Abstract
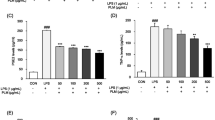
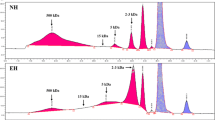
In this study, the immunomodulatory function of egg white peptides (EWP) was evaluated using RAW264.7 macrophage cells and an immunosuppressive BALB/c mice model. In vitro, 100 μg/mL EWP significantly increased cell viability and upregulated expression of immunomodulators (NO, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α) in RAW264.7 cells, which contributed to macrophage activation. In vivo, 150 mg/kg/day EWP alleviated splenomegaly and rebound thymic hyperplasia in BALB/c mice during recovery from immunosuppression. Numbers of white blood cells in peripheral blood and levels of cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α) in spleen tissue were significantly increased in mice given 150 mg/kg/day EWP. Spleen pathological changes and oxidation degree showed that EWP promoted the recovery of spleen tissue from immunosuppression and oxidation. Oligopeptides with common characteristics of immunomodulatory peptides might be responsible for the immunomodulatory function of EWP. Therefore, EWP may be considered as a natural immunomodulator that can help immune function recover from immunosuppressive state.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anet J, Back JF, Baker RS, Barnett D, Burley RW, Howden M (2009) Allergens in the white and yolk of Hen’s egg. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 77(3):364–371. https://doi.org/10.1159/000233846
Chalamaiah M, Yu W, Wu J (2018) Immunomodulatory and anticancer protein hydrolysates (peptides) from food proteins: a review. Food Chem 245:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.087
Chan CC, Caspi R, Mochizuki M, Diamantstein T, Gery I, Nussenblatt RB (1987) Cyclosporine and dexamethasone inhibit T-lymphocyte MHC class II antigens and IL-2 receptor expression in experimental autoimmune uveitis. Immunol Investig 16(4):319–331. https://doi.org/10.3109/08820138709087087
Chen MW, Zhang F, Su YJ, Chang CH, Li JH, Gu LP, Yang YJ (2022) Immunomodulatory effects of egg white peptides on immunosuppressed mice and sequence identification of immunomodulatory peptides. Food Biosci 49:101873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101873
Chertoff J, Barth RA, Dickerman JD (1991) Rebound thymic hyperplasia five years after chemotherapy for Wilms’ tumor. Pediatr Radiol 21(8):596–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02012609
den Haan JM, Mebius RE, Kraal G (2012) Stromal cells of the mouse spleen. Front Immunol 3:201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00201
Gao S, Hong H, Zhang CY, Wang K, Zhang BH, Han QA, Liu HG, Luo YK (2019) Immunomodulatory effects of collagen hydrolysates from yak (Bos grunniens) bone on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in BALB/c mice. J Funct Foods 60:103420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103420
Gostner J, Becker K, Ueberall F, Fuchs D (2015) The good and bad of antioxidant foods: an immunological perspective. Food Chem Toxicol 80:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.02.012
Han M, Zhang Z, Li X, Tong H, Xu Z, Ding Z, Yang A, Xie M, Wang X (2022) Effects of collagen peptides from Micropterus salmoides skin on oxidative damage induced by cyclophosphamide in mice. Front Nutr 9:1037212. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.1037212
Harris J, Sengar D, Stewart T, Hyslop D (1976) The effect of immunosuppressive chemotherapy on immune function in patients with malignant disease. Cancer 37(2 Suppl):1058–1069. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(197602)37:2+%3c1058::aid-cncr2820370813%3e3.0.co;2-o
He K, Zeng Y, Tian HQ, Zhang ZW, Zhang HZ, Huang FF, Yu FM (2021a) Macrophage immunomodulatory effects of low molecular weight peptides from Mytilus coruscus via NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways. J Funct Foods 83:104562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2021.104562
He P, Wang Q, Zhan Q, Pan L, Xin X, Wu H, Zhang M (2021b) Purification and characterization of immunomodulatory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of duck egg ovalbumin. Food Funct 12(2):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo02674c
