Abstract
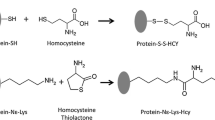
Elevated plasma homocysteine (Hcy) concentrations independently predict cardiovascular disease. However, the transport of Hcy into pathological tissues such as atherosclerotic plaques, characterized by relatively low local thiol concentrations, is largely unknown. We sought to address if albumin-bound Hcy can be released in a thiol-free medium with or without previous incubation with Hcy and homocysteine thiolactone (HTL). We found that Hcy release was dependent on the baseline amount of albumin-bound Hcy. After 48 h incubation in a thiol- free medium the quantity of albumin-bound Hcy released from commercial human serum albumin (HSA) was 1.15 mmol/mol prot. If HSA was pre-incubated with 50 µmol/L reduced Hcy and then transferred into a free-thiol medium (HSA-S-Hcy), the amount of Hcy released after 48 h increased to 33.5 mmol/mol prot. If HSA was pre-incubated with 5 mmol/L HTL and then with 50 µmol/L of reduced Hcy (HSA-HTL-S-Hcy), the amount of Hcy released increased to 92.8 mmol/mol prot. Hcy release from HSA-HTL-S-Hcy further increased in presence of cysteine (Cys), glutathione (GSH), or Cys + GSH in the medium. Therefore, a significant amount of albumin-bound Hcy is released into thiol-free environments, similar to atherosclerotic plaques, with potential deleterious effects on vascular homeostasis, atherosclerosis and thrombosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cys:
-
Cysteine
- Hcy:
-
Homocysteine
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- HSA:
-
Human serum albumin
- HSA-S-Hcy:
-
Albumin-S-homocysteinylated
- HSA-HTL-S-Hcy:
-
Albumin-N-S-homocysteinylated
- HTL:
-
Homocysteine thiolactone
- LMW:
-
Low molecular weight
References
Berman RS, Martin W (1993) Arterial endothelial barrier dysfunction: actions of homocysteine and the hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase free radical generating system. Br J Pharmacol 108:920–926
Carru C, Deiana L, Sotgia S, Pes GM, Zinellu A (2004) Plasma thiols redox status by laser-induced fluorescence capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 25:882–889
de Vries JI, Dekker GA, Huijgens PC, Jakobs C, Blomberg BM, van Geijn HP (1997) Hyperhomocysteinaemia and protein S deficiency in complicated pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104:1248–1254
Eikelboom JW, Lonn E, Genest J Jr, Hankey G, Yusuf S (1999) Homocyst(e)ine and cardiovascular disease: a critical review of the epidemiologic evidence. Ann Intern Med 131:363–375
Finkelstein JD (1990) Methionine metabolism in mammals. J Nutr Biochem 1:228–237
Friedman MH, Fry DL (1993) Arterial permeability dynamics and vascular disease. Atherosclerosis 104:189–194
Jakubowski H (1997) Metabolism of homocysteine thiolactone in human cell cultures. Possible mechanism for pathological consequences of elevated homocysteine levels. J Biol Chem 272:1935–1942
Jakubowski H (2002) Homocysteine is a protein amino acid in humans. Implications for homocysteine-linked disease. J Biol Chem 277:30425–30428
Jakubowski H, Goldman E (1993) Synthesis of homocysteine thiolactone by methionyl-tRNA synthetase in cultured mammalian cells. FEBS Lett 317:237–240
Jiang X, Yang F, Brailoiu E, Jakubowski H, Dun NJ, Schafer AI, Yang X, Durante W, Wang H (2007) Differential regulation of homocysteine transport in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1976–1983
Karner G, Perktold K (2000) Effect of endothelial injury and increased blood pressure on albumin accumulation in the arterial wall: a numerical study. J Biomech 33:709–715
Lepedda AJ, Cigliano A, Cherchi GM, Spirito R, Maggioni M, Carta F, Turrini F, Edelstein C, Scanu AM, Formato M (2009) A proteomic approach to differentiate histologically classified stable and unstable plaques from human carotid arteries. Atherosclerosis 203:112–118
Lepedda AJ, Zinellu A, Nieddu G, Zinellu E, Carru C, Spirito R, Guarino A, De Muro P, Formato M (2013) Protein sulfhydryl group oxidation and mixed-disulfide modifications in stable and unstable human carotid plaques. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:403973
Majors AK, Sengupta S, Willard B, Kinter MT, Pyeritz RE, Jacobsen DW (2002) Homocysteine binds to human plasma fibronectin and inhibits its interaction with fibrin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1354–1359
Malinowska J, Olas B (2012) Homocysteine and its thiolactone-mediated modification of fibrinogen affect blood platelet adhesion. Platelets 23:409–412
Mansoor MA, Svardal AM, Ueland PM (1992) Determination of the in vivo redox status of cysteine, cysteinylglycine, homocysteine, and glutathione in human plasma. Anal Biochem 200:218–229
