Abstract
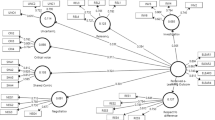
We investigated students’ perceptions of their science classroom environments with the use of the What Is Happening In this Class? (WIHIC) questionnaire at the university level in Myanmar. The translated questionnaire was administered to 251 students in first-year science classes at a university. Both exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analysis supported the reliability and factorial validity of the Myanmar version of the WIHIC. The constructs of the WIHIC were significantly correlated, but gender differences were not detected in correlations between WIHIC scales. Future research is needed to see if our Myanmar version of the WIHIC fits other samples in schools and universities in this context. It is also suggested that future studies include measures of student attitudes and academic achievement to permit investigation of associations between the learning environment and student outcomes in this country.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamski, A., Fraser, B. J., & Peiro, M. M. (2013). Parental involvement in schooling, classroom environment and student outcomes. Learning Environments Research, 16(3), 315–328.
Afari, E., Aldridge, J. M., Fraser, B. J., & Khine, M. S. (2013). Students’ perceptions of the learning environment and attitudes in game-based mathematics classrooms. Learning Environments Research, 16(1), 131–150.
Aldridge, J. M., & Fraser, B. J. (2008). Outcomes-focused learning environments: Determinants and effects (Advances in Learning Environments Research series). Rotterdam: Sense Publishers.
Aldridge, J. M., Fraser, B. J., Bell, L., & Dorman, J. P. (2012). Using a new learning environment questionnaire for reflection in teacher action research. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 23, 259–290.
Aldridge, J. M., Fraser, B. J., & Huang, I. T. C. (1999). Investigating classroom environments in Taiwan and Australia with multiple research methods. Journal of Educational Research, 93, 48–62.
Alt, D. (2015). Using structural equation modeling and multidimensional scaling to assess students’ perceptions of the learning environment and justice experiences. International Journal of Educational Research, 69, 38–49.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2010). IBM SPSS Amos TM 19 User’s Guide. Crawfordville, FL: AMOS Development Corporation.
Barclay, D., Higgins, C., & Thompson, R. (1995). The partial least squares (PLS) approach to causal modeling: Person computer adoption and uses as an illustration. Technology Studies, 2, 285–309.
Bartlett, M. S. (1954). A note on the multiplying factors for various Chi square approximations. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 16(Series B), 296–298.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238–246.
Bentler, P. M., & Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88, 588–606.
Bi, X. (2015). Associations between psychosocial aspects of English classroom environments and motivation types of Chinese tertiary-level English majors. Learning Environments Research, 18(1), 95–110.
Brislin, R. (1970). Back translation for cross-cultural research. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 1, 185–216.
Brown, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In K. A. Bollen & J. S. Long (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 136–162). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Byrne, B. M. (2010). Structural equation modeling with AMOS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming. New York: Routledge.
Cattell, R. B. (1966). The scree test for the number of factors. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 1, 245–276.
Charalampous, K., & Kokkinos, C. M. (2017). The Greek elementary “What Is Happening In this Class?”(G-EWIHIC): A three-phase multi-sample mixed-methods study. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 52, 55–70.
Chipangura, A., & Aldridge, J. (2016). Impact of multimedia on students’ perceptions of the learning environment in mathematics classrooms. Learning Environments Research, 20, 121–138.
Chua, S. L., Wong, A. F., & Chen, D. T. V. (2011). The nature of Chinese language classroom learning environments in Singapore secondary schools. Learning Environments Research, 14(1), 75–90.
Cohen, J. W. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Cohn, S. T., & Fraser, B. J. (2016). Effectiveness of student response systems in terms of learning environment, attitudes and achievement. Learning Environments Research, 19, 153–167.
Den Brok, P., Telli, S., Cakiroglu, J., Taconis, R., & Tekkaya, C. (2010). Learning environment profiles of Turkish secondary biology classrooms. Learning Environments Research, 13(3), 187–204.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18, 39–50.
Fraser, B. J. (1981). Test of Science Related Attitudes (TOSRA). Melbourne: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Fraser, B. J. (1994). Research on classroom and school climate. In D. Gabel (Ed.), Handbook of research on science teaching and learning (pp. 493–541). New York: Macmillan.
Fraser, B. J. (2012). Classroom learning environments: Retrospect, context and prospect. In B. J. Fraser, K. G. Tobin, & C. J. McRobbie (Eds.), Second international handbook of science education (pp. 1191–1239). New York: Springer.
Fraser, B. J. (2014). Classroom learning environments: Historical and contemporary perspectives. In N. G. Lederman & S. K. Abell (Eds.), Handbook of research on science education (Vol. II, pp. 104–117). New York: Routledge.
Fraser, B. J., Aldridge, J. M., & Adolphe, F. G. (2010). A cross-national study of secondary science classroom environments in Australia and Indonesia. Research in Science Education, 40(4), 551–571.
Fraser, B. J., Fisher, D. L., & McRobbie, C. J. (1996, April). Development, validation and use of personal and class forms of a new classroom environment instrument. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York.
Fraser, B. J., Giddings, G. J., & McRobbie, C. J. (1995). Evolution and validation of a personal form of an instrument for assessing science laboratory classroom environments. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 32, 399–422.