Jacquot A, Gauthier SF, Drouin R, Boutin Y (2010) Proliferative effects of synthetic peptides from β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin on murine splenocytes. Int Dairy J 20(8):514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2010.02.013
Jia L, Wang L, Liu C, Liang Y, Lin Q (2021) Bioactive peptides from foods: production, function, and application. Food Funct 12(16):7108–7125. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo01265g
Karachi A, Yang C, Dastmalchi F, Sayour EJ, Huang J, Azari H, Long Y, Flores C, Mitchell DA, Rahman M (2019) Modulation of temozolomide dose differentially affects T-cell response to immune checkpoint inhibition. Neuro Oncol 21(6):730–741. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz015
Kasimu R, Chen C, Xie X, Li X (2017) Water-soluble polysaccharide from Erythronium sibiricum bulb: structural characterisation and immunomodulating activity. Int J Biol Macromol 105(Pt 1):452–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.060
Kelly B, Pearce EL (2020) Amino assets: how amino acids support immunity. Cell Metab 32(2):154–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.010
Koopman R, Crombach N, Gijsen AP, Walrand S, Fauquant J, Kies AK, Lemosquet S, Saris WH, Boirie Y, van Loon LJ (2009) Ingestion of a protein hydrolysate is accompanied by an accelerated in vivo digestion and absorption rate when compared with its intact protein. Am J Clin Nutr 90(1):106–115. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.27474
Kumar BV, Connors TJ, Farber DL (2018) Human T cell development, localization, and function throughout life. Immunity 48(2):202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.01.007
Lewis SM, Williams A, Eisenbarth SC (2019) Structure and function of the immune system in the spleen. Sci Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.aau6085
Li WJ, Li L, Zhen WY, Wang LF, Pan M, Lv JQ, Wang F, Yao YF, Nie SP, Xie MY (2017) Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide ameliorates ROS generation and apoptosis in spleen and thymus of immunosuppressed mice. Food Chem Toxicol 99:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.11.033
Liu J, Sun H, Nie C, Ge W, Wang Y, Zhang W (2018) Oligopeptide derived from solid-state fermented cottonseed meal significantly affect the immunomodulatory in BALB/c mice treated with cyclophosphamide. Food Sci Biotechnol 27(6):1791–1799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0414-1
Lozano-Ojalvo D, Martinez-Blanco M, Perez-Rodriguez L, Molina E, Lopez-Fandino R (2019a) Oral immunotherapy with egg peptides induces innate and adaptive tolerogenic responses. Mol Nutr Food Res 63(17):e1900144. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201900144
Lozano-Ojalvo D, Martinez-Blanco M, Perez-Rodriguez L, Molina E, Pelaez C, Requena T, Lopez-Fandino R (2019b) Egg white peptide-based immunotherapy enhances vitamin A metabolism and induces ROR gamma t(+) regulatory T cells. J Funct Foods 52:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.11.012
Manente FA, Quinello C, Ferreira LS, de Andrade CR, Jellmayer JA, Portuondo DL, Batista-Duharte A, Carlos IZ (2018) Experimental sporotrichosis in a cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice model. Med Mycol 56(6):711–722. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myx098
Mao RX, Wu L, Zhu N, Liu XR, Hao YT, Liu R, Du Q, Li Y (2020) Immunomodulatory effects of walnut (Juglans regia L.) oligopeptides on innate and adaptive immune responses in mice. J Funct Foods 73:104068. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Jff.2020.104068
Markova M, Koelman L, Hornemann S, Pivovarova O, Sucher S, Machann J, Rudovich N, Thomann R, Schneeweiss R, Rohn S, Pfeiffer AFH, Aleksandrova K (2020) Effects of plant and animal high protein diets on immune-inflammatory biomarkers: a 6-week intervention trial. Clin Nutr 39(3):862–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2019.03.019
Sokol E, Huang E, Pytel P, Cohn SL, Pinto N (2017) Rebound thymic hyperplasia following high dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant in three neuroblastoma patients. Pediatr Blood Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.26226