Meigs JB, Jacques PF, Selhub J, Singer DE, Nathan DM, Rifai N, D’Agostino Sr RB, Wilson PW (2001) Fasting plasma homocysteine levels in the insulin resistance syndrome: the Framingham offspring study. Diabetes Care 24:1403–1410
Mills JL, McPartlin JM, Kirke PN, Lee YJ, Conley MR, Weir DG, Scott JM (1995) Homocysteine metabolism in pregnancies complicated by neural-tube defects. Lancet 345:149–151
Mudd SH, Finkelstein JD, Refsum H, Ueland PM, Malinow MR, Lentz SR, Jacobsen DW, Brattstrom L, Wilcken B, Wilcken DE, Blom HJ, Stabler SP, Allen RH, Selhub J, Rosenberg IH (2000) Homocysteine and its disulfide derivatives: a suggested consensus terminology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1704–1706
Perła-Kaján J, Twardowski T, Jakubowski H (2007) Mechanisms of homocysteine toxicity in humans. Amino Acids 32:561–572
Pianka P, Almog Y, Man O, Goldstein M, Sela BA, Loewenstein A (2000) Hyperhomocystinemia in patients with nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, central retinal artery occlusion, and central retinal vein occlusion. Ophthalmology 107:1588–1592
Regland B, Johansson BV, Grenfeldt B, Hjelmgren LT, Medhus M (1995) Homocysteinemia is a common feature of schizophrenia. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 100:165–169
Sengupta S, Chen H, Togawa T, DiBello PM, Majors AK, Büdy B, Ketterer ME, Jacobsen DW (2001a) Albumin thiolate anion is an intermediate in the formation of albumin-S-S-homocysteine. J Biol Chem 276:30111–30117
Sengupta S, Wehbe C, Majors AK, Ketterer ME, DiBello PM, Jacobsen DW (2001b) Relative roles of albumin and ceruloplasmin in the formation of homocystine, homocysteine-cysteine-mixed disulfide, and cystine in circulation. J Biol Chem 276:46896–46904
Seshadri S, Beiser A, Selhub J, Jacques PF, Rosenberg IH, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PW, Wolf PA (2002) Plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 346:476–483
Sikora M, Marczak L, Twardowski T, Stobiecki M, Jakubowski H (2010) Direct monitoring of albumin lysine-525 N-homocysteinylation in human serum by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 405:132–134
Spahr PF, Edsall JT (1964) Amino acid composition of Human and bovine serum mercaptalbumin. J Biol Chem 239:850–854
Steed MM, Tyagi SC (2011) Mechanisms of cardiovascular remodeling in hyperhomocysteinemia. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1927–1943
Ueland PM (1995) Homocysteine species as components of plasma redox thiol status. Clin Chem 41:340–342
Wang H, Tan H, Yang F (2005) Mechanisms in homocysteine-induced vascular disease. Drug Discov Today 2:25–31
Wierzbicki AS (2007) Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: a review of the evidence. Diab Vasc Dis Res 4:143–150
Zinellu A, Carru C, Galistu F, Usai MF, Pes GM, Baggio G, Federici G, Deiana L (2003) N-methyl-d-glucamine improves the laser-induced fluorescence capillary electrophoresis performance in the total plasma thiols measurement. Electrophoresis 24:2796–2804
Zinellu A, Carru C, Sotgia S, Deiana L (2004) Plasma D-penicillamine redox state evaluation by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence. J Chromatogr B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 803:299–304
Zinellu A, Lepedda AJ, Sotgia S, Zinellu E, Scanu B, Turrini F, Spirito R, Deiana L, Formato M, Carru C (2009a) Evaluation of low molecular mass thiols content in carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Clin Biochem 42:796–801
Zinellu A, Sotgia S, Scanu B, Pintus G, Posadino AM, Cossu A, Deiana L, Sengupta S, Carru C (2009b) S-homocysteinylated LDL apolipoprotein B adversely affects human endothelial cells in vitro. Atherosclerosis 206:40–46
Zinellu A, Lepedda AJ, Sotgia S, Zinellu E, Marongiu G, Usai MF, Gaspa L, De Muro P, Formato M, Deiana L, Carru C (2010a) Albumin-bound low molecular weight thiols analysis in plasma and carotid plaques by CE. J Sep Sci 33:126–131
Zinellu A, Sotgia S, Scanu B, Pisanu E, Sanna M, Sati S, Deiana L, Sengupta S, Carru C (2010b) Determination of homocysteine thiolactone, reduced homocysteine, homocystine, homocysteine-cysteine mixed disulfide, cysteine and cystine in a reaction mixture by overimposed pressure/voltage capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 82:1281–1285
Acknowledgements
Arduino A. Mangoni has participated to this work during a Visiting Professorship at the University of Sassari.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zinellu, A., Sotgia, S., Mangoni, A.A. et al. Spontaneous Release of Human Serum Albumin S-Bound Homocysteine in a Thiol-Free Physiological Medium. Int J Pept Res Ther 25, 187–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9663-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9663-8