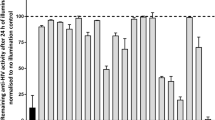
Abstract
Peptidic drugs have many advantages as compared to small chemical molecules; however, they also possess some limitations as their poor membrane transducing properties. Our group has recently reported the potent anti-HIV antiviral activity of CIGB-210, a peptide derived from human keratin 10. Previous experiments showed that this peptide is internalized in MT4 cells. The aim of this study was to expand our knowledge on the uptake of CIGB-210 by assessing the peptide penetration in four other human cell lines. Cells were treated with 10, 20 and 40 µM of fluorescein-labelled CIGB-210 and the percentage of fluorescent cells was determined by flow cytometry at 15 min, 1 and 24 h. The uptake of fluorescein-labelled CIGB-210 in THP-1, HEp-2, HepG2 and PC-3 cell lines was directly proportional to both, peptide concentration and incubation times. However, some differences in the kinetics of cell entry were found. While the initial uptake was faster in HepG2 and PC-3 cells, after 24 h of incubation the percentage of fluorescence cells was equalized, although HEp-2 cells exhibited the higher numbers. The efficiency of CIGB-210 uptake was lower than a control cell penetrating peptide. However, despite the differences found, CIGB-210 was capable of transducing four human cell lines of different origins without any help. Finally, circular dichroism spectrometry data indicated that the peptide adopt a mostly disordered structure in aqueous solution, with an estimated alpha helical content of less than 5%. This study contributes to the characterization of CIGB-210 as a novel drug candidate against HIV/AIDS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar H, Srivastava S, Chung EJ, Schnorenberg MR, Barrett JC, LaBelle JL, Tirrell M (2016) Self-assembling peptide-based building blocks in medical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.08.006
Andreev OA, Engelman DM, Reshetnyak YK (2010) pH-sensitive membrane peptides (pHLIPs) as a novel class of delivery agents. Mol Membr Biol 27:341–352 doi:10.3109/09687688.2010.509285
Anko M, Majhenc J, Kogej K, Sillard R, Langel U, Anderluh G, Zorko M (2012) Influence of stearyl and trifluoromethylquinoline modifications of the cell penetrating peptide TP10 on its interaction with a lipid membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:915–924. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.12.028
Ayoub M, Scheidegger D (2006) Peptide drugs, overcoming the challenges, a growing business. Chim Oggi 24:46–48
Chandrudu S, Simerska P, Toth I (2013) Chemical methods for peptide and protein production. Molecules 18:4373–4388. doi:10.3390/molecules18044373
Colucci-Guyon E, Portier MM, Dunia I, Paulin D, Pournin S, Babinet C (1994) Mice lacking vimentin develop and reproduce without an obvious phenotype. Cell 79:679–694
Craik DJ, Fairlie DP, Liras S, Price D (2013) The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem Biol Drug Des 81:136–147. doi:10.1111/cbdd.12055
Duchardt F, Fotin-Mleczek M, Schwarz H, Fischer R, Brock R (2007) A comprehensive model for the cellular uptake of cationic cell-penetrating peptides. Traffic 8:848–866. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00572.x
Eriksson JE, Dechat T, Grin B, Helfand B, Mendez M, Pallari HM, Goldman RD (2009) Introducing intermediate filaments: from discovery to disease. J Clin Invest 119:1763–1771. doi:10.1172/JCI38339
Fernández-Ortega C et al (2016) Identification of vimentin as a potential therapeutic target against HIV infection. Viruses 8:98. doi:10.3390/v8060098
Fields GB, Noble RL (1990) Solid phase peptide synthesis utilizing 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl amino acids. Int J Pept Prot Res 35:161–214
Fischer RS, Fowler VM (2015) Thematic minireview series: the state of the cytoskeleton in 2015. J Biol Chem 290:17133–17136. doi:10.1074/jbc.R115.663716
Fosgerau K, Hoffmann T (2015) Peptide therapeutics: current status and future directions. Drug Discov Today 20:122–128 doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2014.10.003
Goldman RD, Khuon S, Chou YH, Opal P, Steinert PM (1996) The function of intermediate filaments in cell shape and cytoskeletal integrity. J Cell Biol 134:971–983
Hallbrink M, Floren A, Elmquist A, Pooga M, Bartfai T, Langel U (2001) Cargo delivery kinetics of cell-penetrating peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1515:101–109
He J, Kauffman WB, Fuselier T, Naveen SK, Voss TG, Hristova K, Wimley WC (2013) Direct cytosolic delivery of polar cargo to cells by spontaneous membrane-translocating peptides. J Biol Chem 288:29974–29986. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.488312
Heitz F, Morris MC, Divita G (2009) Twenty years of cell-penetrating peptides: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Br J Pharmacol 157:195–206. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00057.x
