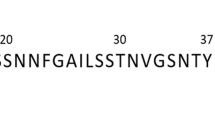Abstract
Human islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) is the major component of amyloid deposits found in the pancreas of over 90% of all cases of type-2 diabetes. Although it may be a secondary event in the etiology of diabetes, the accumulation of insoluble IAPP fibrils is considered to be a primary cause of β-cell failure in affected individuals. A possible means of inhibiting this process is through the use of small peptides that bind to IAPP and prevent fibril polymerization. This approach has been examined using a series of overlapping hexamers that target the known amyloidogenic regions of IAPP. Peptides were examined usingin vitroassays and active inhibitors were identified by their ability to prevent amyloid-related conformational transitions and IAPP aggregation. Fragments such as those corresponding to the IAPP-derived sequences, SNNFGA (residues 20–25) and GAILSS (residues 24–29), were potent inhibitors ofβ-sheet folding and amyloid fibril formation. Negative stain electron microscopy revealed that co-incubation of these peptides with IAPP significantly decreased the density of fibrils and any remaining structures displayed altered morphology. In some, but not all cases, inhibition of amyloid fibrils also correlated with an ability to reduce IAPP-mediated cytotoxicity as determined in cell culture studies. The results from these studies suggest that these two peptide inhibitors differ in their mechanisms of action possibly due to unique interactions with the full-length IAPP molecule. These inhibitors form the basis of a therapeutic strategy to prevent amyloid accumulation leading to improved islet survival and a potentially novel treatment for type-2 diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, A., Wells, C.A., Buley, I.D., Cruickshank, J.K., Vanhegan, R.I., Matthews, D.R., Cooper, G.J.S., Holman, R.R. and Turner R.C., Diabetes Res., 9 (1998) 151–159.
Kahn, S.E., Andrikopoulos, S. and Verchere, C.B., Diabetes, 48 (1999) 241–253.
Hoppener, J.W.M., Ahren, B. and Lips, C.J.M., Eng. J. Med., 343 (2000) 411–419.
Ferrannini, E., Endocr. Rev., 19 (1998) 477–490.
Rachman, J., Payne, M.J., Levy, J.C., Barrow, B.A., Holman, R.R. and Turner, R.C. Diabetes Care, 21 (1998) 810–816.
Higham, C.E., Hull, R.L., Lawrie, L., Shennan, K.I.J., Morris, J.F. and Birch, N.P., et al., Eur. J. Biochem., 267 (2000) 4998–5004.
Park, K. and Verchere, C.B., J. Biol. Chem., 20 (2001) 16611–16616.
Clark, A., deKoning, E.J.P., Baker, C.A., Charge, S. and Morris, J.F., Diabetologia, 36 (1993) A136.
Hoenig, M., Hall, G., Ferguson, D., Jordan, K., Henson, M., Johnson, K. and O'Brien, T.D., Amer. J. Pathol., 157 (2000) 2143–2150.
Janson, J., Ashley, R.H., Harrison, D., McIntyre, S. and Butler, P.C., Diabetes, 48 (1999) 491–498.
Lorenzo, A., Razzaboni, R., Weir, G.C. and Yankner, B.A., Nature, 368 (1994) 756–760.
Saafi, E.L., Konarkowska, B., Zhang, S., Kistler, J. and Cooper, G., Cell. Biol. Intl., 25 (2001) 333–335.
O'Brien, T.D., Mol. and Cell. Endo., 197 (2002) 213–219.
deKoning, E.J.P., Bodkin, N.L., Hansen, B.C. and Clark, A., Diabetologia, 36 (1993) 378–384.
Westermark, P., Engstrom, U., Johnson, K.H., Westermark, G.T. and Betsholtz, C., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 87 (1990) 5036–5040.
Moriarty, D.F. and Raleigh, D.P., Biochemistry, 38 (1999) 1811–1818.
Jaikaran, E.T.S., Higham, C.E., Serpell, L.C., Zurdo, J., Gross, M., Clark, A. and Fraser, P.E., J. Mol. Biol., 308 (2001) 515–525.
Scrocchi, L.A., Ha, K., Chen, Y., Wu, L., Wang, F. and Fraser, P.E., J. Structural Biol., 141 (2003) 218–227.
Mazor, Y., Gilead, S., Benhar, I. and Gazit, E., J. Mol. Biol., 322 (2002) 1013–1024.
Nilsson, M. and Raleigh, D., J. Mol. Biol., 294 (1999) 1375–1395.
Padrick, S.B. and Miranker, A.D., J. Mol. Biol., 308 (2001) 783–794.
Kruger, D.F., Gatcomb, P.M. and Owen, S.K., Diabetes Educator, 25 (1999) 389–398.
Rushing, P.A., Hagan, M.M., Seeley, R.J., Lutz, T.A., D'Alessio, D.A., Air, E.L. and Woods, S.C., Endocrinology, 142 (2001) 5035–5038.
Scrocchi, L.A., Chen, Y., Waschuk, S., Wang, F., Cheung, S., Darabie, A.A., McLaurin, J. and Fraser, P.E., J. Mol. Biol., 318 (2002) 697–706.
Thomas, T., Nadackal, G.T. and Thomas, K., Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes, 111 (2003) 8–11.
Aitken, J.F., Loomes, K.M., Konarkowska, B. and Cooper, G.J.S., Biochem. J., 374 (2003) 779–784.
Tjernberg, L.O., Lilliehook, C., Callaway, D.J.E., Naslund, J., Hahne, S. and Thyberg, J., et al., J. Biol. Chem., 272 (1997) 12601–12605.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scrocchi, L.A., Chen, Y., Wang, F. et al. Inhibitors of islet amyloid polypeptide fibrillogenesis, and the treatment of type-2 diabetes. Int J Pept Res Ther 10, 545–551 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-004-2423-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-004-2423-6