E., Ardalan, G., Arifirad, T., et al. (2015). Association between body mass index and perceived weight status with self-rated health and life satisfaction in Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-III study. Quality of Life Research,. doi:10.1007/s11136-014-0757-x.
Jansen, W., van de Looij-Jansen, P. M., de Wilde, E. J., & Brug, J. (2008). Feeling fat rather than being fat may be associated with psychological well-being in young Dutch adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health,. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.07.015.
Kurth, B. M., & Ellert, U. (2008). Perceived or true obesity: Which causes more suffering in adolescents? Findings of the German health interview and examination survey for children and adolescents (KiGGs). Dtsch Arztebl Int,. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2008.0406.
Martin, B. C., Dalton, W. T., I. I. I., Williams, S. L., Slawson, D. L., Dunn, M. S., & Johns-Wommack, R. (2014). Weight status misperception as related to selected health risk behaviors among middle school students. Journal of School Health,. doi:10.1111/josh.12128.
Maximova, K., McGrath, J. J., Barnett, T., O’Loughlin, J., Paradis, G., & Lambert, M. (2008). Do you see what I see? Weight status misperception and exposure to obesity among children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity,. doi:10.1038/ijo.2008.15.
National Survey of Child’s Health (NSCH). (2012). NSCH 2011/12. Data query from the child & adolescent health measurement initiative, data resource center for child and adolescent health. http://www.childhealthdata.org/home. Accessed 9 Nov 2014.
National Survey of Child’s Health (NSCH). (2016). Report from the National Survey of Children’s Health. NSCH 2011/12. Child and adolescent health measurement initiative, data resource center for child and adolescent health website. http://www.childhealthdata.org. Accessed 5 Jan 2016.
Nelson, T. D., Kidwell, K. M., Hoffman, S., Trout, A. L., Epstein, M. H., & Thompson, R. W. (2014). Health-related quality of life among adolescents in residential care: description and correlates. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 84(3), 226–233. doi:10.1037/h0099812.
Ogden, C. L., Carroll, M. D., Kit, B. K., & Flegal, K. M. (2012). Prevalence of obesity and trends in body mass index among U.S. children and adolescents, 1999–2010. Journal of the American Medical Association,. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.40.
Ogden, C. L., Carroll, M. D., Kit, B. K., & Flegal, K. M. (2014). Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. Journal of the American Medical Association,. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.732.
Palermo, T. M., Long, A. C., Lewandowski, A. S., Drotar, D., Quittner, A. L., & Walker, L. S. (2008). Evidence-based assessment of health-related quality of life and functional impairment in pediatric psychology. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 33, 983–996.
Park, E. (2011). Overestimation and underestimation: Adolescents’ weight perception in comparison to BMI-based weight status and how it varies across socio-demographic factors. Journal of School Health,. doi:10.1111/j.1746-1561.2010.00561.x.
Petracci, E., & Cavrini, G. (2013). The effect of weight status, lifestyle, and body image perception on health-related quality of life in children: a quantile approach. Quality of Life Research,. doi:10.1007/s11136-013-0358-0.
Schafer, M. H., & Ferraro, K. F. (2011). The stigma of obesity. Does perceived weight discrimination affect identity and physical health? Social Psychology Quarterly,. doi:10.1177/0190272511398197.
Slawson, D., Dalton, W. T., I. I. I., Dula, T. M., Southerland, J. L., Wang, L., Littleton, M. A., et al. (2015). College students as facilitators in reducing adolescent obesity disparity in Southern Appalachia: Team Up for Healthy Living. Contemporary Clinical Trials,. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2015.04.012.
Southerland, J., Wang, L., Richards, K., Pack, R., & Slawson, D. L. (2013). Misperceptions of overweight: Associations of weight misperception with health-related quality of life among normal-weight college students. Public Health Reports, 128(6), 562–568.
Sutin, A. R., & Terracciano, A. (2015). Body weight misperception in adolescence and incident obesity in young adulthood. Psychological Science,. doi:10.1177/0956797614566319.
Ul-Haq, Z., Mackay, D. F., Fenwick, E., & Pell, J. P. (2013). Meta-analysis of the association between body mass index and health-related quality of life among children and adolescents, assessed using the pediatric quality of life inventory index. Journal of Pediatrics,. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.07.049.
Varni, J., Seid, M., & Kurtin, P. S. (2001). PedsQL™ 4.0: Reliability and validity of the pediatric quality of life inventory™ version 4.0 generic core scales in healthy and patient populations. Medical Care, 39(8), 800–812.
Wang, L., Slawson, D. L., Relyea, G., Southerland, J. L., & Wang, Y. (2014). Prevalence and risk factors for adolescent obesity in Southern Appalachia, 2012. Preventing Chronic Disease,. doi:10.5888/pcd11.140348.
Williams, K. J., Taylor, C. A., Wolf, K. N., Lawson, R. F., & Crespo, R. (2008). Cultural perceptions of healthy weight in rural Appalachian youth. Rural and Remote Health, 8(2), 932.
World Health Organization (WHO). (1948). Constitution of the World Health Organization Basic Document. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
Acknowledgments
The project described was supported by Grant Number R01MD006200 from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Southerland, J.L., Wang, L. & Slawson, D.L. Weight Misperception and Health-Related Quality of Life in Appalachian Adolescents in the United States. Matern Child Health J 21, 168–176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-016-2106-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-016-2106-x