Herrmann H, Strelkov SV, Burkhard P, Aebi U (2009) Intermediate filaments: primary determinants of cell architecture and plasticity. J Clin Invest 119:1772–1783. doi:10.1172/JCI38214
John H (2005) Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in peptide drug discovery and development. Anal Bioanal Chem 381:51–53. doi:10.1007/s00216-004-2868-7
Kerkis A, Hayashi MA, Yamane T, Kerkis I (2006) Properties of cell penetrating peptides (CPPs). IUBMB life 58:7–13 doi:10.1080/15216540500494508
Milletti F (2012) Cell-penetrating peptides: classes, origin, and current landscape. Drug Discov Today 17:850–860. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2012.03.002
Mishra R, Su W, Pohmann R, Pfeuffer J, Sauer MG, Ugurbil K, Engelmann J (2009) Cell-penetrating peptides and peptide nucleic acid-coupled MRI contrast agents: evaluation of cellular delivery and target binding. Bioconjug Chem 20:1860–1868. doi:10.1021/bc9000454
Mlcochova P, Pelchen-Matthews A, Marsh M (2013) Organization and regulation of intracellular plasma membrane-connected HIV-1 assembly compartments in macrophages. BMC Biol 11:89. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-11-89
Munoz V, Serrano L (1997) Development of the multiple sequence approximation within the AGADIR model of alpha-helix formation: comparison with Zimm-Bragg and Lifson-Roig formalisms. Biopolymers 41:495–509. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-0282
Nuutila J, Lilius EM (2005) Flow cytometric quantitative determination of ingestion by phagocytes needs the distinguishing of overlapping populations of binding and ingesting cells. Cytom Part A 65:93–102 doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20139
Patel LN, Zaro JL, Shen WC (2007) Cell penetrating peptides: intracellular pathways and pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm Res 24:1977–1992. doi:10.1007/s11095-007-9303-7
Perea SE et al (2004) Antitumor effect of a novel proapoptotic peptide that impairs the phosphorylation by the protein kinase 2 (casein kinase 2). Cancer Res 64:7127–7129. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-2086
Rhee M, Davis P (2006) Mechanism of uptake of C105Y, a novel cell-penetrating peptide. J Biol Chem 281:1233–1240 doi:10.1074/jbc.M509813200
Richard JP et al (2003) Cell-penetrating peptides. A reevaluation of the mechanism of cellular uptake. J Biol Chem 278:585–590 doi:10.1074/jbc.M209548200
Sreerama N, Woody RW (2004) Computation and analysis of protein circular dichroism spectra. Methods Enzymol 383:318–351 doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(04)83013-1
Stevenson M (2003) Dissecting HIV-1 through RNA interference. Nat Rev Immunol 3:851–858. doi:10.1038/nri1227
Su Y, Doherty T, Waring AJ, Ruchala P, Hong M (2009) Roles of arginine and lysine residues in the translocation of a cell-penetrating peptide from (13)C, (31)P, and (19)F solid-state NMR. BioChemistry 48:4587–4595. doi:10.1021/bi900080d
Thoren PE, Persson D, Esbjorner EK, Goksor M, Lincoln P, Norden B (2004) Membrane binding and translocation of cell-penetrating peptides. BioChemistry 43:3471–3489. doi:10.1021/bi0360049
van Bracht E et al (2014) Enhanced cellular uptake of albumin-based lyophilisomes when functionalized with cell-penetrating peptide TAT in HeLa cells. PloS ONE 9:e110813. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0110813
Vlieghe P, Lisowski V, Martinez J, Khrestchatisky M (2010) Synthetic therapeutic peptides: science and market. Drug Discov Today 15:40–56 doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2009.10.009
Weiss RA (2013) Thirty years on: HIV receptor gymnastics and the prevention of infection. BMC Biol 11:57. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-11-57
Zhang H et al (2008) A cell-penetrating helical peptide as a potential HIV-1 inhibitor. J Mol Biol 378:565–580 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.02.066
Zorko M, Langel U (2005) Cell-penetrating peptides: mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:529–545. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2004.10.010
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Silvio Perea and Dr. Yasser Perera for providing the CIGB-300 peptide used as positive controls in our experiments. We also thank Milagros Freyre for her support in flow cytometry experiments; Haydeé Gerónimo for providing some of the cell lines used in this work and Raimundo Ubieta for the very helpful scientific discussions and recommendations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paneque, T.E., Ramírez-Suárez, A.C., Casillas, D. et al. Cell Penetration and Secondary Structure of a Synthetic Peptide with Anti-HIV Activity. Int J Pept Res Ther 23, 531–539 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9587-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9587-3