Giles, R. M., & Fraser, B. J. (2017, April). Learning environment and attitudes in middle-school mathematics. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, San Antonio, TX.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Hayton, J. C., Allen, D. G., & Scarpello, V. (2004). Factor retention decisions in exploratory factor analysis: A tutorial on Parallel Analysis. Organizational Research Methods, 7, 191–205.
Helding, K. A., & Fraser, B. J. (2013). Effectiveness of National Board Certified (NBC) teachers in terms of classroom environment, attitudes and achievement among secondary science students. Learning Environments Research, 16(1), 1–21.
Horn, J. L. (1965). A rationale and test for the number of factors in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 30, 179–185.
Hu, L.-T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Hubbard, R., & Allen, S. J. (1987). An empirical comparison of alternative methods for Principal Component Extraction. Journal of Business Research, 15, 173–190.
Kaiser, H. (1974). An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika, 39, 31–36.
Kline, R. B. (2010). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (3rd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
MacLeod, C., & Fraser, B. J. (2010). Development, validation and application of a modified Arabic translation of the What Is Happening In this Class? (WIHIC) questionnaire. Learning Environments Research, 13, 105–125.
Majeed, A., Fraser, B. J., & Aldridge, J. M. (2002). Learning environment and its association with student satisfaction among mathematics students in Brunei Darussalam. Learning Environments Research, 5, 203–226.
Martin-Dunlop, C., & Fraser, B. J. (2007). Learning environment and attitudes associated with an innovative science course designed for prospective elementary teachers. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 6, 163–190.
Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). Psychometric theory (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Opolot-Okurut, C. (2010). Classroom learning environment and motivation towards mathematics among secondary school students in Uganda. Learning Environments Research, 13(3), 267–277.
Peer, J., & Fraser, B. J. (2015). Sex, grade-level and stream differences in learning environment and attitudes to science in Singapore primary schools. Learning Environments Research, 18(1), 143–161.
Rahmi, R. A., & Diem, C. D. (2014). Junior high school students’ perception of classroom environment and their English achievement. International Journal of Applied Linguistics and English Literature, 3(3), 41–47.
Raykov, T., & Marcoulides, G. A. (2008). An introduction to applied multivariate analysis. New York: Routledge.
Rita, R. D., & Martin-Dunlop, C. S. (2011). Perceptions of the learning environment and associations with cognitive achievement among gifted biology students. Learning Environments Research, 14(1), 25–38.
Robinson, E., & Fraser, B. J. (2013). Kindergarten students’ and parents’ perceptions of science classroom environments: Achievement and attitudes. Learning Environments Research, 16(2), 151–167.
Singh, M., & McNeil, J. T. (2014). Do learning environments differ across subjects and nations: Case studies in Hawaii and Singapore using the WIHIC questionnaire. Learning Environments Research, 17(2), 173–189.
Soebari, T. S., & Aldridge, J. M. (2015). Using student perceptions of the learning environment to evaluate the effectiveness of a teacher professional development programme. Learning Environments Research, 18(2), 163–178.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (5th ed.). Boston: Pearson Education.
Tanaka, J. S. (1993). Multifaceted conceptions of fit in structural equation models. In J. A. Bollen & J. S. Long (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 10–39). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Taylor, B. A., & Fraser, B. J. (2013). Relationships between learning environment and mathematics anxiety. Learning Environments Research, 16(2), 297–313.
Taylor, P. C., Fraser, B. J., & Fisher, D. L. (1997). Monitoring constructivist classroom learning environments. International Journal of Educational Research, 27, 293–302.
Teo, T., & Lee, C. B. (2012). Assessing the factorial validity of the Metacognitive Awareness Inventory (MAI) in an Asian Country: A confirmatory factor analysis. The International Journal of Educational and Psychological Assessment, 10(2), 92–103.
Trickett, E. J., & Moos, R. H. (1973). Social environment of junior high and high school classrooms. Journal of Educational Psychology, 65(1), 93–102.
Walberg, H. J., & Anderson, G. J. (1968). Classroom climate and individual learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 59, 414–419.
Watkins, M. W. (2000). Monte Carlo PCA for parallel analysis [computer software]. State College, PA: Ed & Psych Associates.
Yang, X. (2015). Rural junior secondary school students’ perceptions of classroom learning environments and their attitude and achievement in mathematics in West China. Learning Environments Research, 18(2), 249–266.
Zaragoza, J. M., & Fraser, B. J. (2017). Field-study science classrooms as positive and enjoyable learning environments. Learning Environments Research, 20, 1–20.
Zubaidi, E., Aldridge, J. M., & Khine, M. S. (2016). Learning English as a second language at the university level in Jordan: Motivation, self-regulation and learning environment perceptions. Learning Environments Research, 19(1), 133–152.
Zwick, W. R., & Velicer, W. F. (1986). Comparison of five rules for determining the number of components to retain. Psychological Bulletin, 99, 432–442.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khine, M.S., Fraser, B.J., Afari, E. et al. Students’ perceptions of the learning environment in tertiary science classrooms in Myanmar. Learning Environ Res 21, 135–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-017-9250-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-017-9250-0