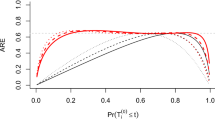
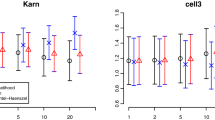
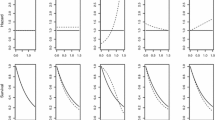
Abstract
In studies with time-to-event outcomes, multiple, inter-correlated, and time-varying covariates are commonly observed. It is of great interest to model their joint effects by allowing a flexible functional form and to delineate their relative contributions to survival risk. A class of semiparametric transformation (ST) models offers flexible specifications of the intensity function and can be a general framework to accommodate nonlinear covariate effects. In this paper, we propose a partial-linear single-index (PLSI) transformation model that reduces the dimensionality of multiple covariates into a single index and provides interpretable estimates of the covariate effects. We develop an iterative algorithm using the regression spline technique to model the nonparametric single-index function for possibly nonlinear joint effects, followed by nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation. We also propose a nonparametric testing procedure to formally examine the linearity of covariate effects. We conduct Monte Carlo simulation studies to compare the PLSI transformation model with the standard ST model and apply it to NYU Langone Health de-identified electronic health record data on COVID-19 hospitalized patients’ mortality and a Veteran’s Administration lung cancer trial.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The COVID-19 de-identified EHR data that support the findings of this study are available from New York University Langone Health. Restrictions apply to the availability of the data.
References
Alkenani A, Yu K (2013) Penalized single-index quantile regression. Int J Stat Probab 2(3):12
Andersen PK, Gill RD (1982) Cox’s regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Ann Stat 10:1100–1120
Breslow NE (1972) Contribution to discussion of paper by DR Cox. J Roy Statist Soc Ser B 34:216–217
Carroll RJ, Fan J, Gijbels I, Wand MP (1997) Generalized partially linear single-index models. J Am Stat Assoc 92(438):477–489
Charlson M, Pompei P, Ales K, MacKenzie R (1987) Charlson Comorbidity Index. J Chronic Dis 40(5):373–383
Chen K, Jin Z, Ying Z (2002) Semiparametric analysis of transformation models with censored data. Biometrika 89(3):659–668
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life-tables. J Roy Stat Soc Ser B 34(2):187–202
Cox DR (1975) Partial likelihood. Biometrika 62(2):269–276
De Boor C (2001) Calculation of the smoothing spline with weighted roughness measure. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 11(01):33–41
Efron B (1992) Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife. In: Breakthroughs in statistics: methodology and distribution, Springer, pp 569–593
Galvao AF, Wang L (2015) Uniformly semiparametric efficient estimation of treatment effects with a continuous treatment. J Am Stat Assoc 110(512):1528–1542
Guo J, Tang M, Tian M, Zhu K (2013) Variable selection in high-dimensional partially linear additive models for composite quantile regression. Comput Stat Data Anal 65:56–67
Hardle W, Hall P, Ichimura H (1993) Optimal smoothing in single-index models. Ann Stat 21(1):157–178
Härdle W, Stoker TM (1989) Investigating smooth multiple regression by the method of average derivatives. J Am Stat Assoc 84(408):986–995
Huang JZ, Liu L (2006) Polynomial spline estimation and inference of proportional hazards regression models with flexible relative risk form. Biometrics 62(3):793–802
Ichimura H (1993) Semiparametric least squares (SLS) and weighted SLS estimation of single-index models. J Econ 58(1–2):71–120
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL (2011) The statistical analysis of failure time data. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Liang H, Liu X, Li R, Tsai C-L (2010) Estimation and testing for partially linear single-index models. Ann Stat 38(6):3811
Lv Y, Zhang R, Zhao W, Liu J (2015) Quantile regression and variable selection of partial linear single-index model. Ann Inst Stat Math 67(2):375–409
Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, Rajagopalan H, O’Donnell L, Chernyak Y, Tobin KA, Cerfolio RJ, Francois F, Horwitz LI (2020) Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1966
Ponti G, Maccaferri M, Ruini C, Tomasi A, Ozben T (2020) Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 57(6):389–399
Stoker TM (1986) Consistent estimation of scaled coefficients. Econom J Econom Soc. https://doi.org/10.2307/1914309
Sun J, Kopciuk KA, Lu X (2008) Polynomial spline estimation of partially linear single-index proportional hazards regression models. Comput Stat Data Anal 53(1):176–188
Wang Y, Wu Y, Jacobson MH, Lee M, Jin P, Trasande L, Liu M (2020) A family of partial-linear single-index models for analyzing complex environmental exposures with continuous, categorical, time-to-event, and longitudinal health outcomes. Environ Health 19(1):1–16
Wang Y, Ghassabian A, Gu B, Afanasyeva Y, Li Y, Trasande L, Liu M (2023) Semiparametric distributed lag quantile regression for modeling time-dependent exposure mixtures. Biometrics 79(3):2619–2632
Wood SN (2006) Generalized additive models: an introduction with R. chapman and hall/CRC
Yu Y, Ruppert D (2002) Penalized spline estimation for partially linear single-index models. J Am Stat Assoc 97(460):1042–1054
Zeng D, Lin D (2006) Efficient estimation of semiparametric transformation models for counting processes. Biometrika 93(3):627–640
Zeng D, Lin D (2007) Maximum likelihood estimation in semiparametric regression models with censored data. J Royal Stat Soc Series B 69(4):507–564
Zeng P, He T, Zhu Y (2012) A lasso-type approach for estimation and variable selection in single index models. J Comput Graph Stat 21(1):92–109
Zhang J, Wang X, Yu Y, Gai Y (2014) Estimation and variable selection in partial linear single index models with error-prone linear covariates. Statistics 48(5):1048–1070
Zhou J, Zhang J, Lu W (2022) TransModel: an R package for linear transformation model with censored data. J Stat Softw 101:1–12
Zhu L-P, Qian L-Y, Lin J-G (2011) Variable selection in a class of single-index models. Ann Inst Stat Math 63(6):1277–1293
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Donglin Zeng for sharing the original MATLAB code and materials for the semiparametric transformation models. The authors thank the associate editor and two reviewers for their constructive and insightful suggestions that greatly improved the paper. This work was partially supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health grant R01ES032808.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M., Troxel, A.B. & Liu, M. Partial-linear single-index transformation models with censored data. Lifetime Data Anal (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10985-024-09624-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10985-024-09624-z