Sun C, Yang J, Pan L, Guo N, Li B, Yao J, Wang M, Qi C, Zhang G, Liu Z (2018) Improvement of icaritin on hematopoietic function in cyclophosphamide-induced myelosuppression mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 40(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923973.2017.1392564
Van Kasteren S, Neefjes J, Ovaa H (2018) Creating molecules that modulate immune responses. Nat Rev Chem 2:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-018-0023-9
Wang YK, He HL, Wang GF, Wu H, Zhou BC, Chen XL, Zhang YZ (2010) Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) hydrolysates produced on a plant scale have antitumor activity and immunostimulating effects in BALB/c mice. Mar Drugs 8(2):255–268. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8020255
Wang DD, Pan WJ, Mehmood S, Cheng XD, Chen Y (2018a) Polysaccharide isolated from Sarcodon aspratus induces RAW264.7 activity via TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Biol Macromol 120(Pt A):1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.147
Wang X, Chu Q, Jiang X, Yu Y, Wang L, Cui Y, Lu J, Teng L, Wang D (2018b) Sarcodon imbricatus polysaccharides improve mouse hematopoietic function after cyclophosphamide-induced damage via G-CSF mediated JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Cell Death Dis 9(6):578. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0634-6
Wang X, Zhang R, Lindaman BD, Leeper CN, Ulery BD (2021) Vasoactive intestinal peptide amphiphile micelle chemical structure and hydrophobic domain influence immunomodulatory potentiation. ACS Appl Bio Mater 5(4):1464–1475. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.1c00981
Warner HR (1994) Superoxide dismutase, aging, and degenerative disease. Free Radic Biol Med 17(3):249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(94)90080-9
Xie Z, Bai Y, Chen G, Rui Y, Chen D, Sun Y, Zeng X, Liu Z (2020) Modulation of gut homeostasis by exopolysaccharides from Aspergillus cristatus (MK346334), a strain of fungus isolated from Fuzhuan brick tea, contributes to immunomodulatory activity in cyclophosphamide-treated mice. Food Funct 11(12):10397–10412. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo02272a
Yang M, Yang C, Nau F, Pasco M, Juneja LR, Okubo T, Mine Y (2009) Immunomodulatory effects of egg white enzymatic hydrolysates containing immunodominant epitopes in a BALB/c mouse model of egg allergy. J Agric Food Chem 57(6):2241–2248. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803372b
Yu FM, He K, Dong XZ, Zhang ZW, Wang FL, Tang YP, Chen Y, Ding GF (2020) Immunomodulatory activity of low molecular-weight peptides from Nibea japonica skin in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. J Funct Foods 68:103888. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.Jff.2020.103888
Zha Z, Wang SY, Chu W, Lv Y, Kan H, Chen Q, Zhong L, Yue L, Xiao J, Wang Y, Yin H (2018) Isolation, purification, structural characterization and immunostimulatory activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from Lepidium meyenii. Phytochemistry 147:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.01.006
Zhou N, Zhao Y, Yao Y, Wu N, Xu MS, Du HY, Wu JP, Tu YG (2022) Antioxidant stress and anti-inflammatory activities of egg white proteins and their derived peptides: a review. J Agric Food Chem 70(1):5–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04742
Zhu G, Jiang Y, Yao Y, Wu N, Luo J, Hu M, Tu Y, Xu M (2019) Ovotransferrin ameliorates the dysbiosis of immunomodulatory function and intestinal microbiota induced by cyclophosphamide. Food Funct 10(2):1109–1122. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo02312c
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the grants from the “Collaborative innovation center of food safety and quality control in Jiangsu Province” industry development program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, FZ; writing—review and editing, YS; validation, JL; software, CC; data curation, LG; conceptualization, resources, supervision, YY All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Li, J., Chang, C. et al. Immunomodulatory Function of Egg White Peptides in RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells and Immunosuppressive Mice Induced by Cyclophosphamide. Int J Pept Res Ther 29, 9 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10481-3
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10481-3